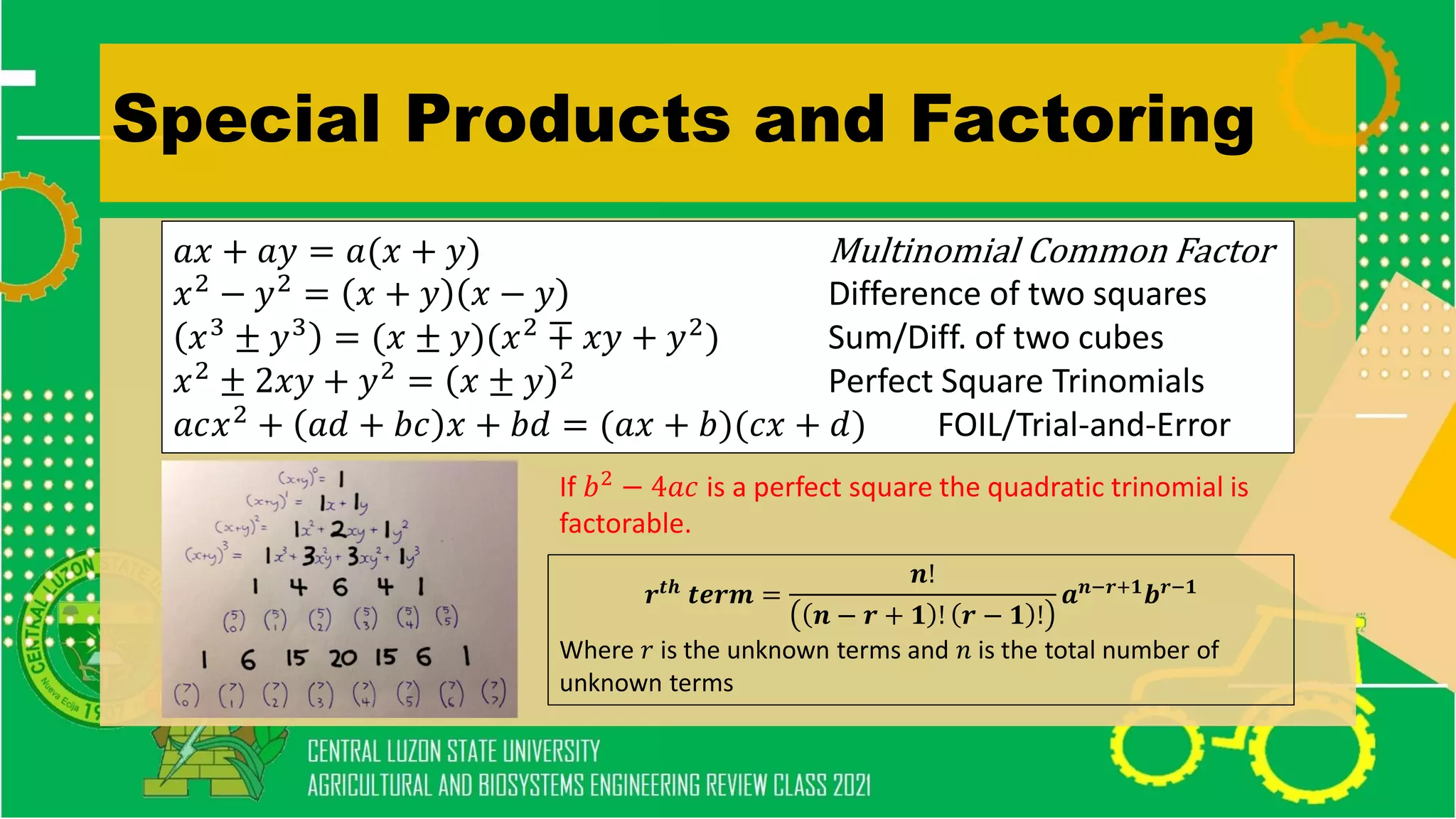
