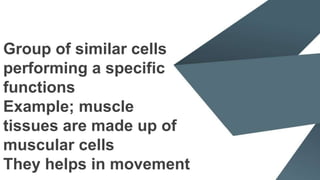
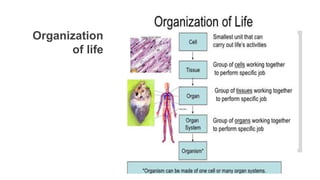
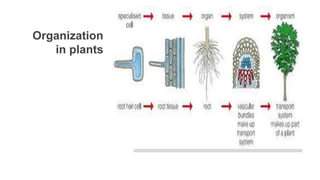
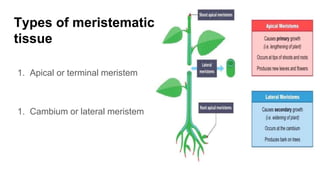
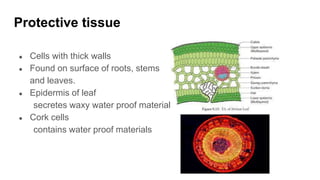
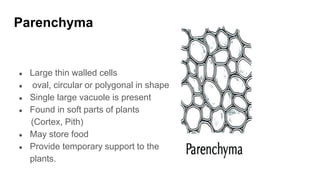
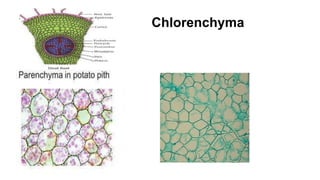
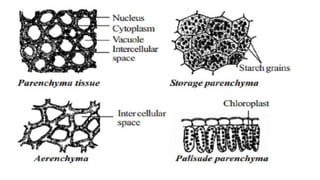
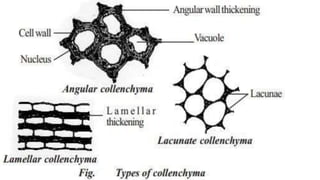
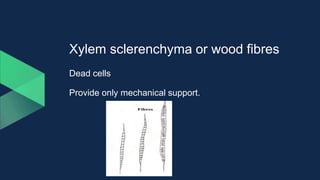
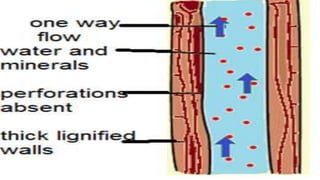
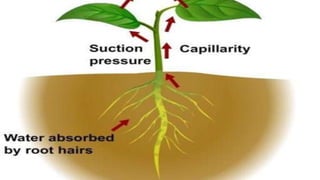
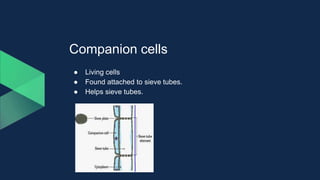
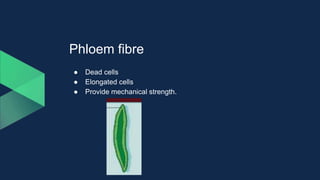
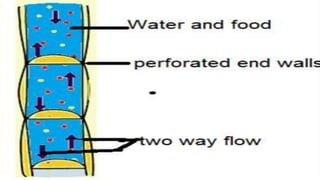
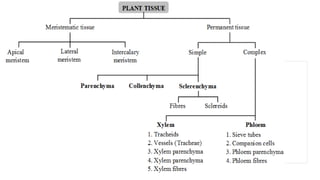
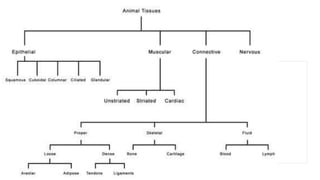
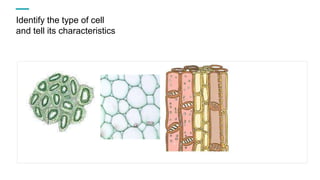
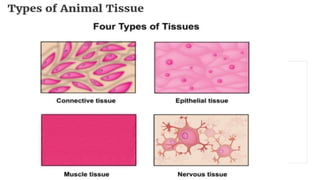
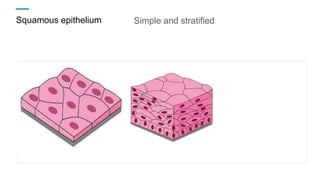
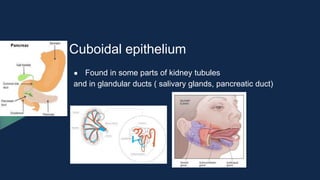
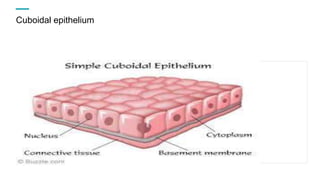
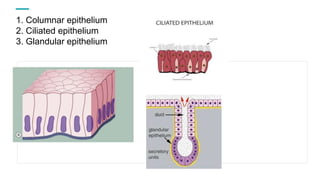
