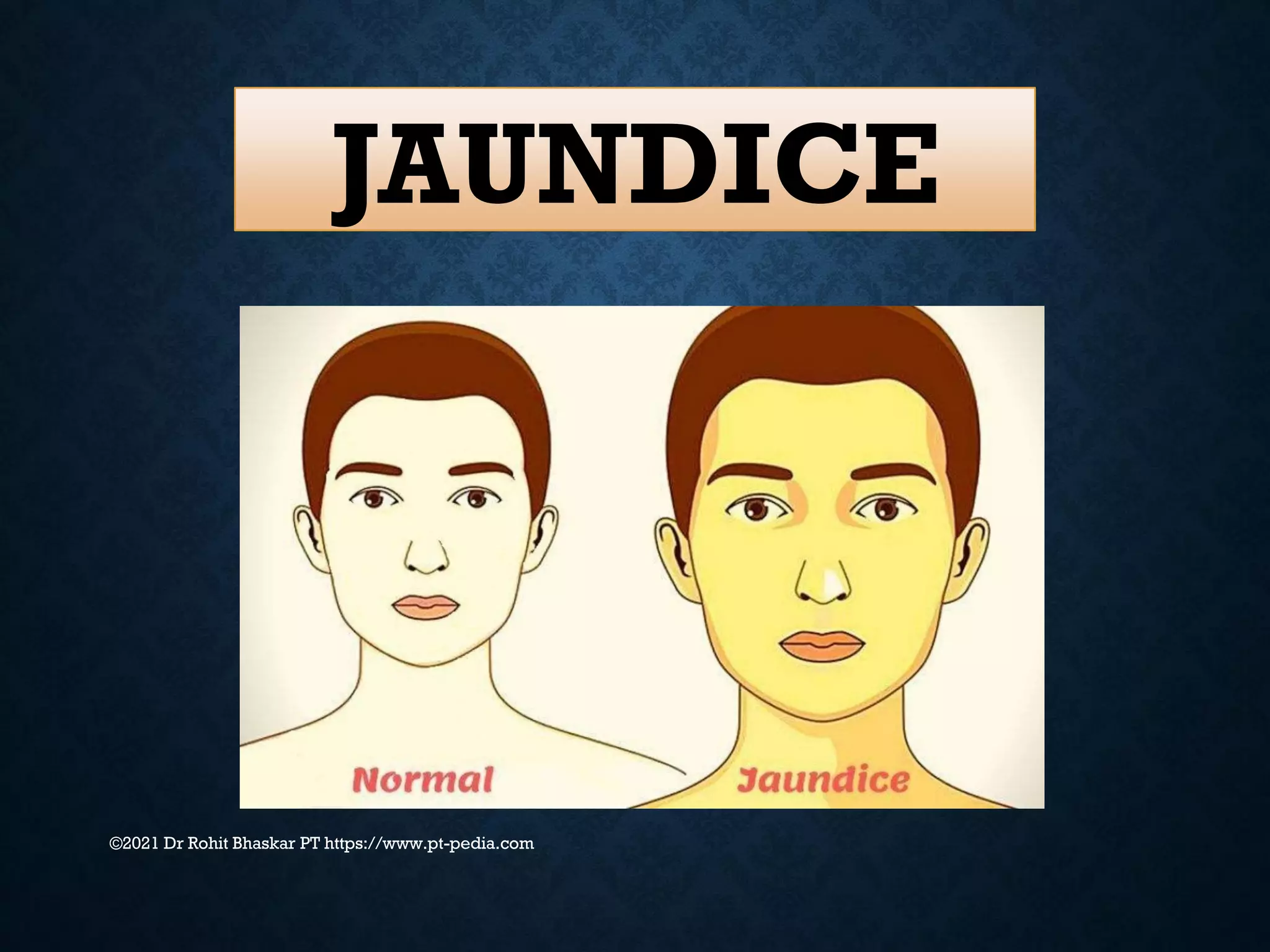
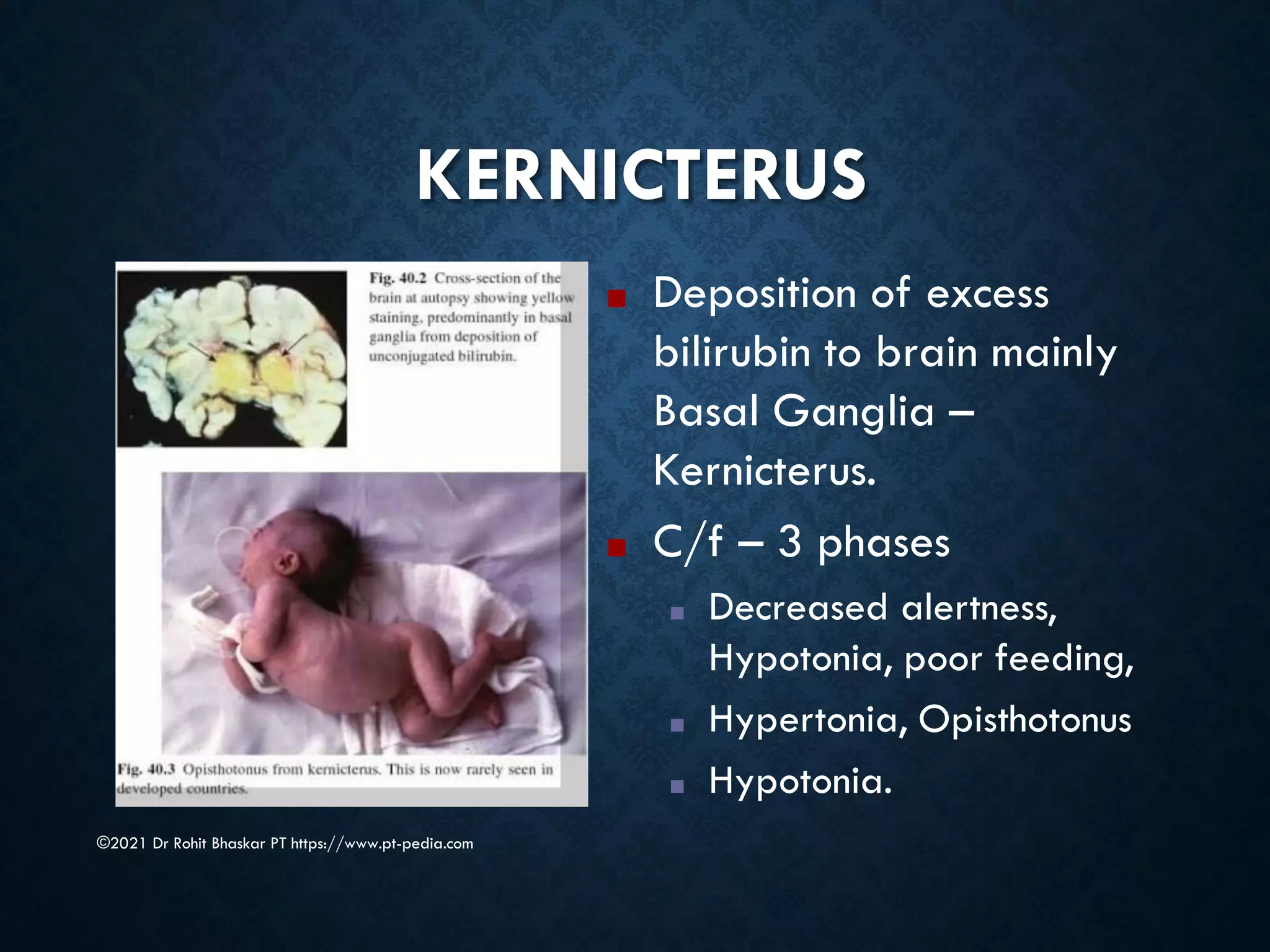
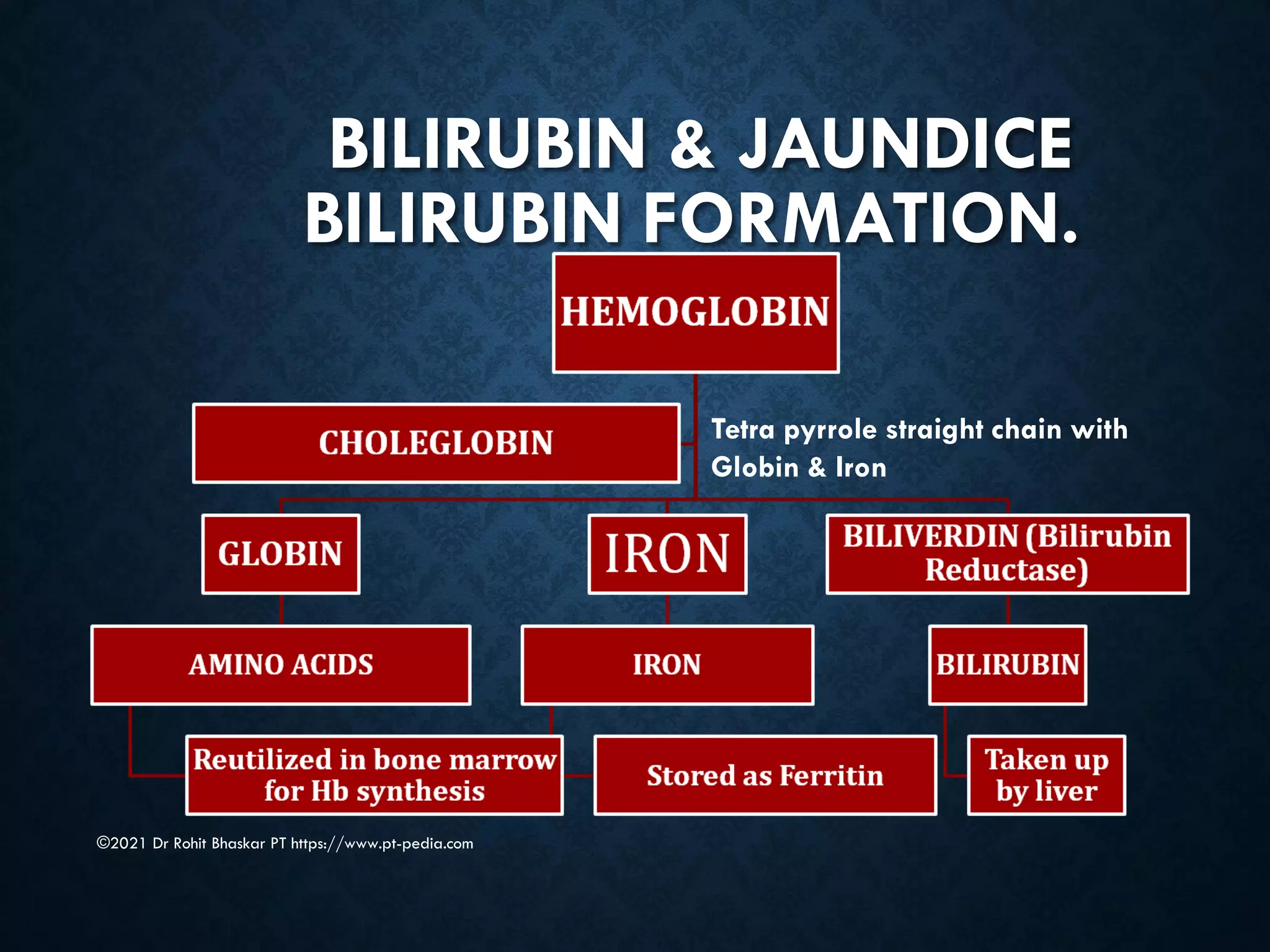