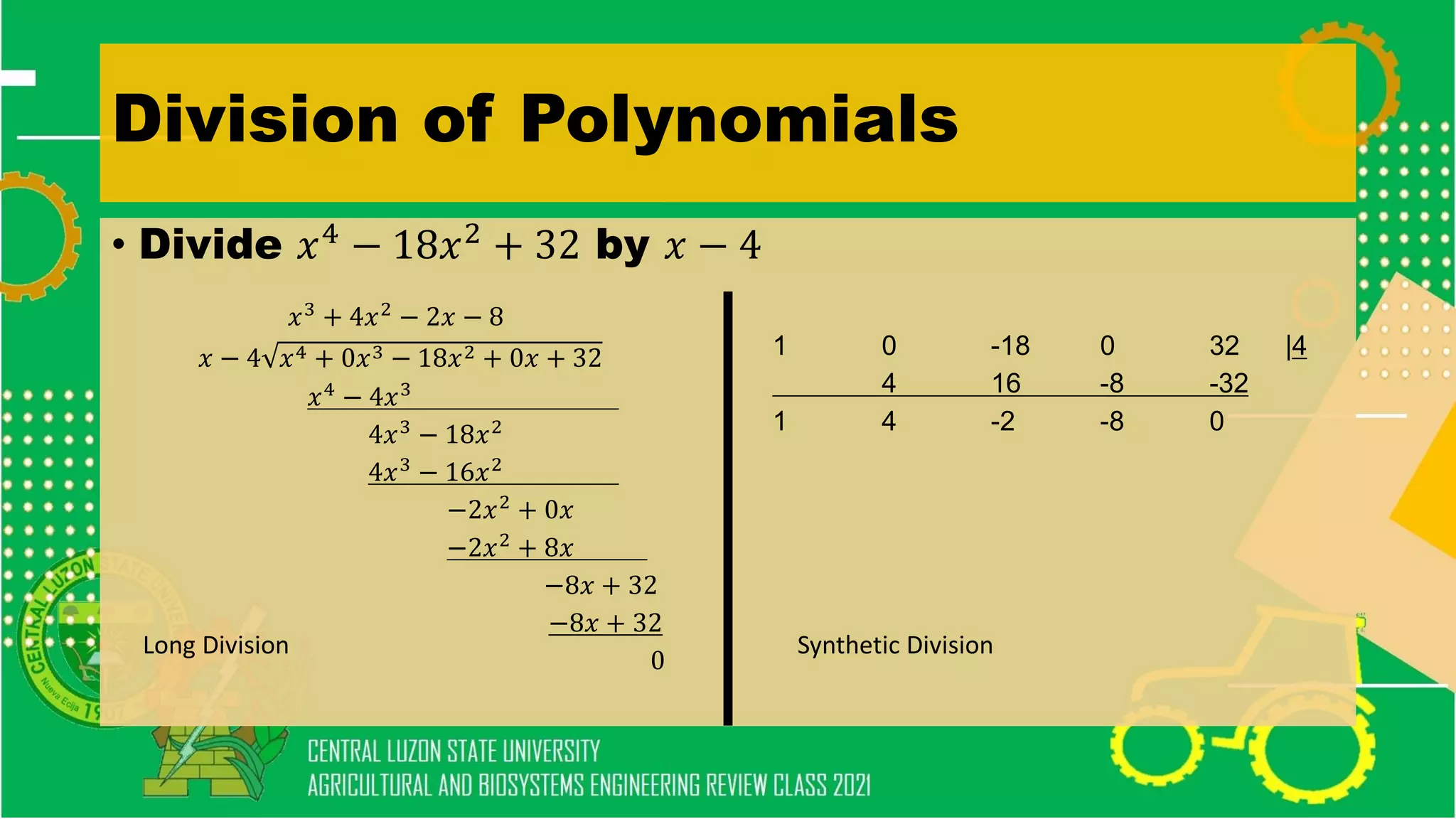
