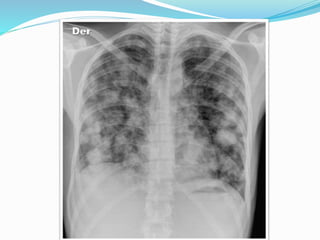
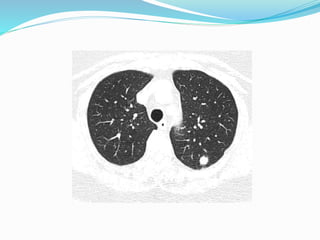
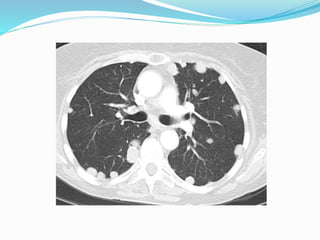
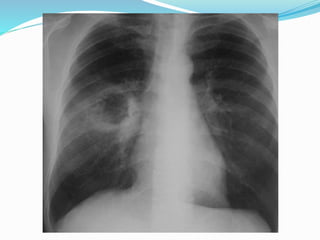
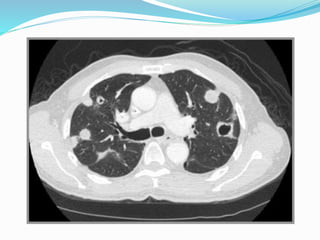
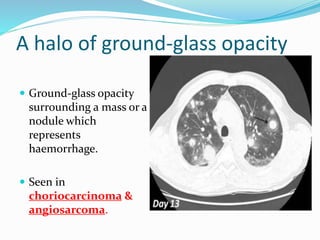
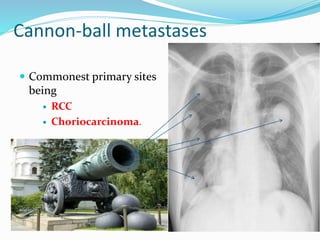
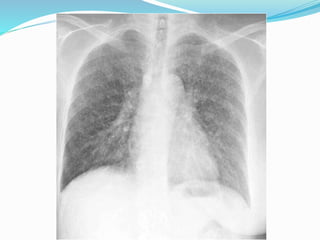
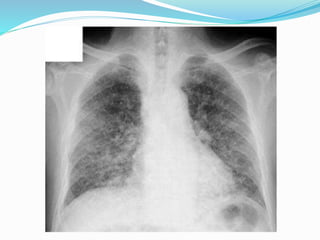
Metastases are tumor implants discontinuous from the primary tumor. Pulmonary metastases most commonly present as multiple pulmonary nodules and are usually bilateral with a basal predominance. They most often spread to the lungs via the bloodstream. The lungs act as a filter for the blood, allowing cancer cells from primary tumors in many sites like breast, bone, and urogenital organs to become lodged in the lungs. Radiologically, metastases typically appear as rounded nodules but can also cavitate, calcify, or cause consolidations. Diagnosis involves determining the primary site through clinical evaluation, imaging, and biopsy of lesions. Treatment options include chemotherapy, radiation, surgery, and palliative care.