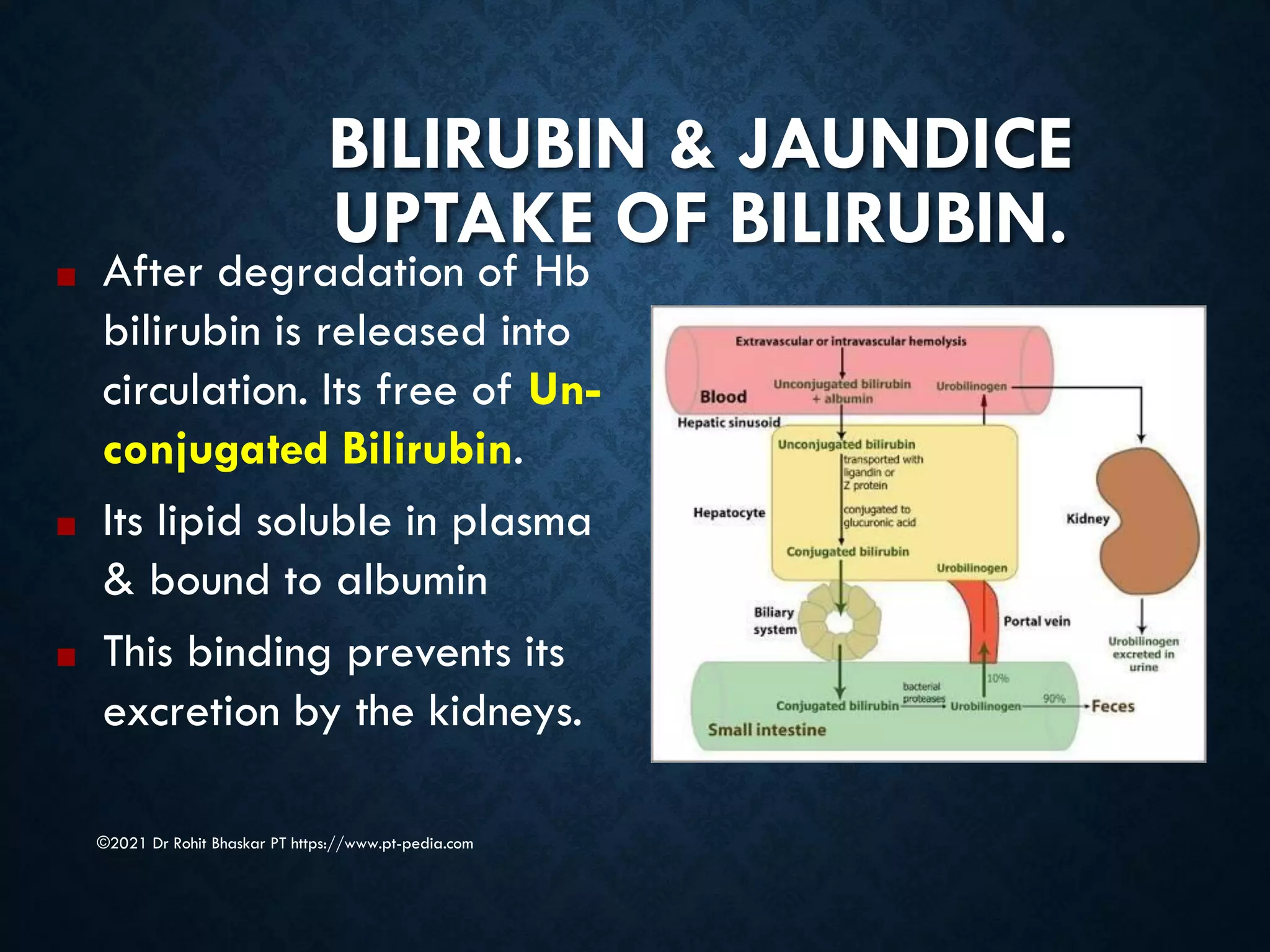
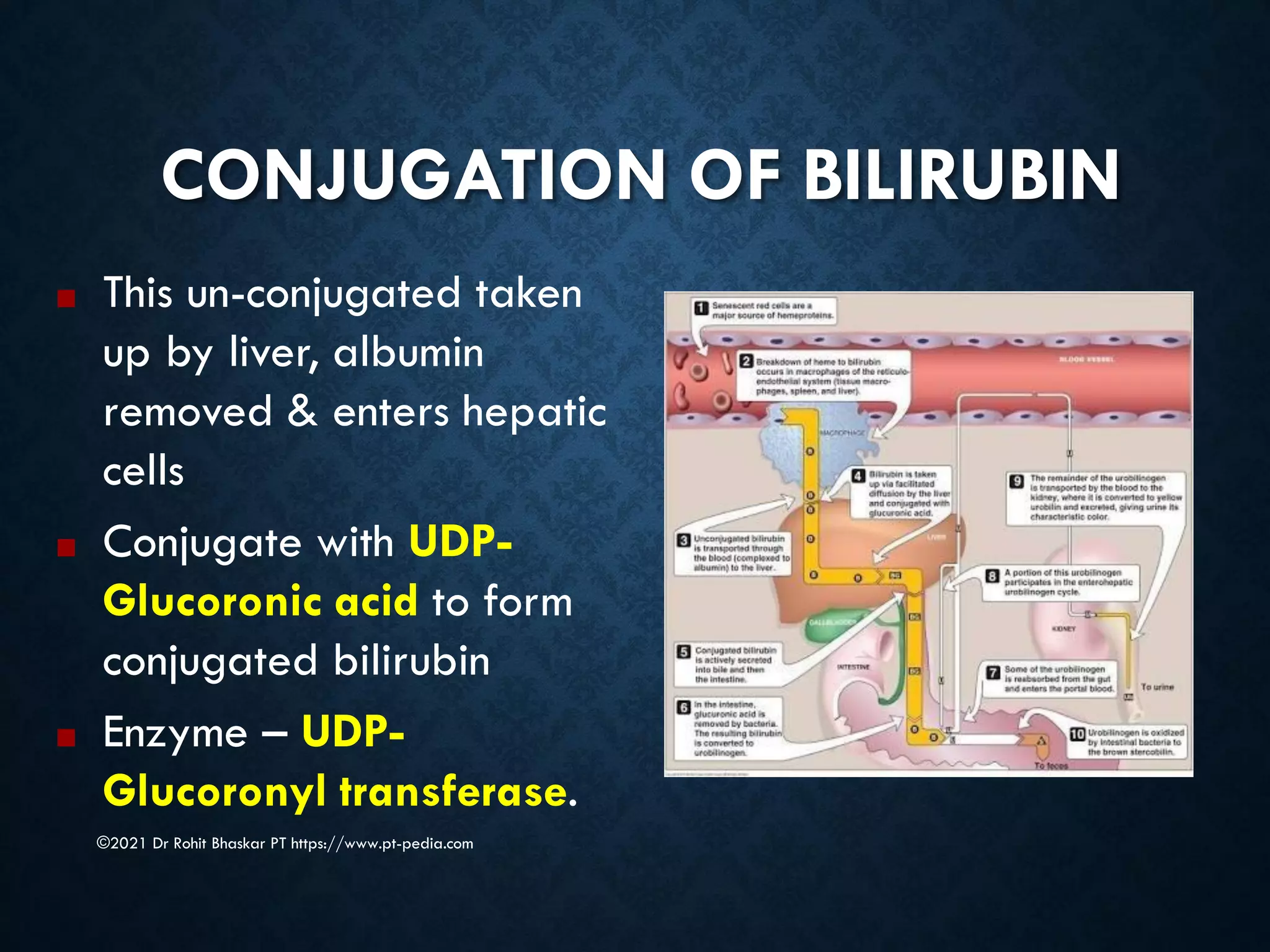
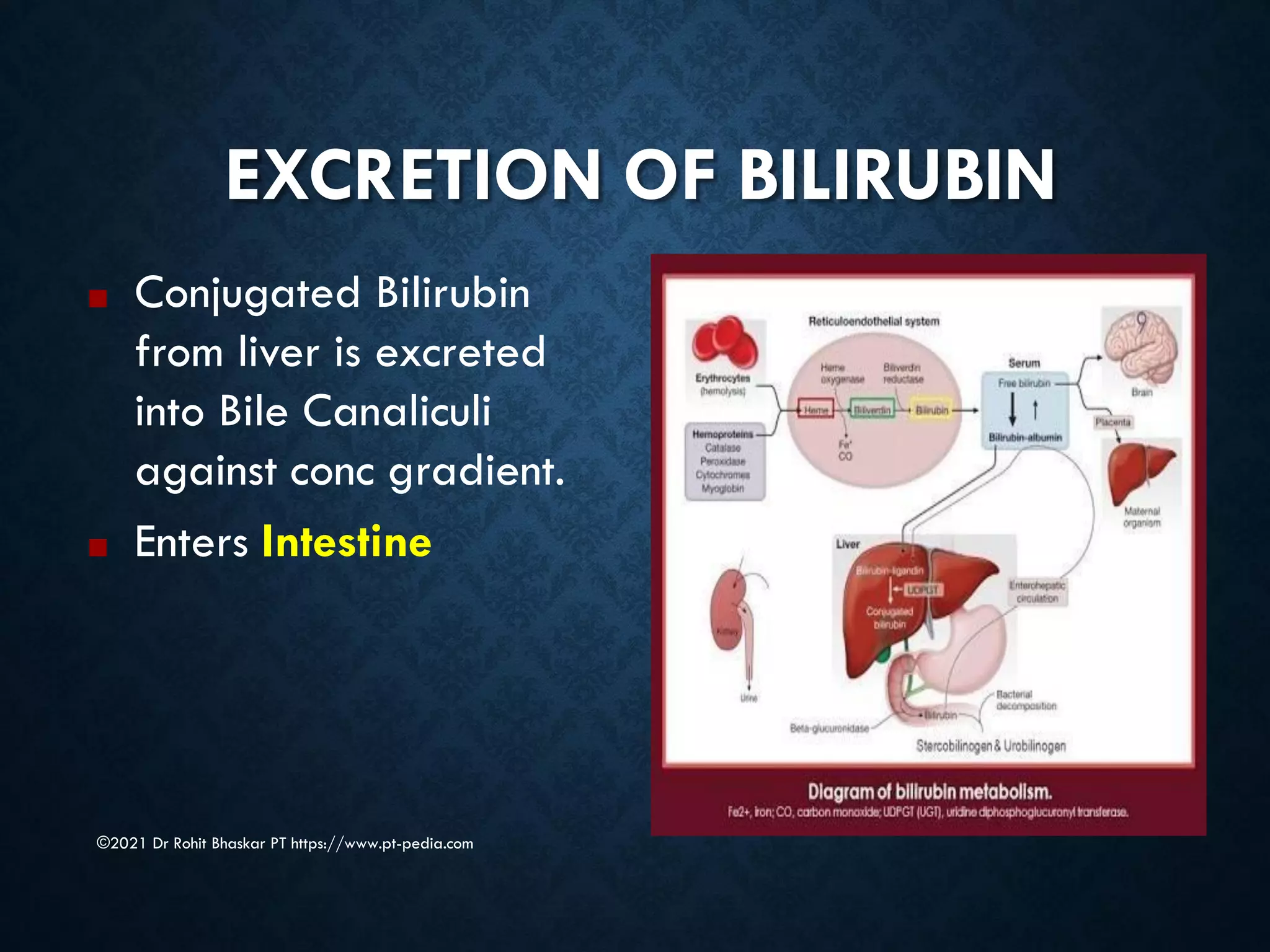
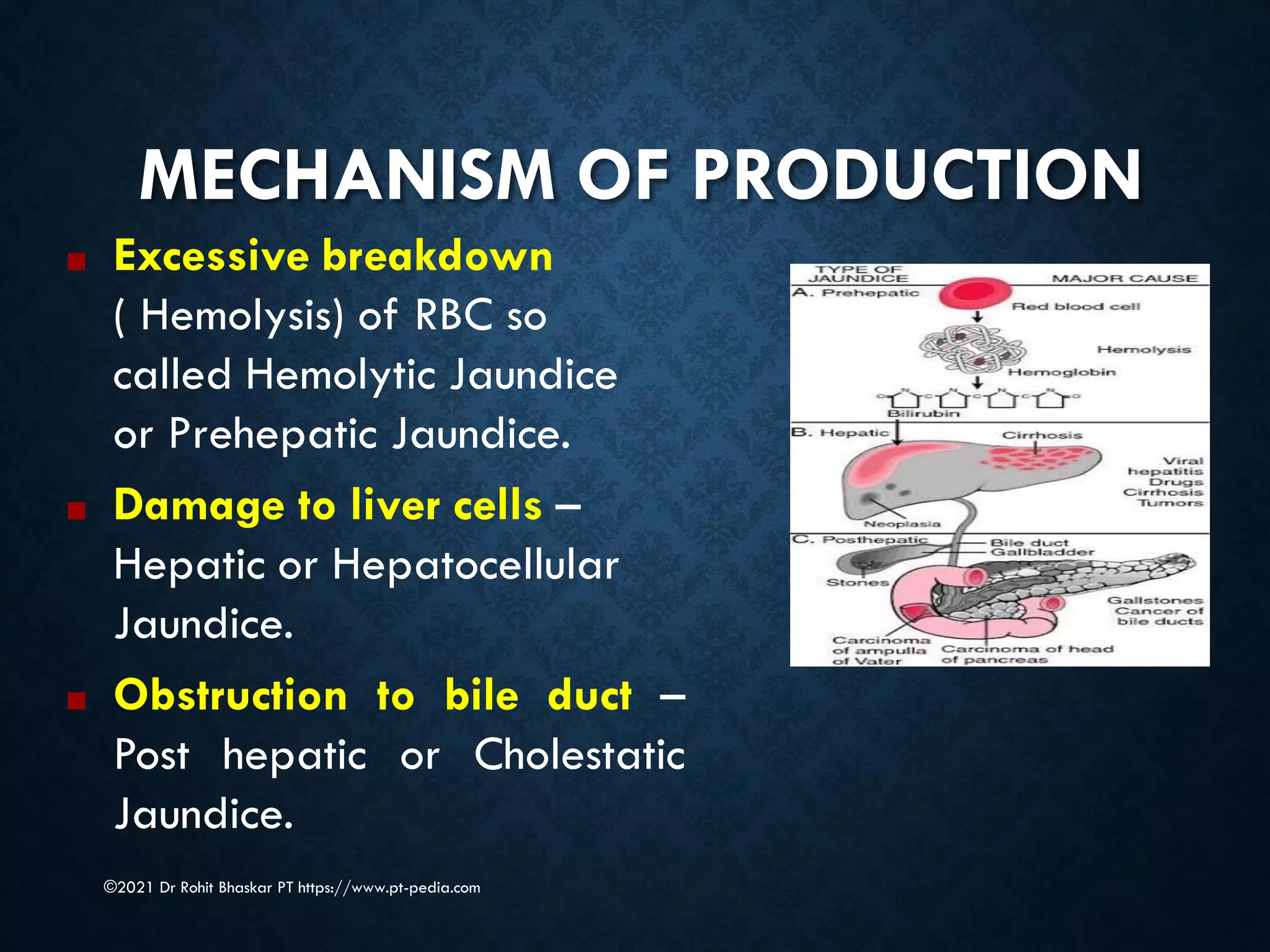