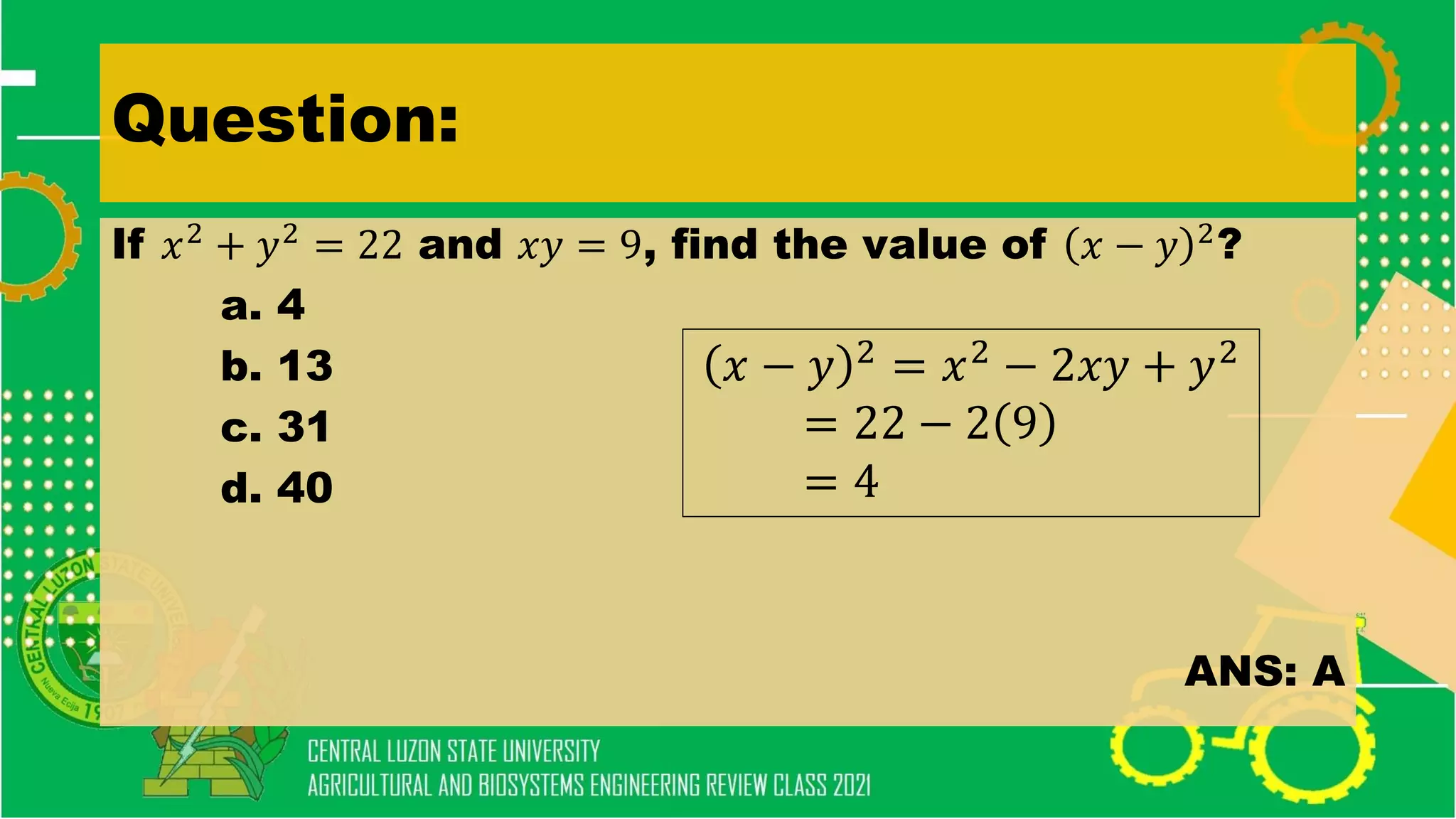
