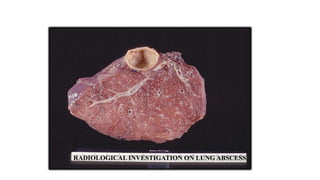
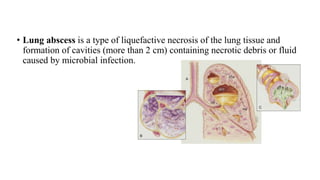
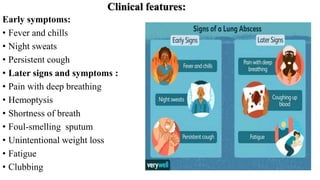
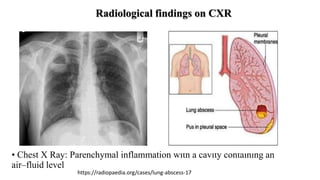
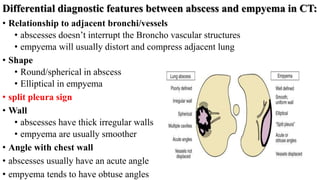
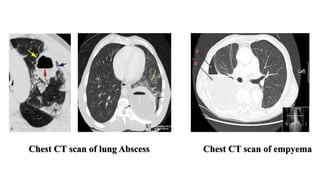
The presentation provides information on lung abscesses, including their pathophysiology, clinical features, and radiological investigation. It notes that lung abscesses are caused by microbial infection which leads to liquefactive necrosis and cavity formation in the lung tissue. Common symptoms include fever, cough, and chest pain. Radiological exams like chest X-rays and CT scans are used to identify characteristics of lung abscesses such as thick-walled cavities containing air-fluid levels. CT scans provide additional details to differentiate abscesses from similar conditions like empyemas.






![Reference:
• En.wikipedia.org. 2022. Lung abscess - Wikipedia. [online] Available at:
<https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lung_abscess> [Accessed 15 March 2022].
• Verywell Health. 2022. What Is a Lung Abscess?. [online] Available at:
<https://www.verywellhealth.com/lung-abscess-overview-4768089> [Accessed 15 March
2022].
• Emedicine.medscape.com. 2022. Lung Abscess: Background, Pathophysiology, Etiology.
[online] Available at: <https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/299425-overview#a5>
[Accessed 17 March 2022].
• Learningradiology.com. 2022. Learning Radiology - Lung, Abscess, pulmonary. [online]
Available at: <http://www.learningradiology.com/archives2008/COW%20306-
Lung%20abscess/lungabscesscorrect.html> [Accessed 17 March 2022].
• Learningradiology.com. 2022. Learning Radiology - Lung, Abscess, pulmonary. [online]
Available at: <http://www.learningradiology.com/archives2008/COW%20306-
Lung%20abscess/lungabscesscorrect.html> [Accessed 17 March 2022].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mimlungabscess-220523172546-4ad184e3/85/MIM-Lung-abscess-pptx-14-320.jpg)
