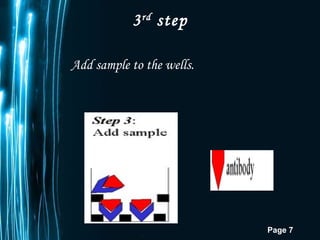
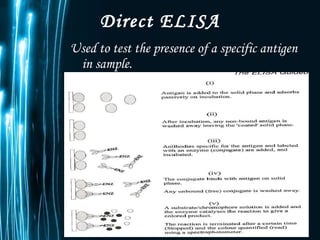
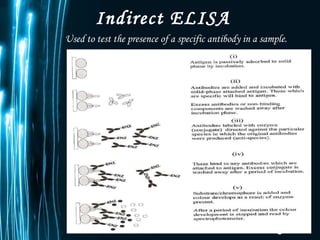
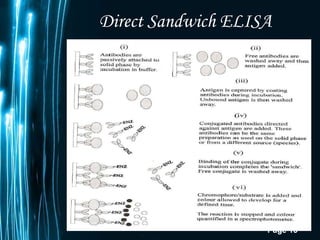
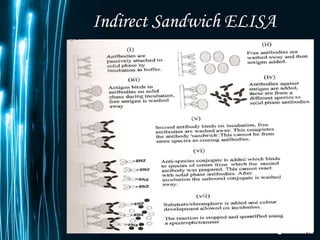
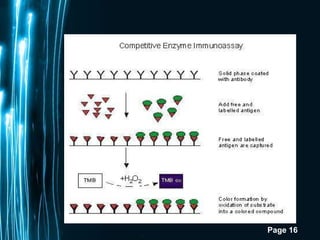
ELISA is a biochemical technique used in immunology to detect the presence of an antibody or antigen in a sample. It involves coating microtiter plate wells with an antigen or antibody and using conjugated enzymes and substrates to produce a colored product to indicate a positive result. There are different types of ELISA including direct, indirect, sandwich, and competitive ELISA which are used to test for various antigens or antibodies. ELISA has many applications such as measuring serum antibody concentrations, detecting food allergens or diseases, and identifying past exposure to diseases.