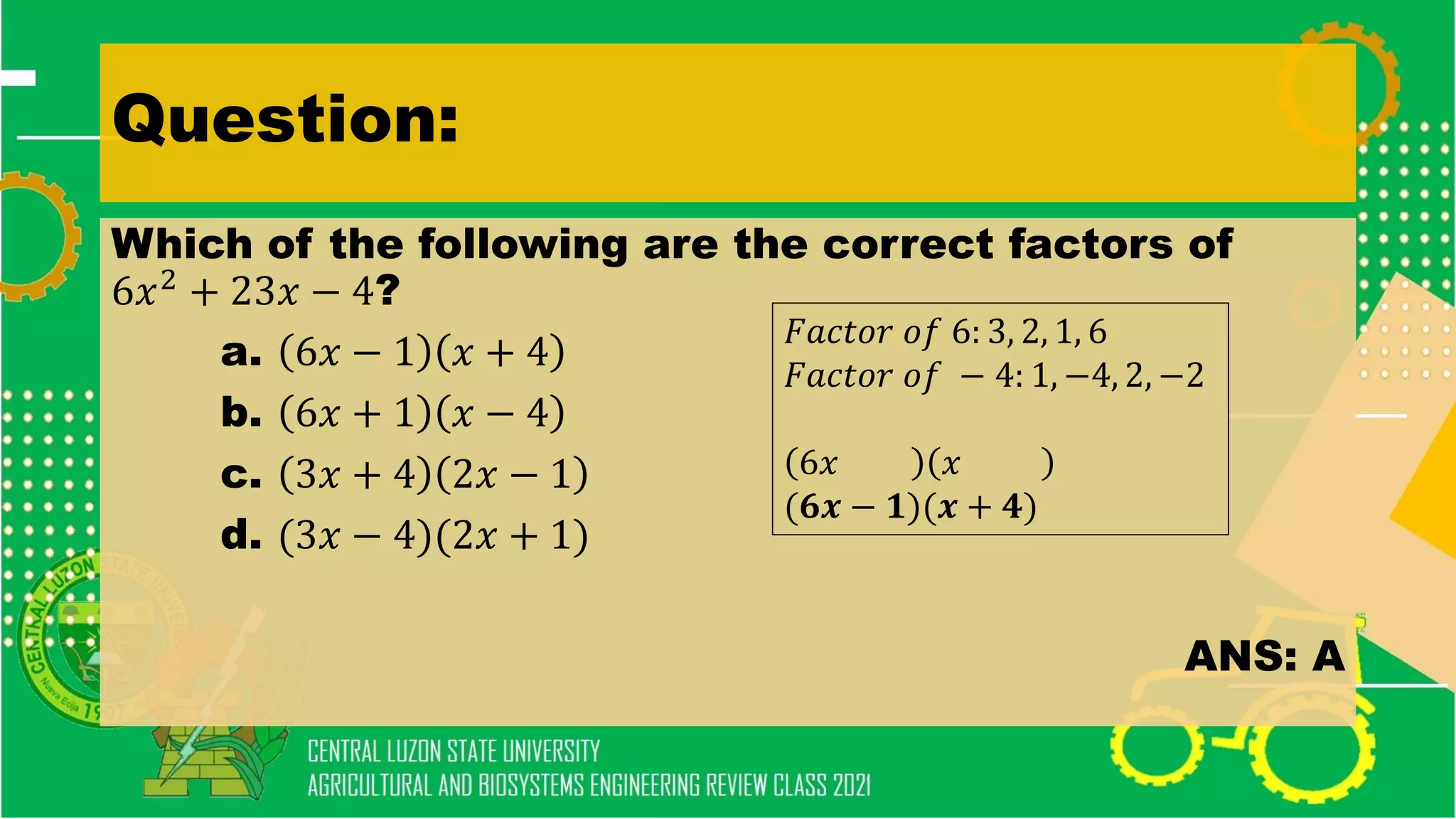
