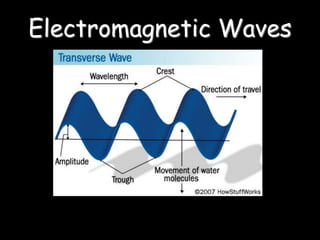
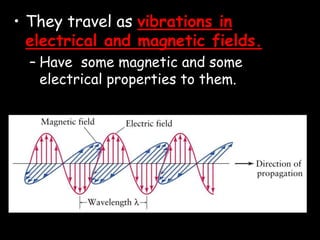
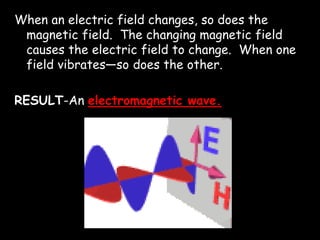
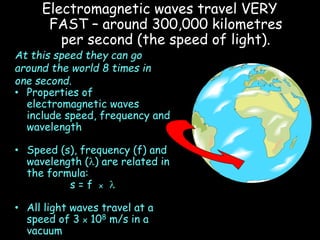
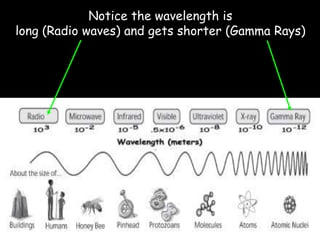
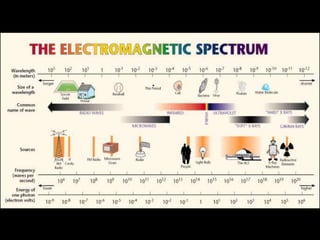
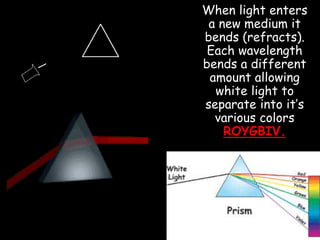
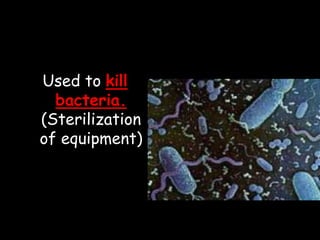
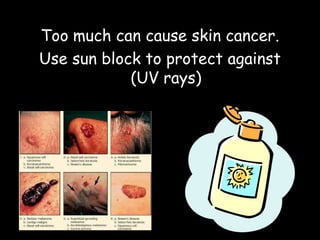
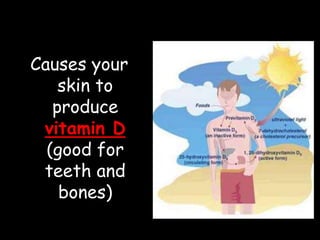
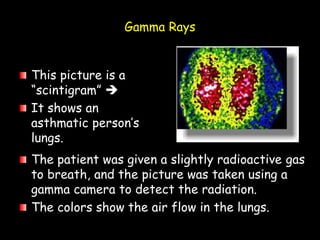
Electromagnetic waves travel as vibrations in electric and magnetic fields and include radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. They are arranged in order of increasing frequency and decreasing wavelength in the electromagnetic spectrum. Electromagnetic waves have various properties including speed, frequency, wavelength, and energy level, with higher frequency waves having higher energy. Different types of electromagnetic waves are used for various applications such as communication technologies, cooking, medical imaging, sterilization, and radiation therapy.