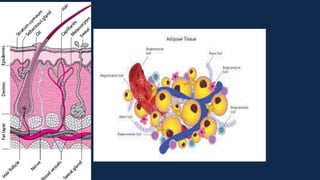
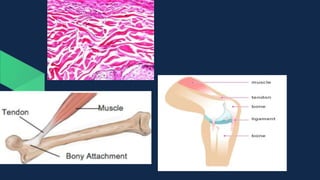
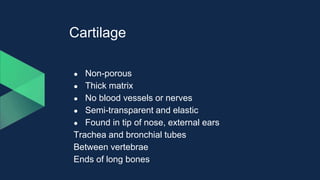
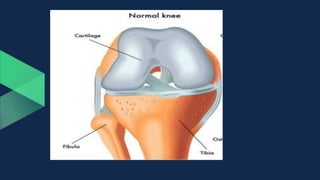
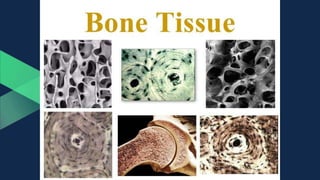
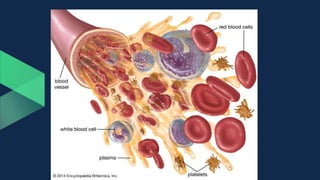
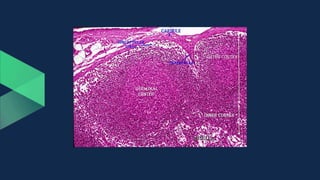
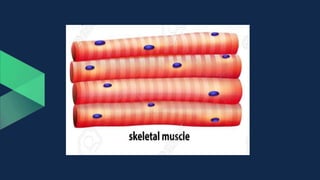
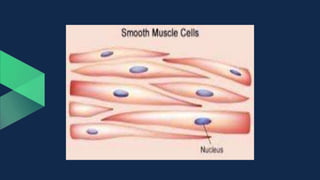
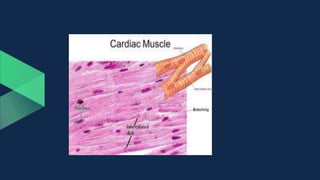
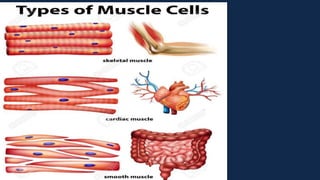
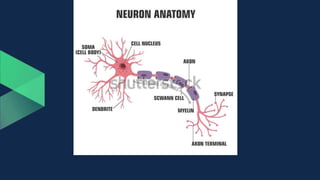
Tissues are groups of similar cells that perform specific functions. There are four main types of tissues in plants and animals: epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous tissue. In plants, the main tissues are meristematic and permanent tissues. Meristematic tissues are dividing cells found at growing points that produce new cells. Permanent tissues are specialized cells that perform functions but cannot divide further.