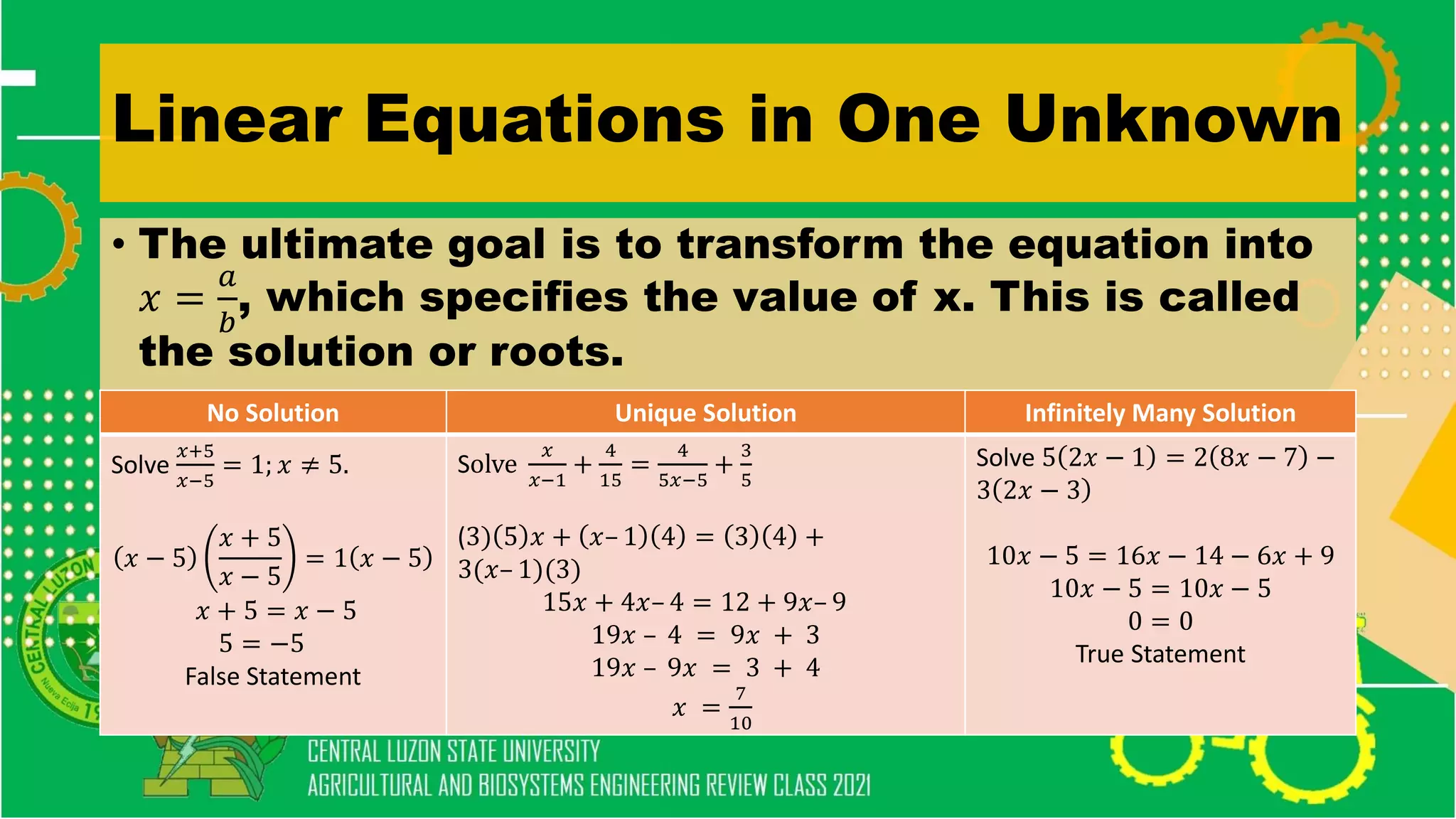
