1. A hydro-collator pack is a fabric envelope containing silica gel or bentonite crystal packs that are heated in a hydro-collator unit to provide moist heat therapy.
2. The hydro-collator unit maintains water at 70-80°C to heat the packs for 30-40 minutes of moist heat application.
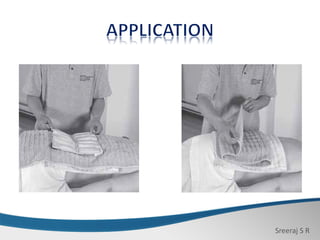
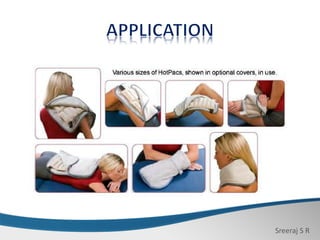
3. When applied with adequate toweling insulation, hydro-collator packs provide penetrating heat therapy above 75°C without raising skin temperature excessively, helping to reduce pain, muscle spasm, and inflammation.