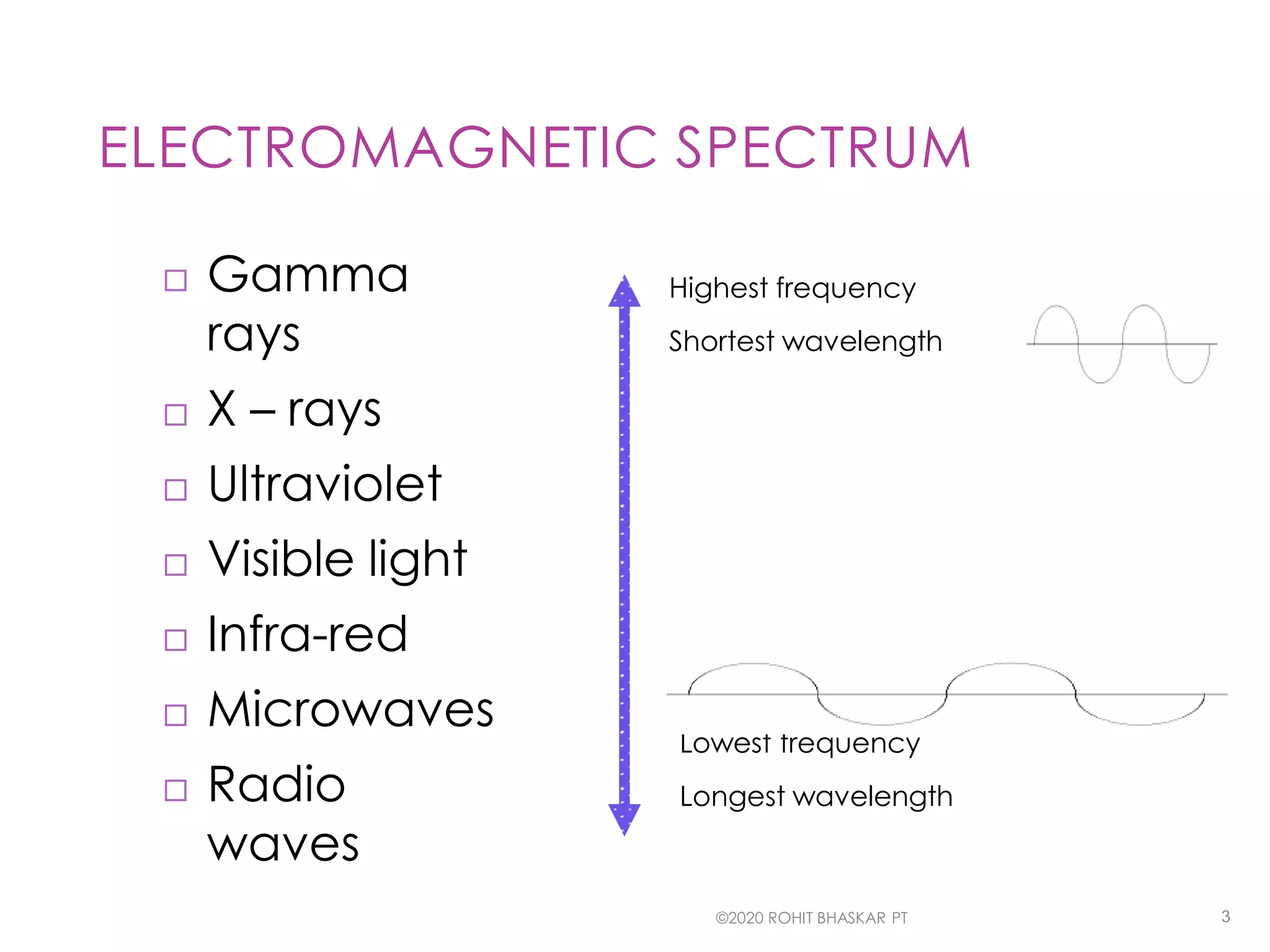
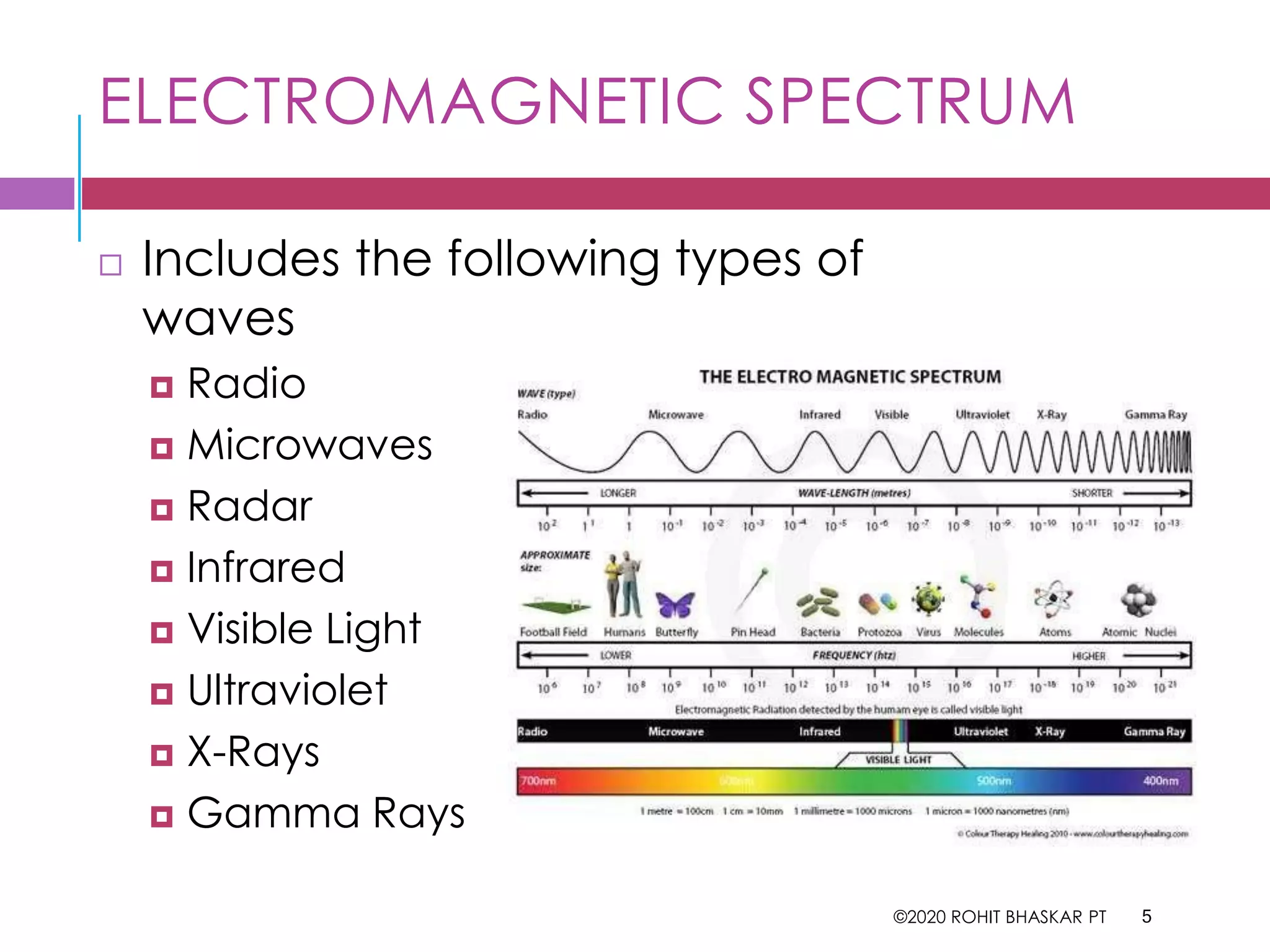
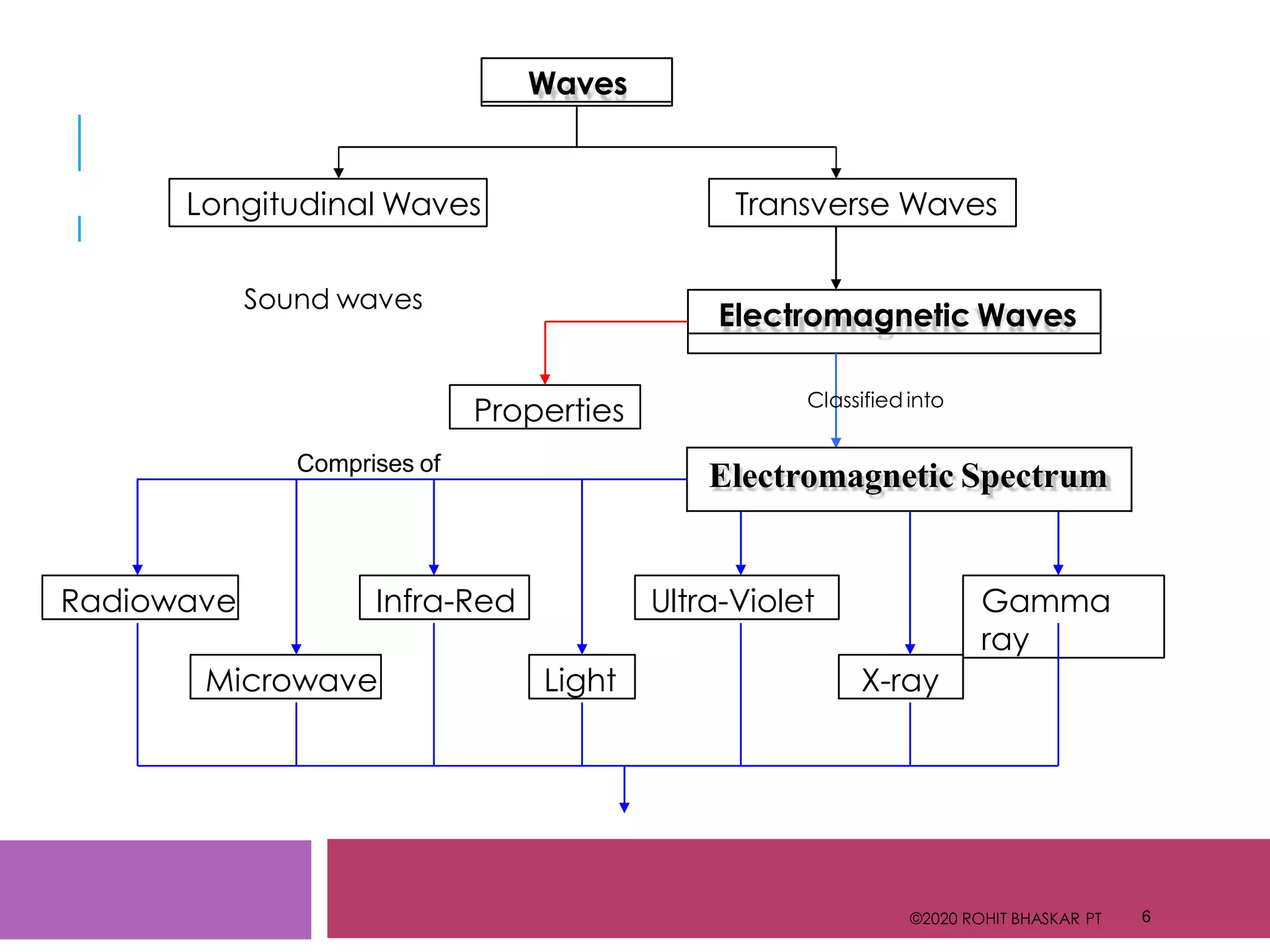
The document provides an overview of the electromagnetic spectrum, detailing different types of electromagnetic waves such as gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet, visible light, infrared, microwaves, and radio waves, along with their speeds, characteristics, and uses. It highlights applications in medicine, industry, and communication, while noting the potential hazards of excessive exposure to certain waves like ultraviolet and X-rays. Overall, it emphasizes the diverse roles these waves play in various fields.