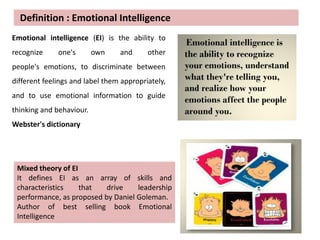
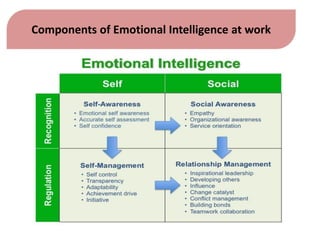
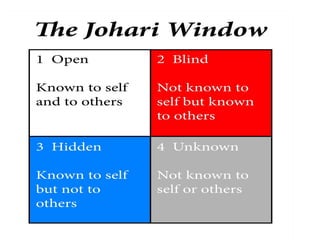
This document discusses emotional intelligence and its importance. It defines emotional intelligence as the ability to recognize one's own emotions and others' emotions and to use this information to guide thinking and behavior. The document notes that research found emotional intelligence is an essential trait for 78% of leaders. It discusses components of emotional intelligence like self-awareness, self-regulation, self-motivation, empathy, and relationship management. The document provides examples of how to apply emotional intelligence to handle non-performance at work and home. It argues that practicing emotional intelligence can help people deal with difficult situations in a balanced way and achieve desired results.