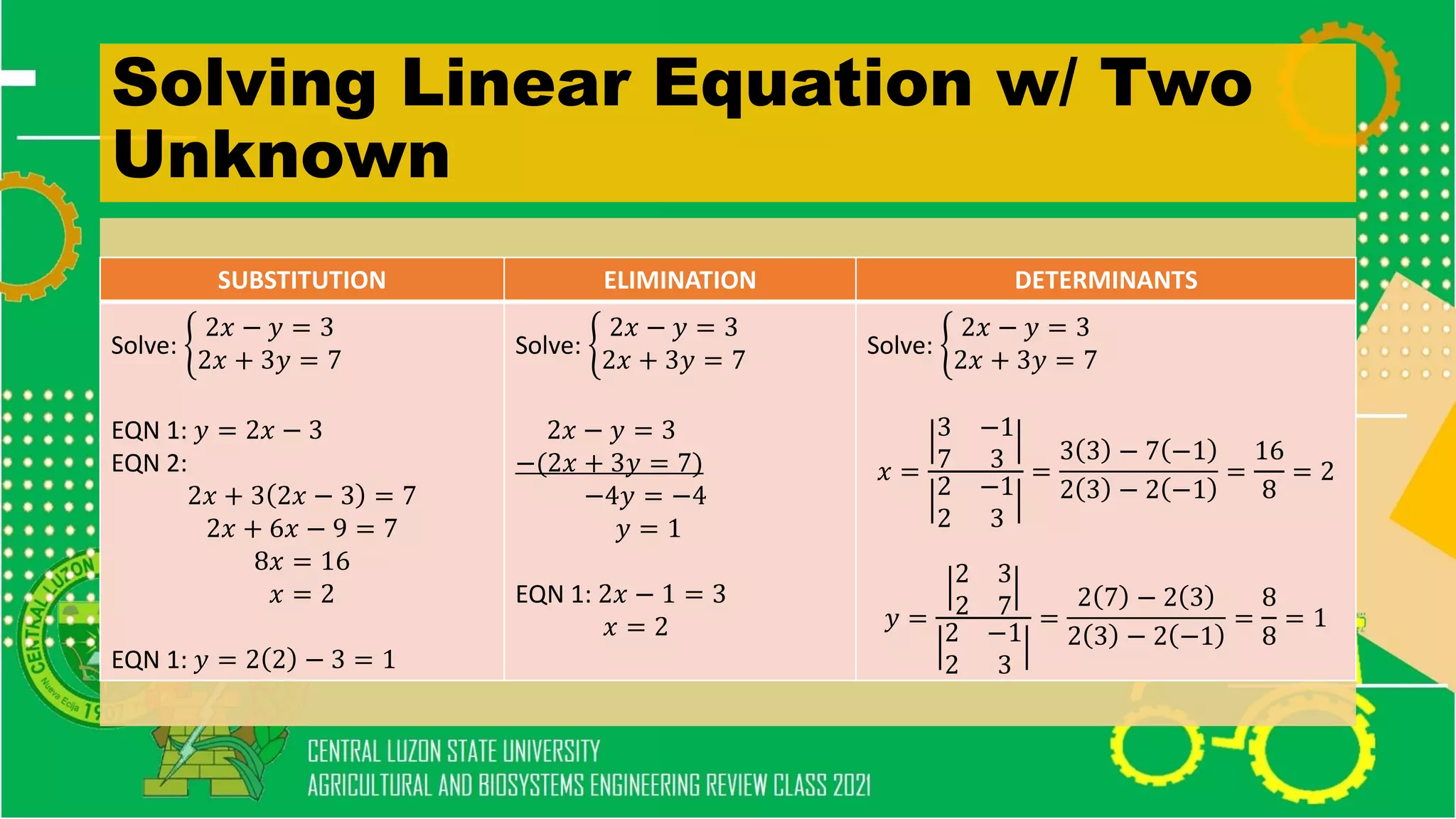
