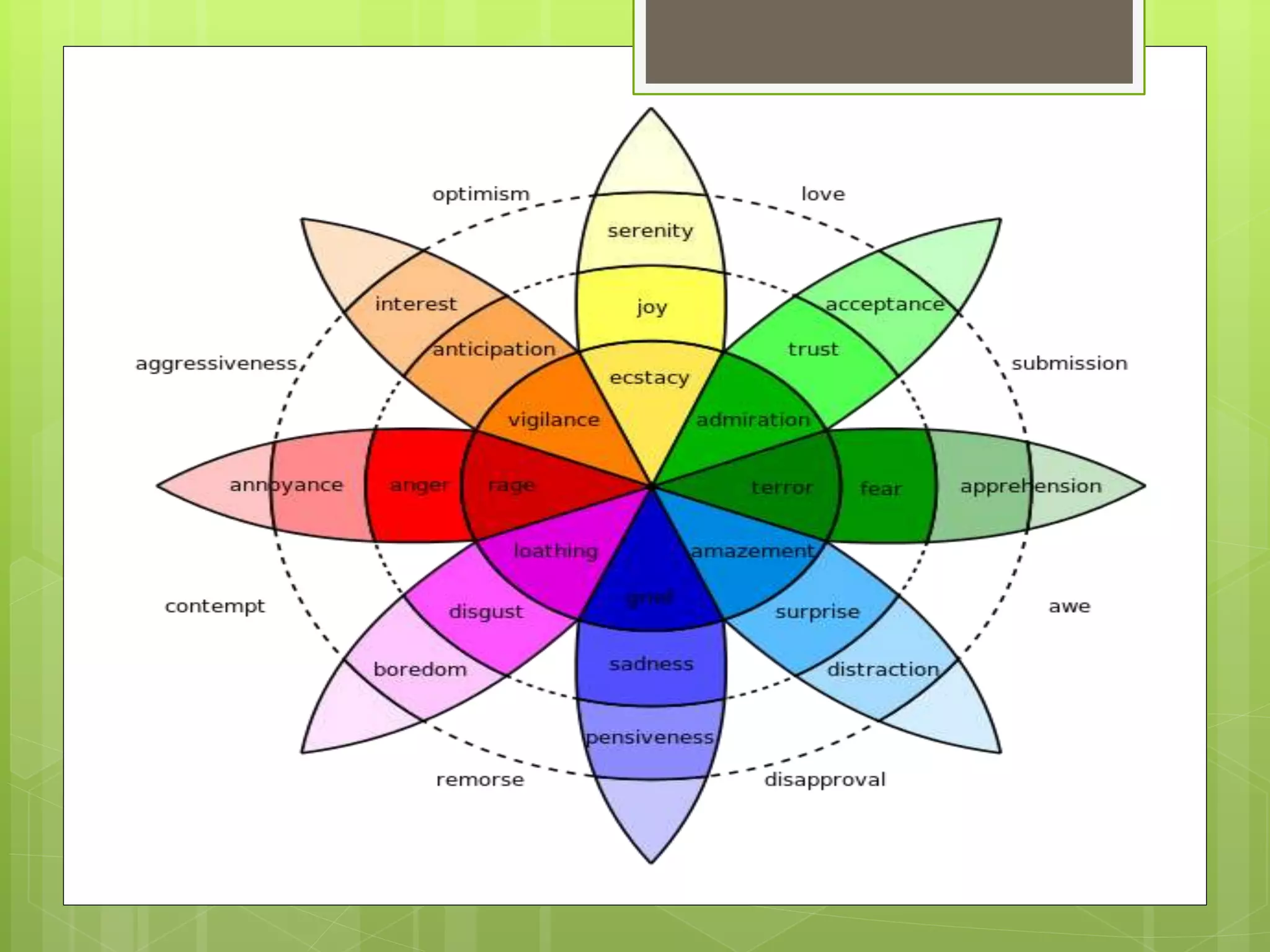
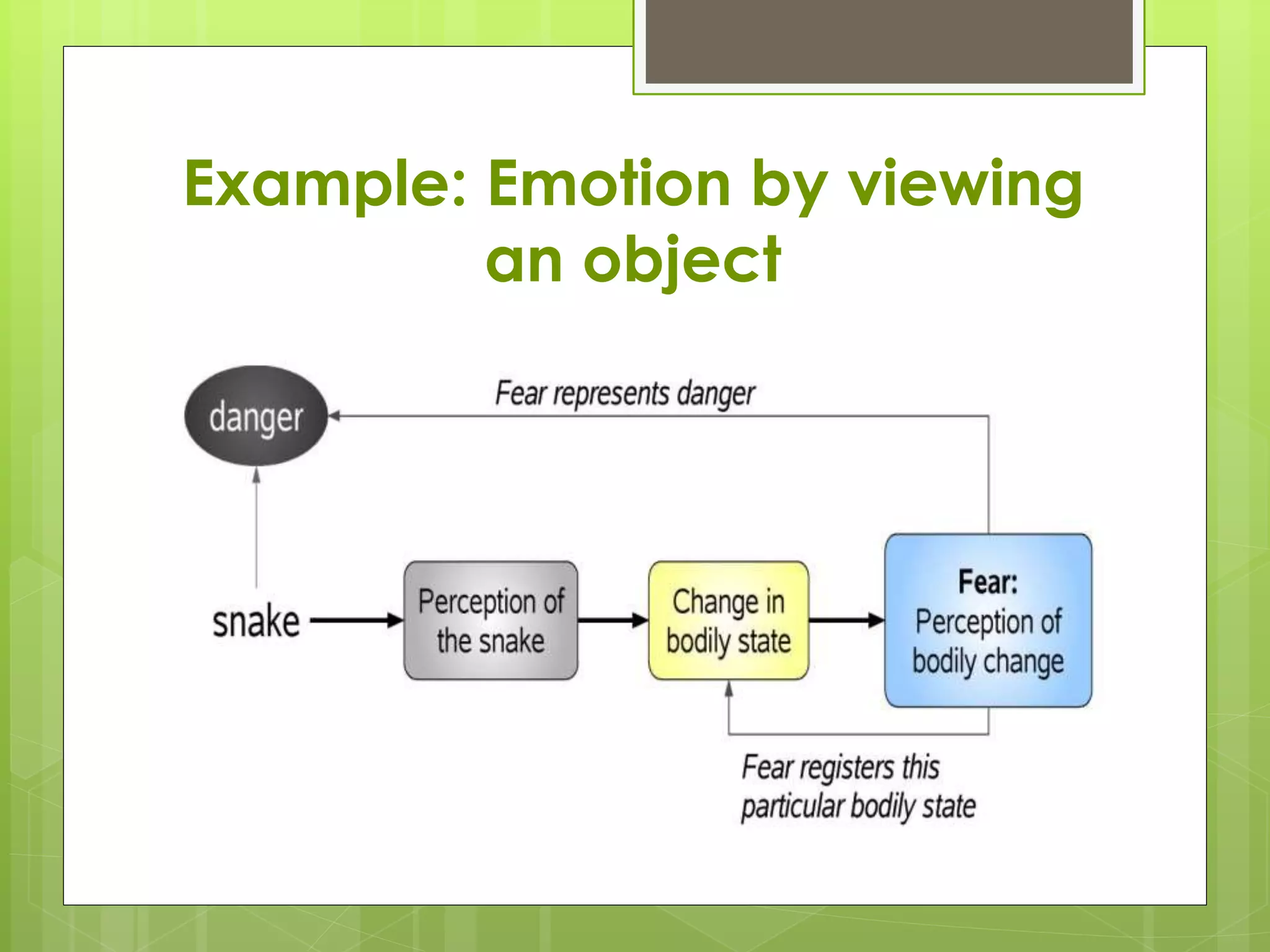
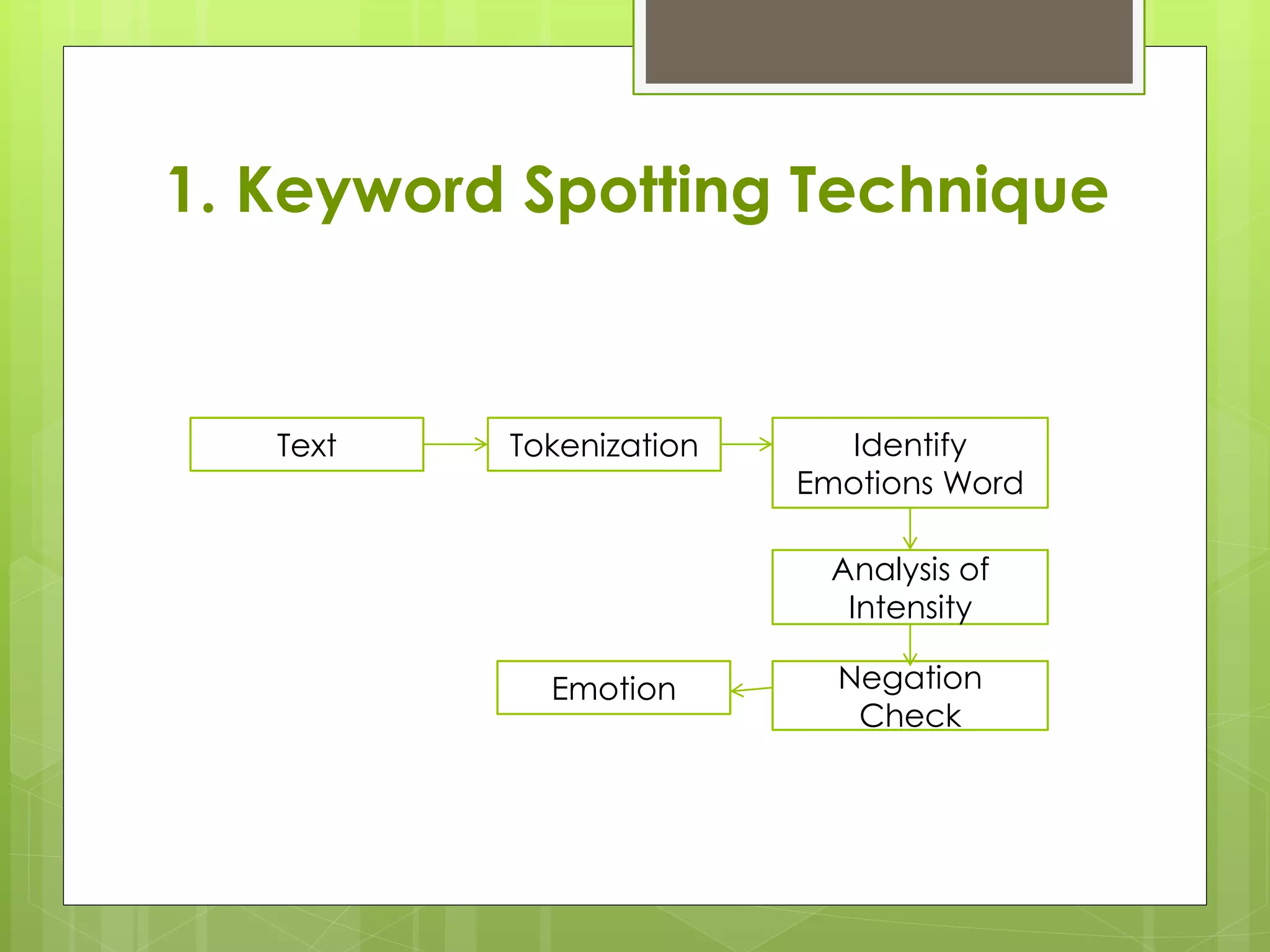
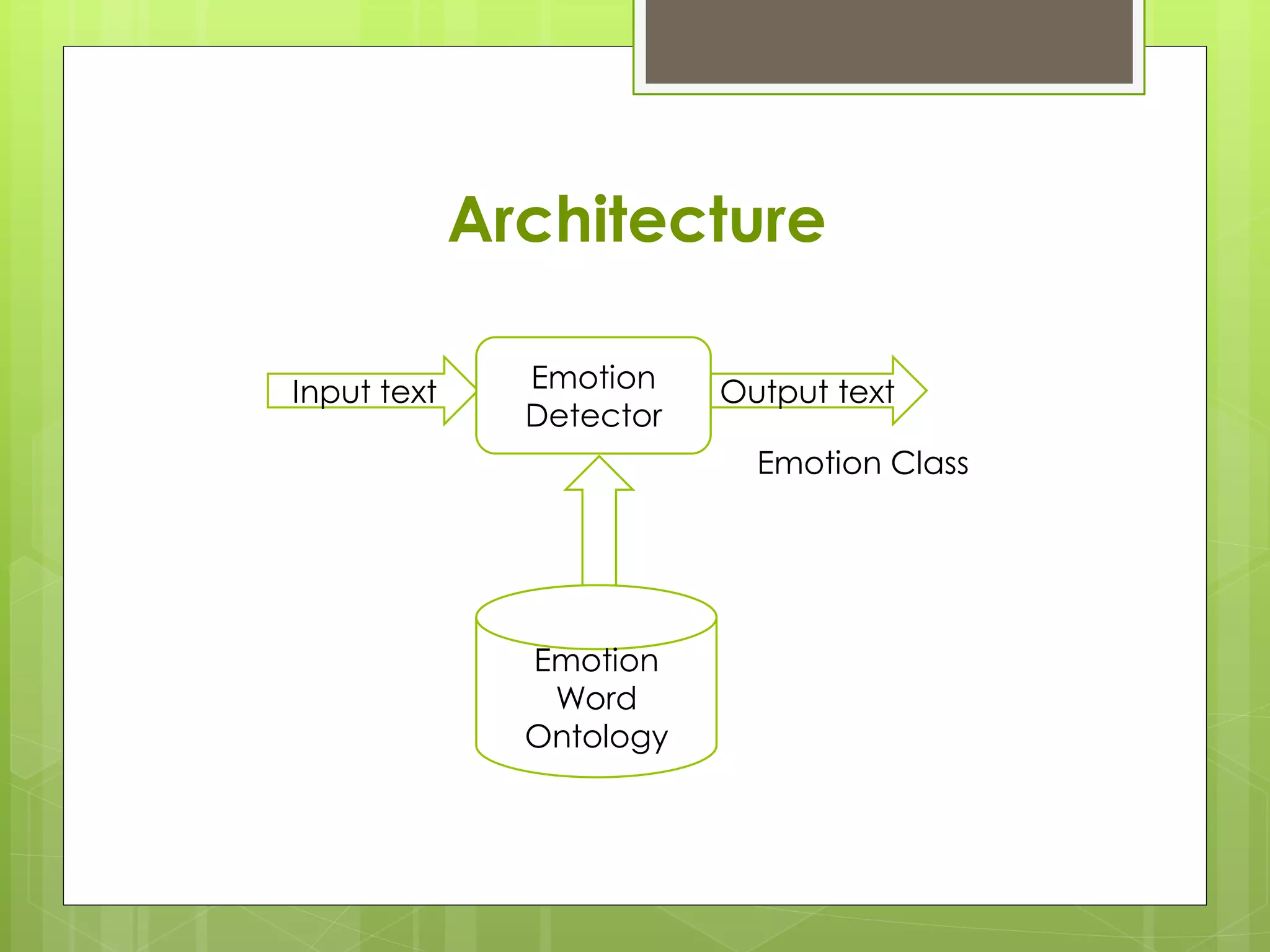
The document discusses emotion mining in text. It defines text mining and emotions and discusses elements of emotions like thoughts, body responses, and behaviors. It explains that emotion mining seeks the emotional state of a writer from text. Major theories of emotion are physiological, neurological, and cognitive. Positive emotions make one feel good while negative emotions stop rational thinking. Techniques for emotion detection discussed are keyword spotting, lexical affinity, learning-based, and hybrid methods. Limitations include ambiguity in keywords, inability to recognize text without keywords, and lack of linguistic information. An example of analyzing social network comments is provided.