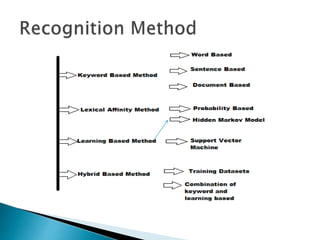
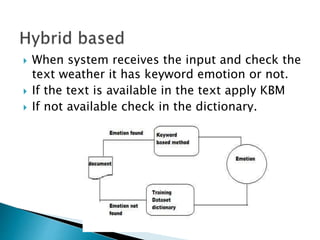
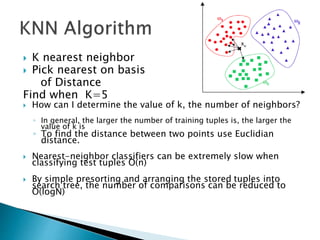
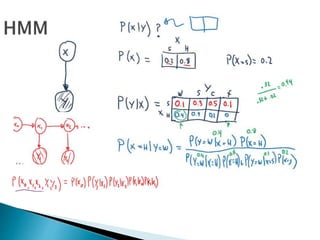
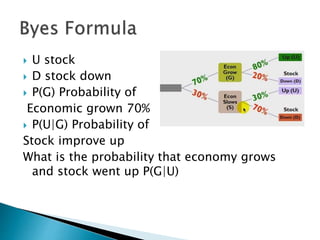
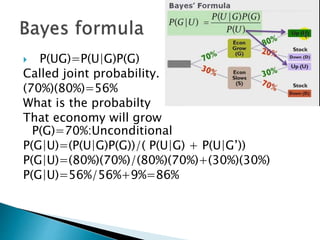
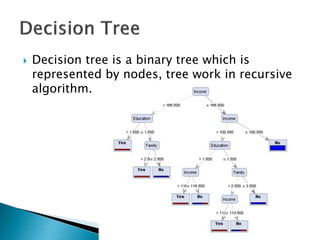
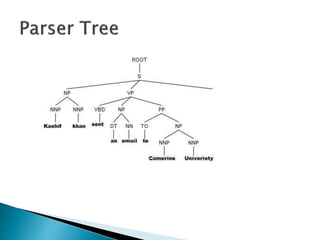
This document discusses text-based emotion recognition. It describes how emotions are expressed through text messages and the challenges in developing algorithms to accurately recognize emotions from text for machines. Various approaches are discussed, including sentiment analysis, using emotion keywords, and machine learning classifiers like KNN and Hidden Markov Models. Challenges around ambiguity, negation, and multiple opinions in sentences are also outlined. The goal is to develop systems that can detect emotions beyond just keywords to gain a deeper understanding of emotional expression and changes over time from text.