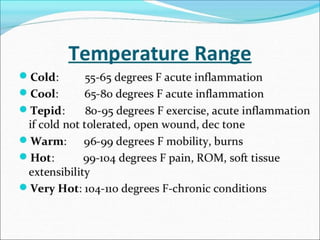
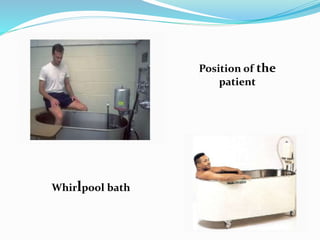
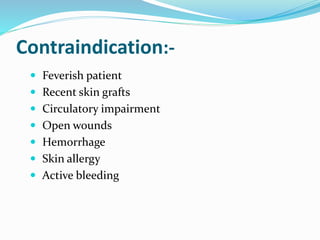
The document details whirlpool bath therapy, a treatment where a body part is submerged in agitated water to enhance circulation, mobility, and comfort post-injury or surgery. It discusses various applications, techniques, uses, indications, and contraindications, emphasizing its benefits in treating conditions like ankle fractures and arthritis, along with risks to be cautious of during therapy. Treatments typically last 10-20 minutes with water temperatures ranging from 36-45 degrees Celsius.