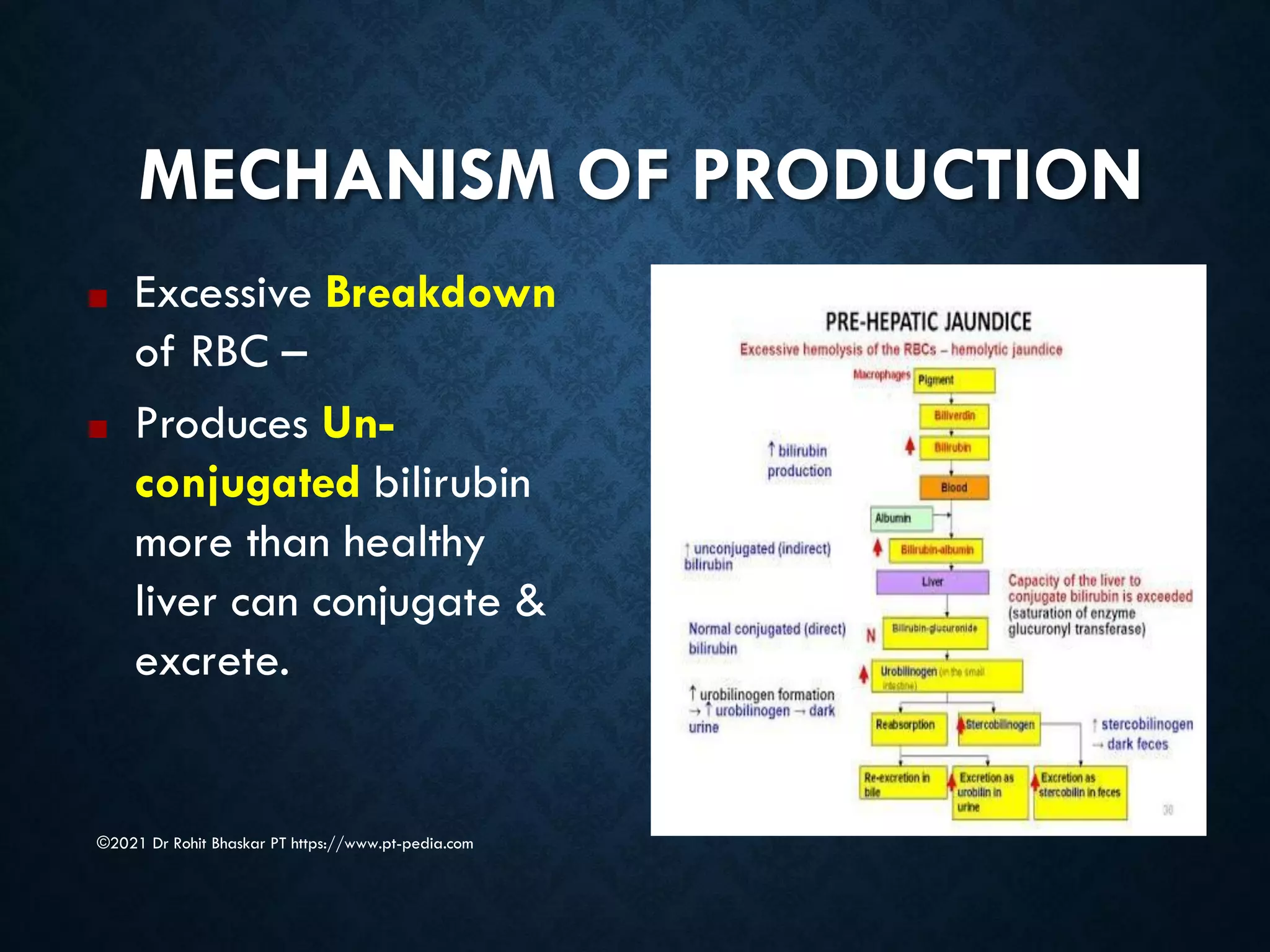
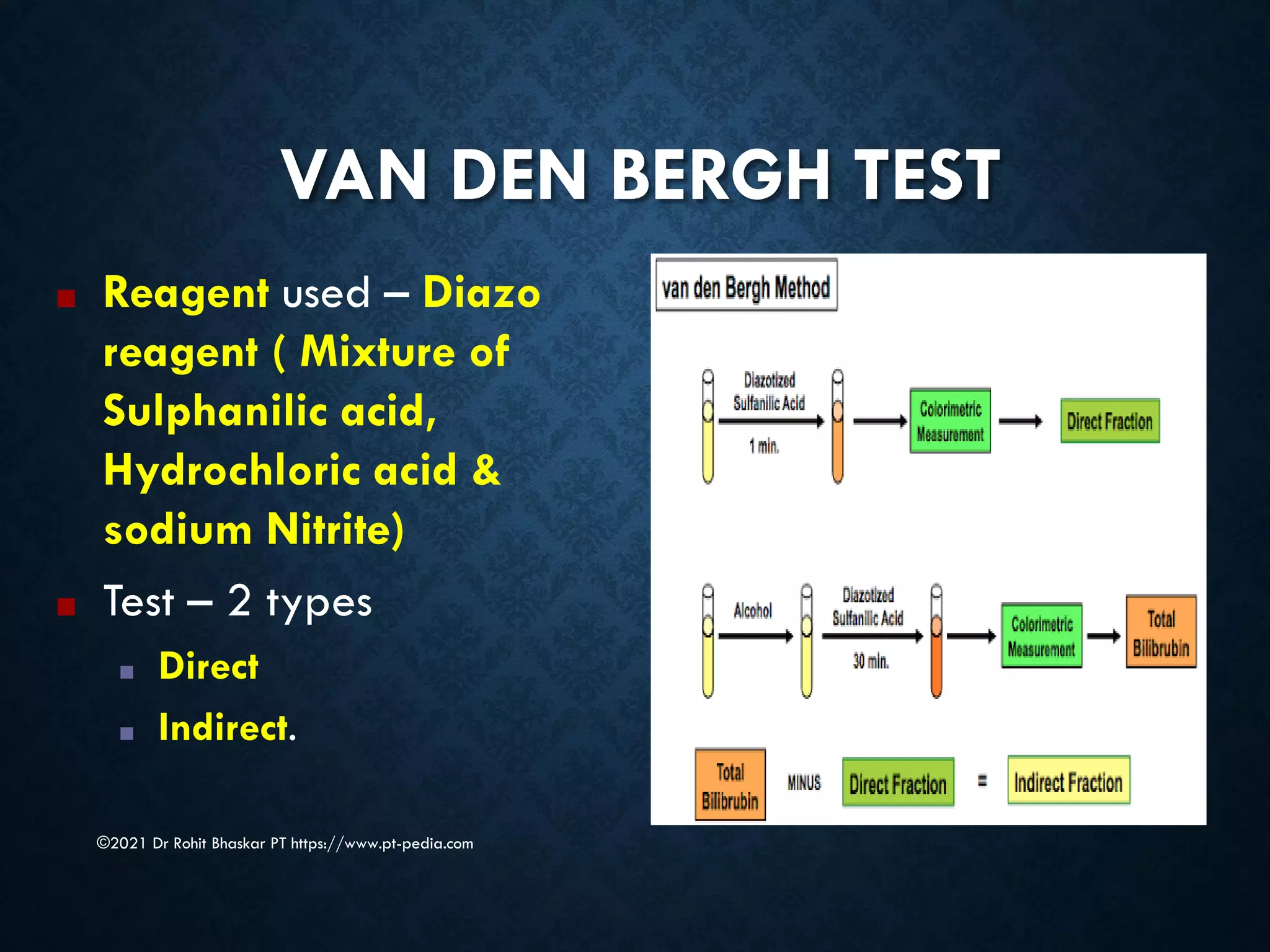
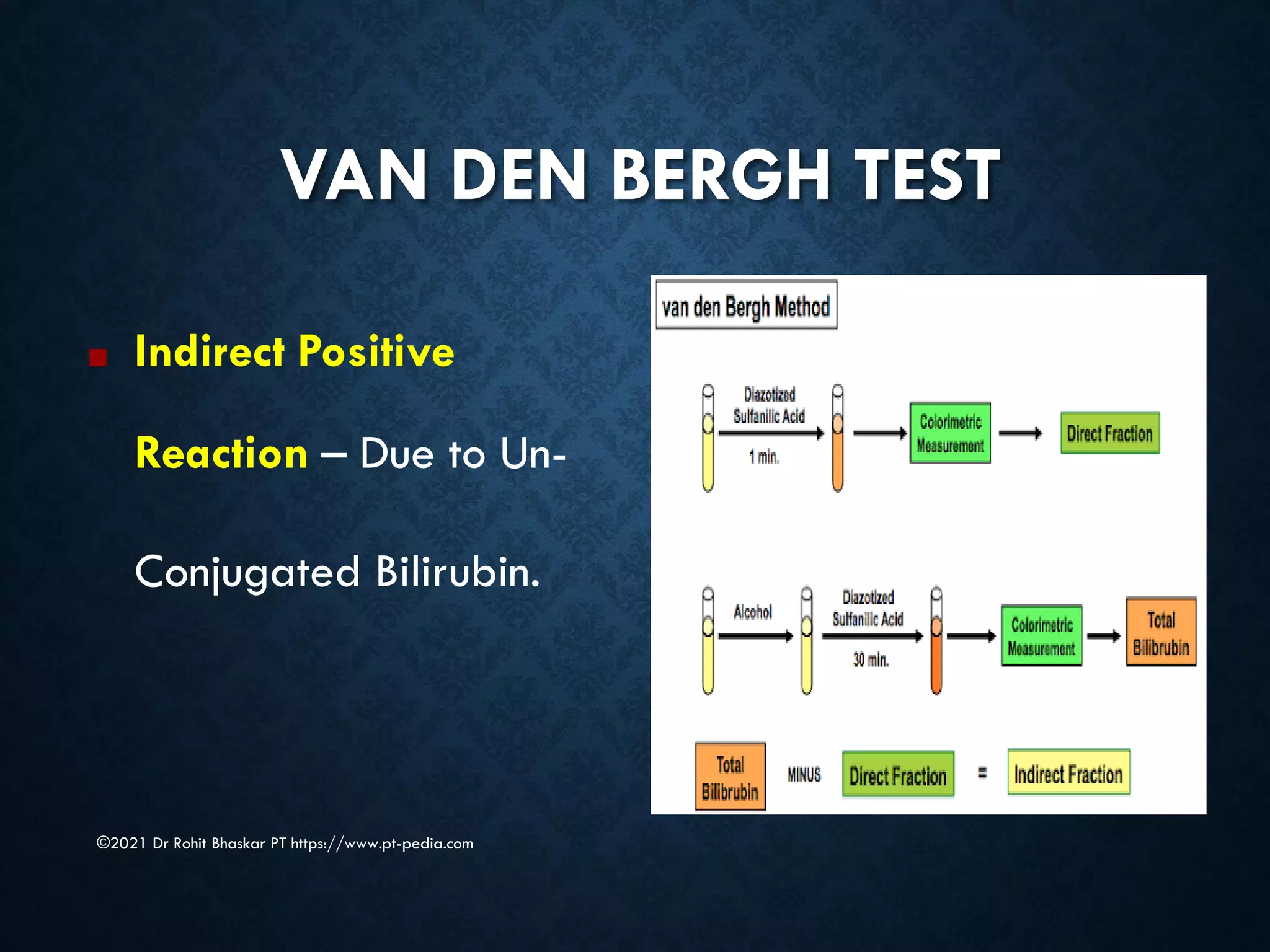
