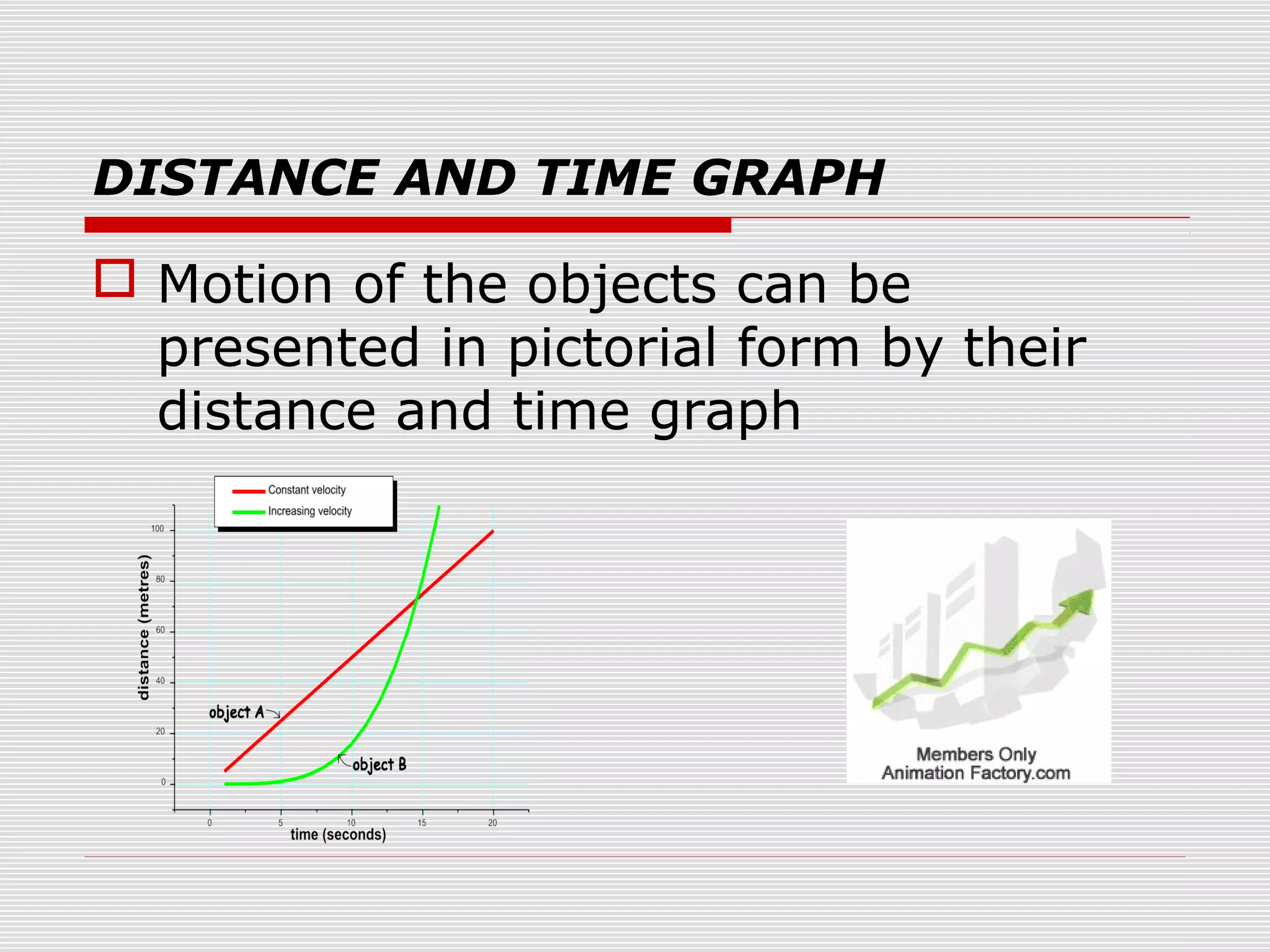
This document discusses motion, speed, and time. It defines motion as a change in an object's position and speed as the distance covered by an object per unit of time. Uniform motion has constant speed while non-uniform motion has changing speed. Time is measured using periodic events like the sun's motion or a pendulum's oscillations. A simple pendulum's time period is the time taken to complete one oscillation. Distance and time graphs can represent motion, with uniform motion shown as a straight line.