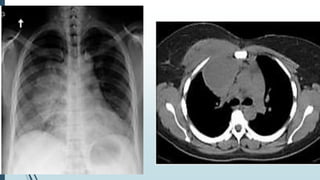
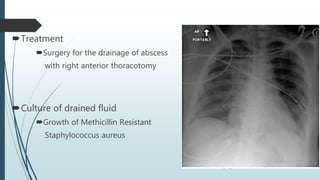
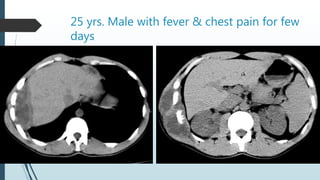
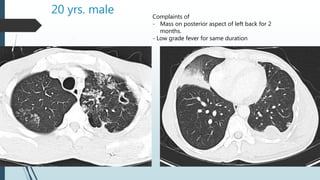
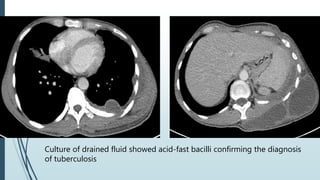
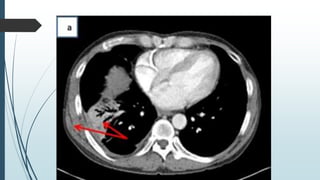
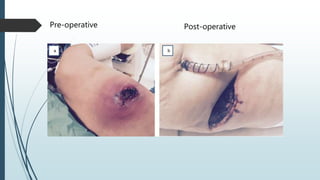
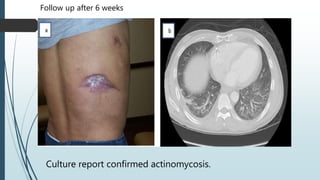
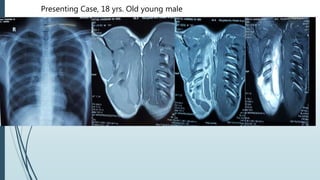
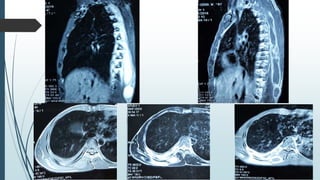
Empyema necessitans is a rare complication of empyema thoracis where the pleural infection extends out of the thorax into the chest wall or surrounding soft tissues. It can be caused by various organisms such as mycobacteria, actinomyces, or fungi. Patients may present with chest pain, erythema, swelling over the chest wall, and symptoms of pulmonary infection. Imaging such as chest X-ray, CT, or MRI can show fluid densities extending into subcutaneous tissues from the pleural space. Treatment involves surgical drainage of abscesses followed by cultures to identify the causative organism and administer appropriate antibiotics.