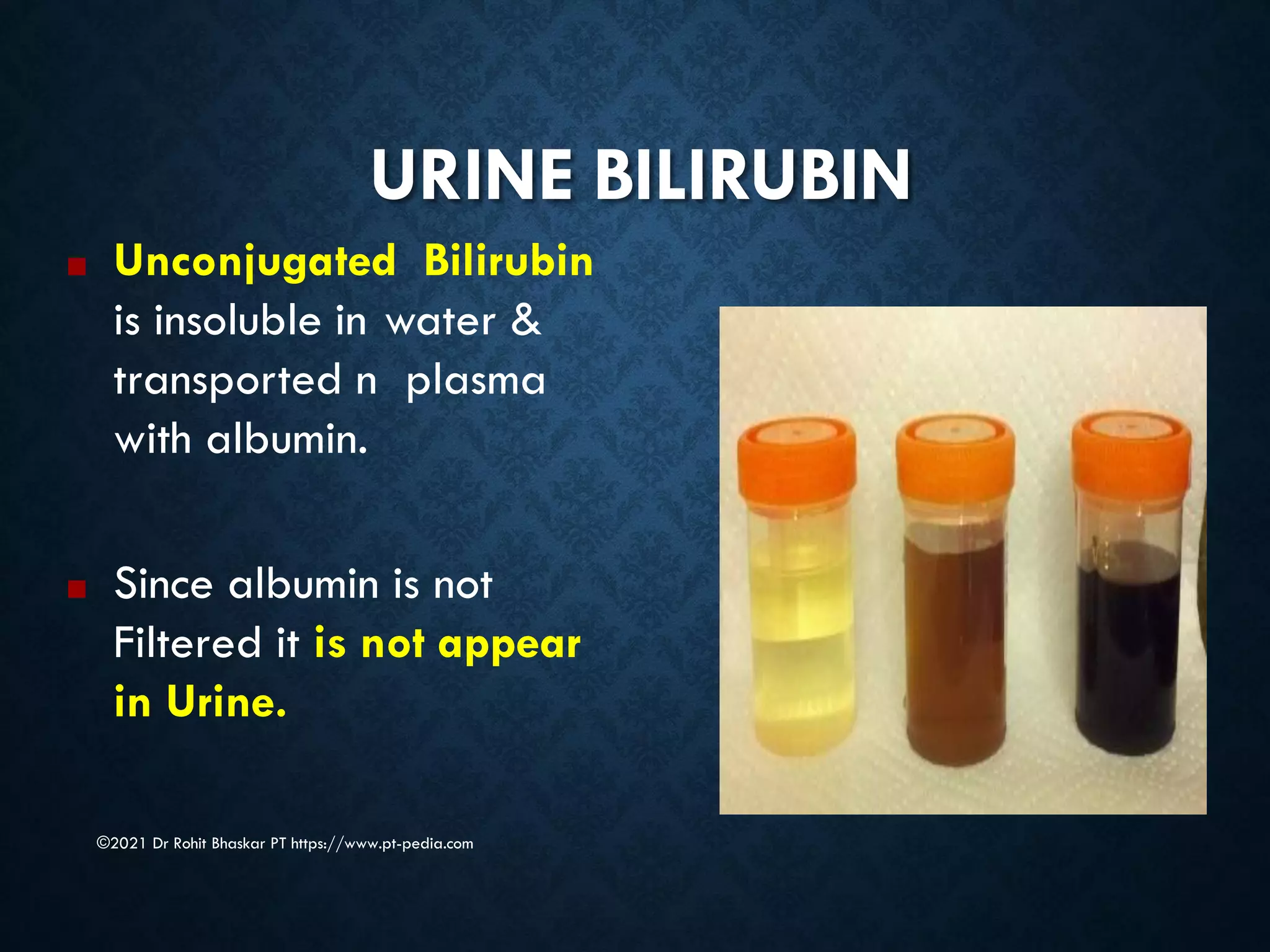
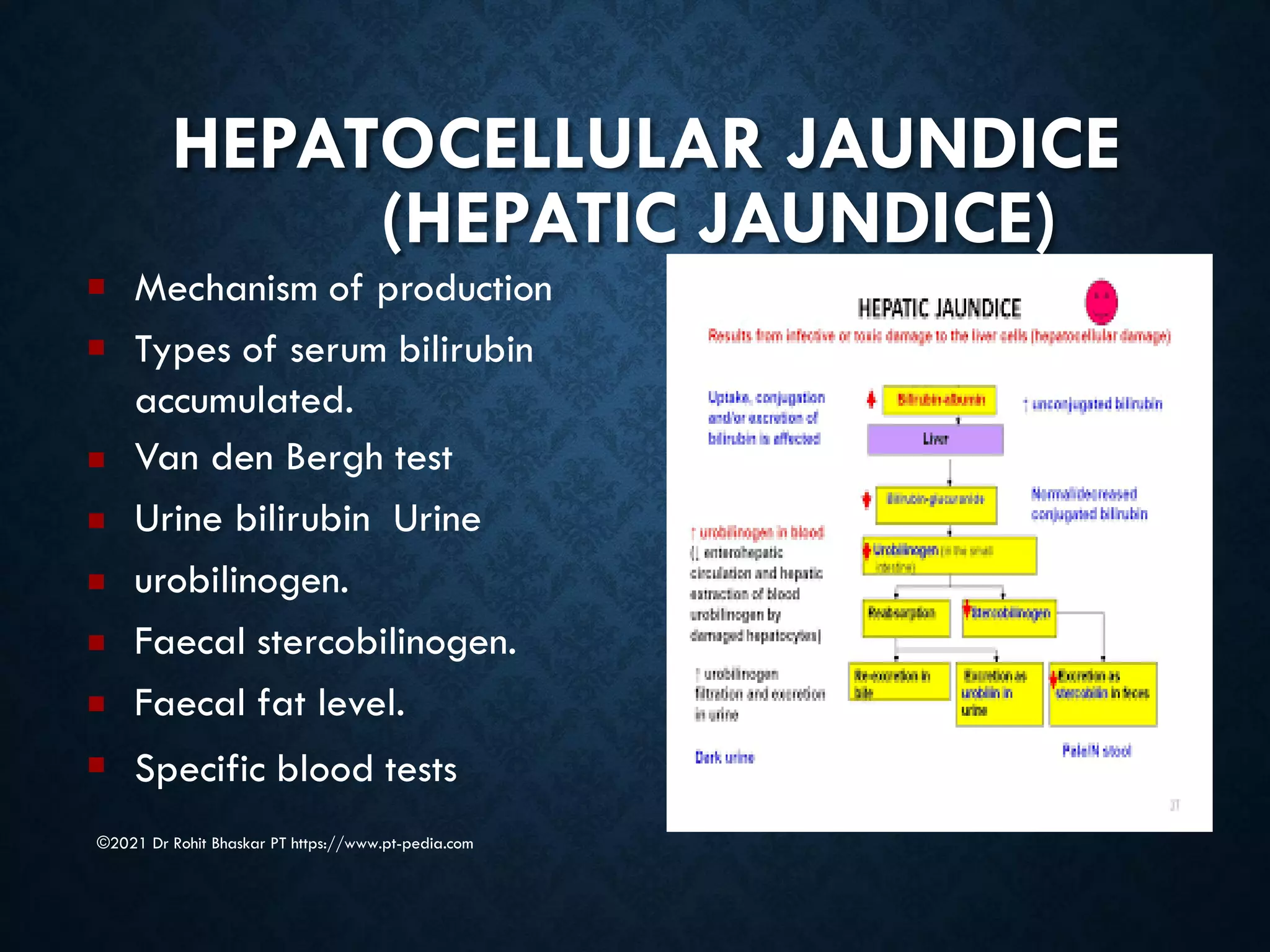
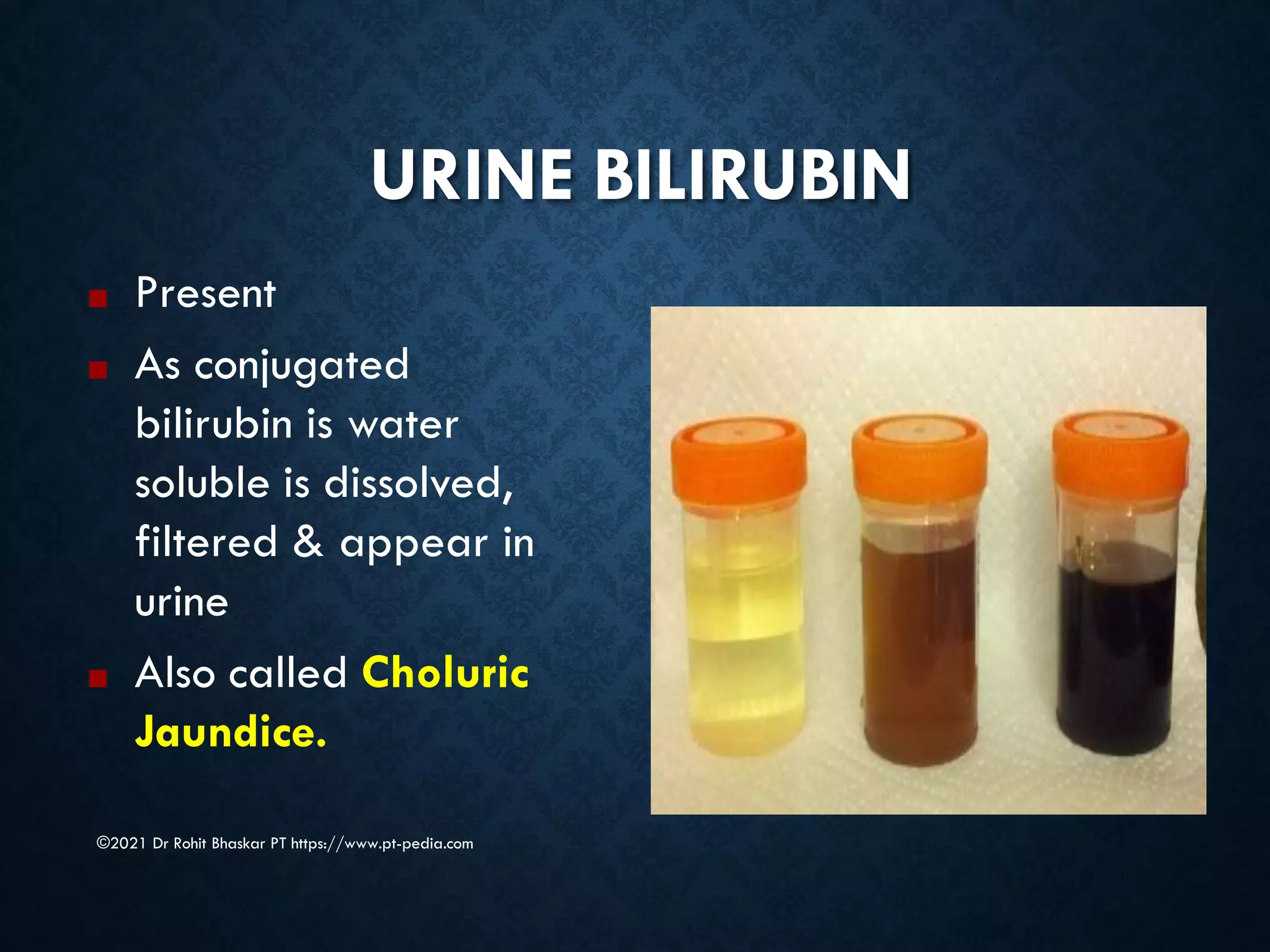
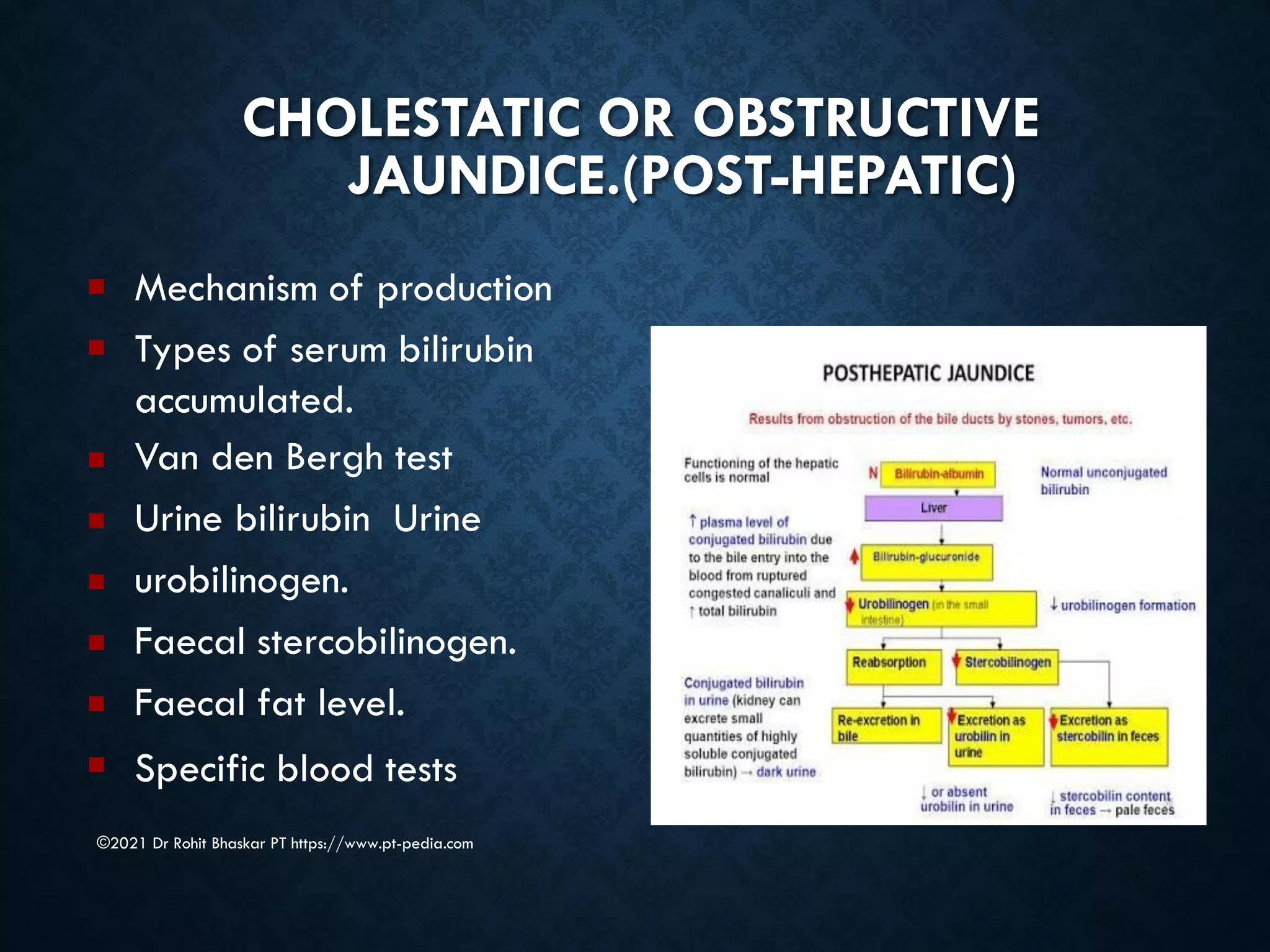
