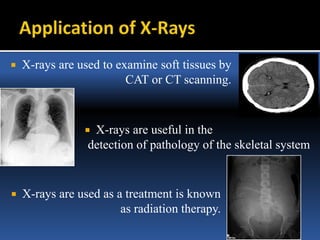
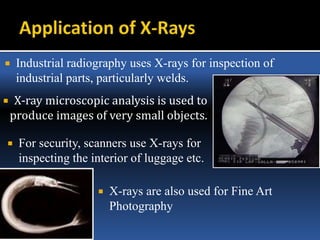
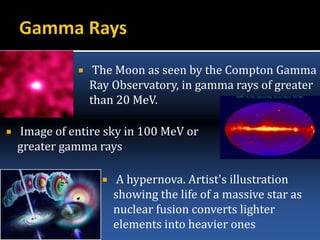
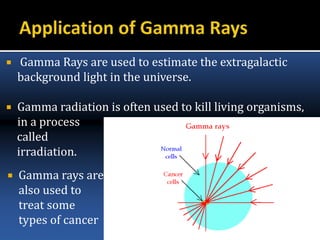
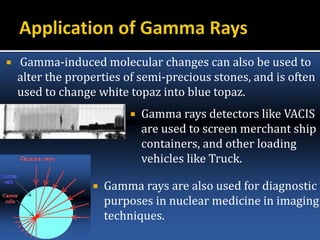
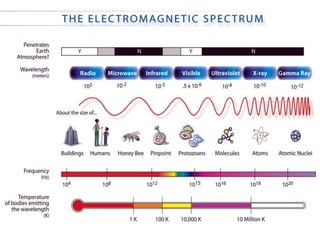
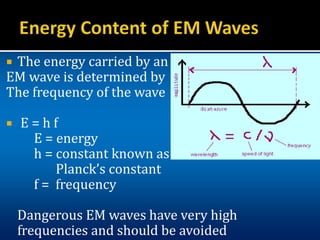
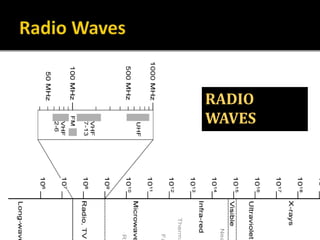
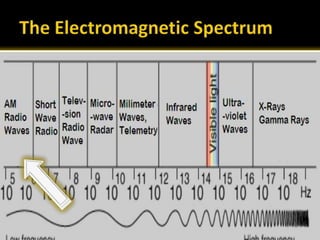
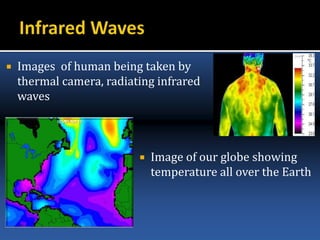
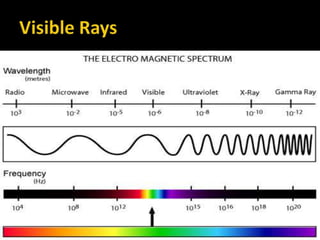
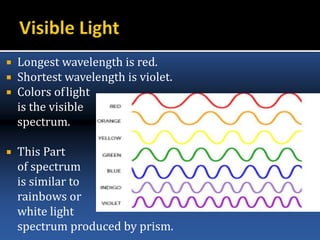
The document provides an overview of electromagnetic (em) waves and the electromagnetic spectrum, detailing their properties, classifications, and various uses. It discusses wave types from radio waves to gamma rays, highlighting their frequencies, energy characteristics, and applications in communication, medical imaging, and treatment. The dangers of high-frequency em waves, particularly in relation to health risks, are also addressed.














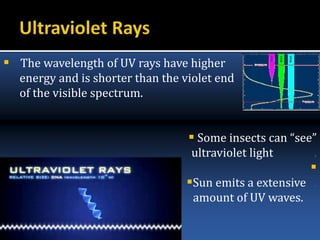
![ They are too energetic that they can break chemical
bonds making molecules unusually reactive or ionizing.
The disruptive effects of UV radiation on
skin cells can cause Sunburn, or Skin
cancer.
It can irreparably damage the complex
DNA molecules in the cells.
The sun emits a large amount of UV radiation, which
could potentially turn Earth into a barren desert.
Ultraviolet waves are of 3 types.
[NUV,EUV,FUV]
NUV
FUV
FUV
EUV
EUV
FUV
NUV](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/emspectrum-160724170016/85/Em-spectrum-24-320.jpg)