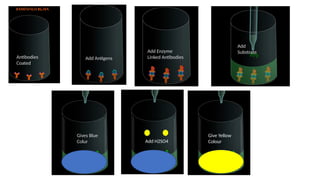
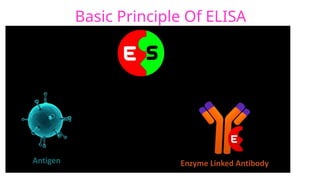
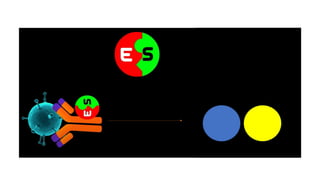
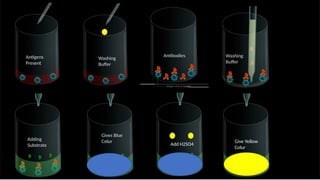
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a versatile biochemical technique used for the detection and quantification of biomolecules, particularly antibodies and antigens, with high sensitivity and specificity. It has important applications in clinical diagnostics, food safety, and research, allowing for the analysis of diseases such as HIV and COVID-19. Different types of ELISA include direct, indirect, and sandwich formats, each with unique methodologies for accurately measuring target analytes.







![[Antigen A Coating]
↓
[Coating Buffer + Washing]
↓
[Add Sample + Incubation]
↓
[Washing Buffer]
↓
[Enzyme-Linked Secondary Antibody]
↓
[Washing Buffer]
↓
[Add Substrate]
↓
[Color Change?] → Yes (Positive) / No (Negative)
The Indirect ELISA Process](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-elisa-principles-techniques-and-applications-241009073003-4d38a12f/85/ELISA-Basics-Easy-Step-by-Step-Guide-EXplained-11-320.jpg)
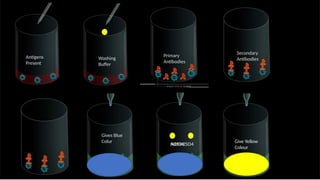
![[Capture Antibody Coating]
↓
[Coating Buffer + Washing]
↓
[Add Sample (Antigen) + Incubation]
↓
[Washing Buffer]
↓
[Enzyme-Linked Detection Antibody + Incubation]
↓
[Washing Buffer]
↓
[Add Substrate]
↓
[Color Change?] → Yes (Positive) / No (Negative)
The Sandwich ELISA Process](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-elisa-principles-techniques-and-applications-241009073003-4d38a12f/85/ELISA-Basics-Easy-Step-by-Step-Guide-EXplained-13-320.jpg)