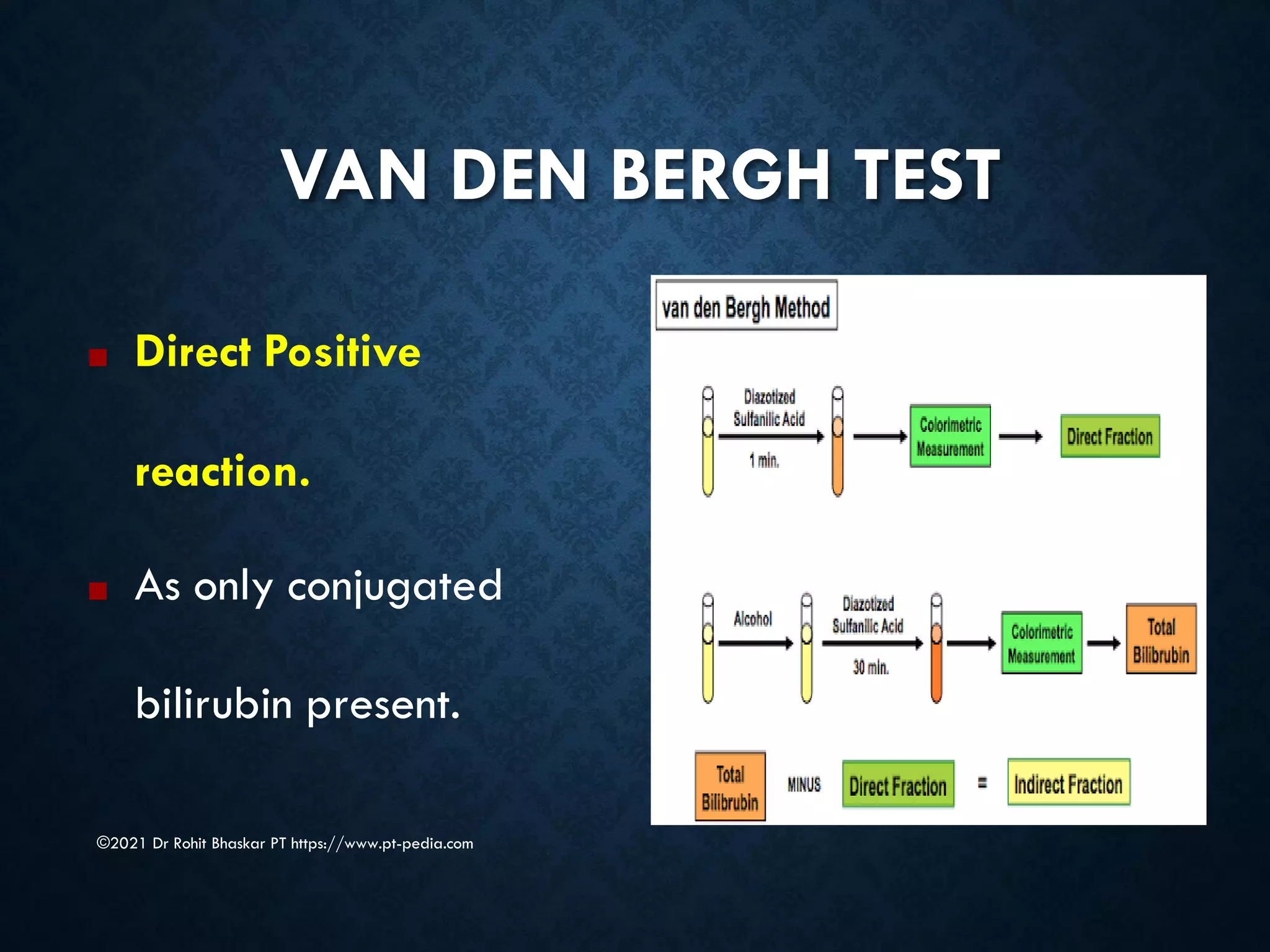
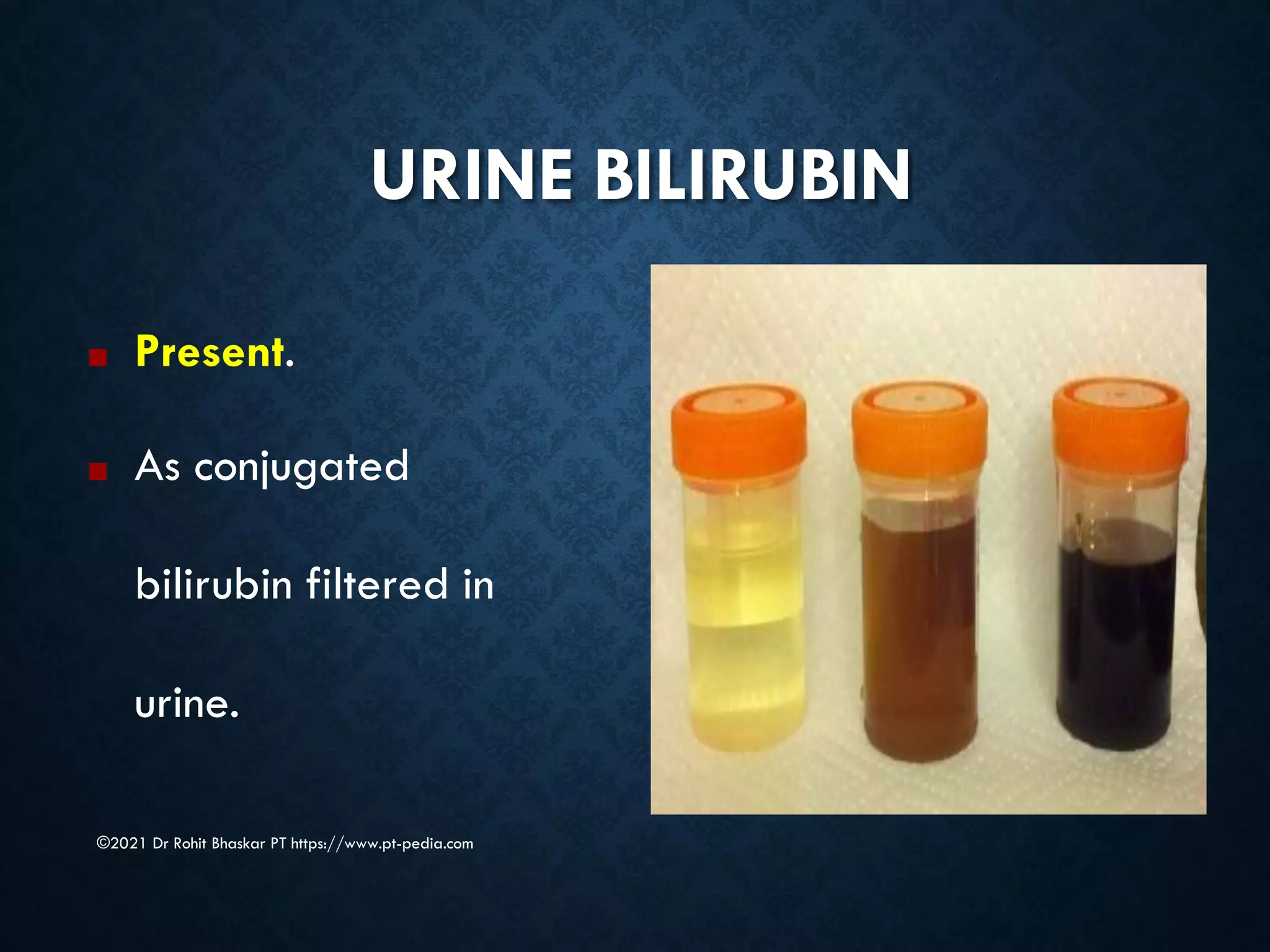
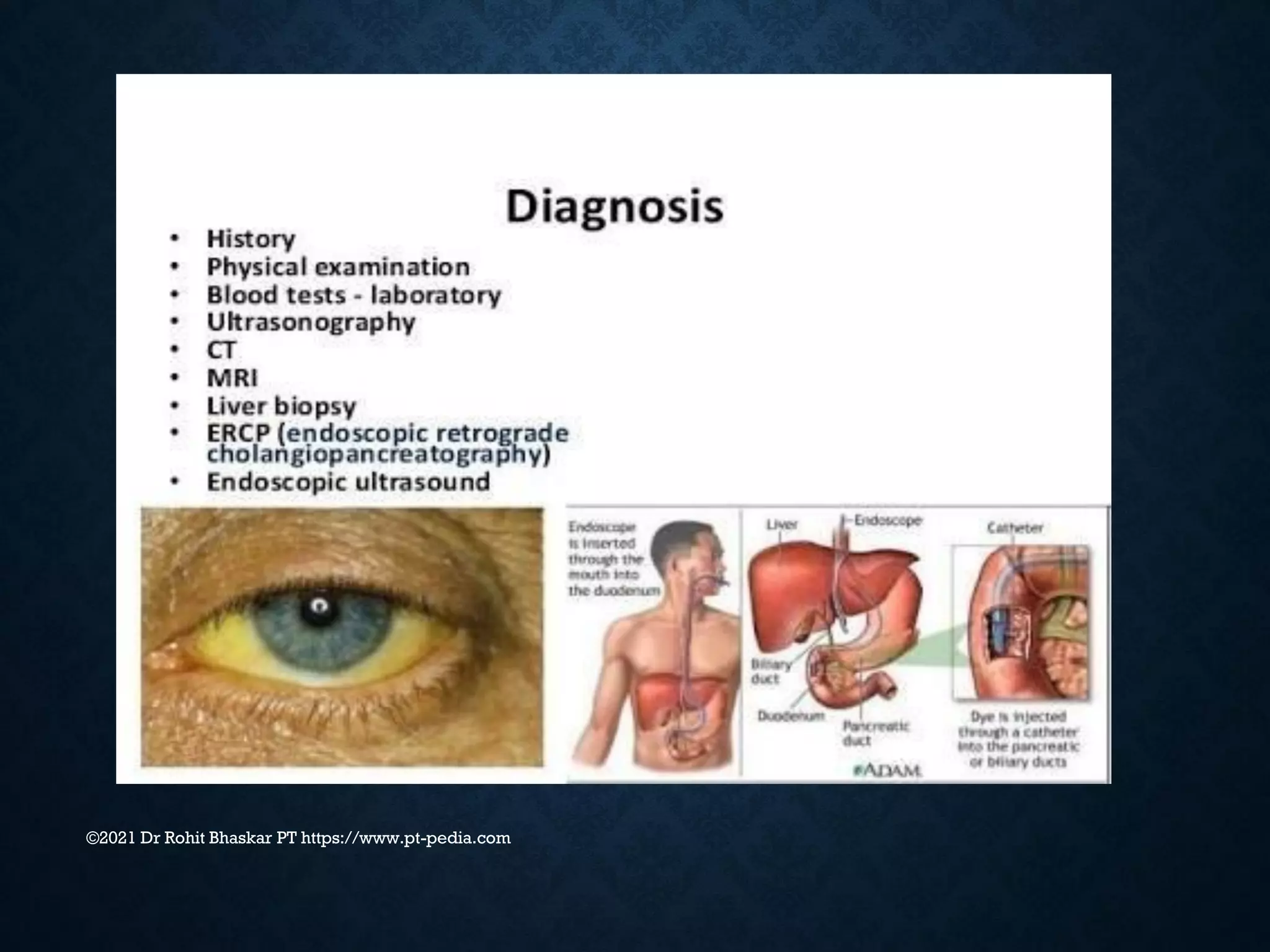
Jaundice is characterized by the yellow discoloration of skin and mucous membranes due to elevated bilirubin levels in the body. It can result from excessive red blood cell breakdown (hemolytic jaundice), liver damage (hepatic jaundice), or bile duct obstruction (cholestatic jaundice). Treatment options include phototherapy for neonates and pharmacological interventions for adults, with prevention measures also available during pregnancy.