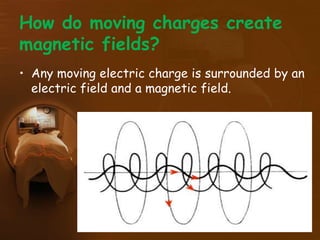
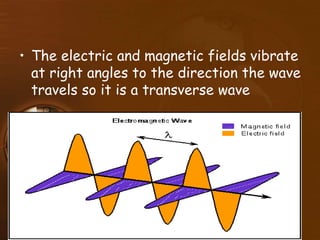
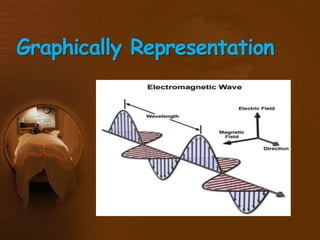
Electromagnetic waves include radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. They are formed by oscillating electric and magnetic fields and travel at the speed of light. Different types of electromagnetic waves interact with matter in different ways depending on their wavelength. Many parts of the electromagnetic spectrum are used in medicine for applications like MRI, infrared therapy, ultrasound, X-rays, and PET scans.