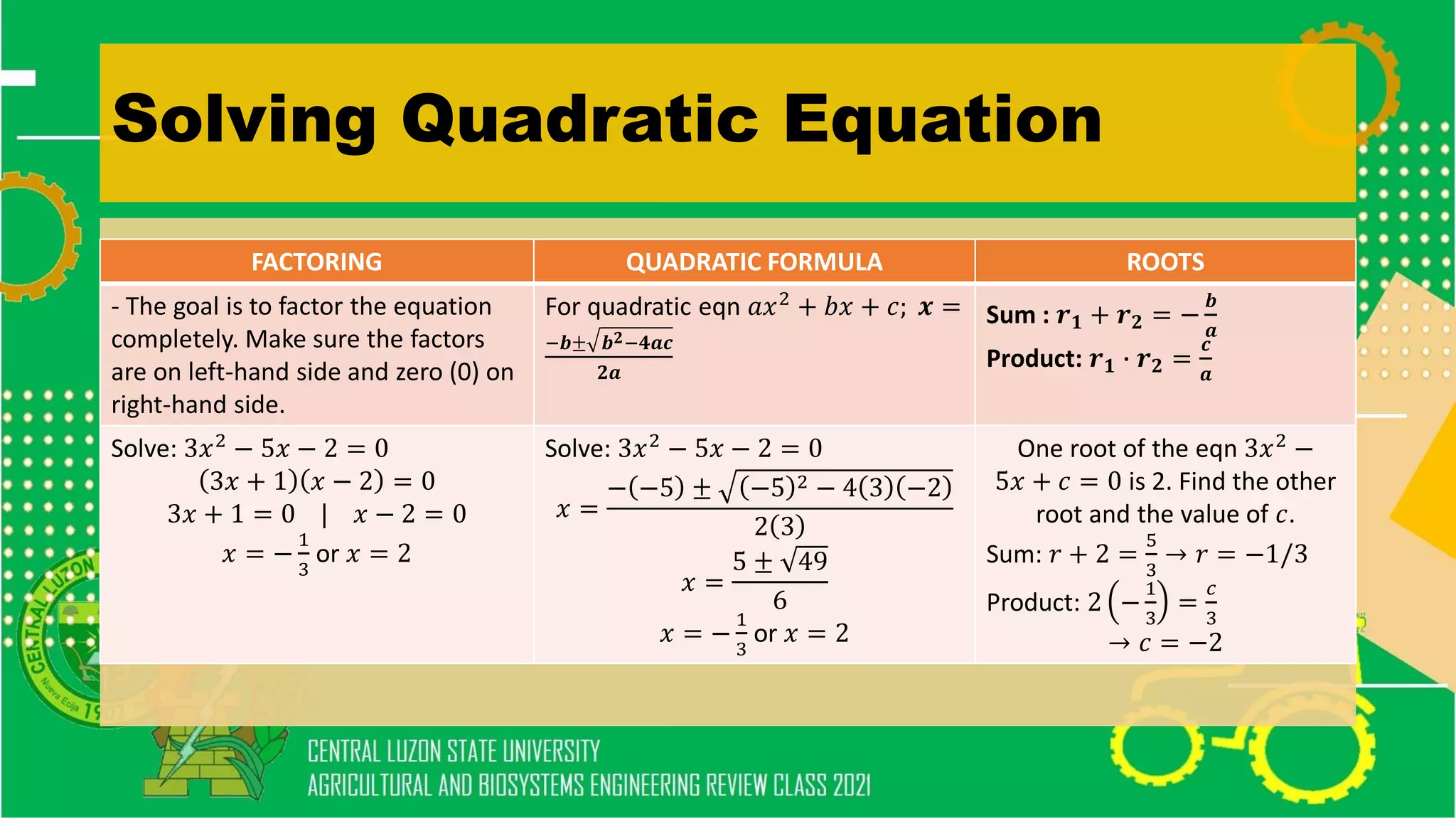
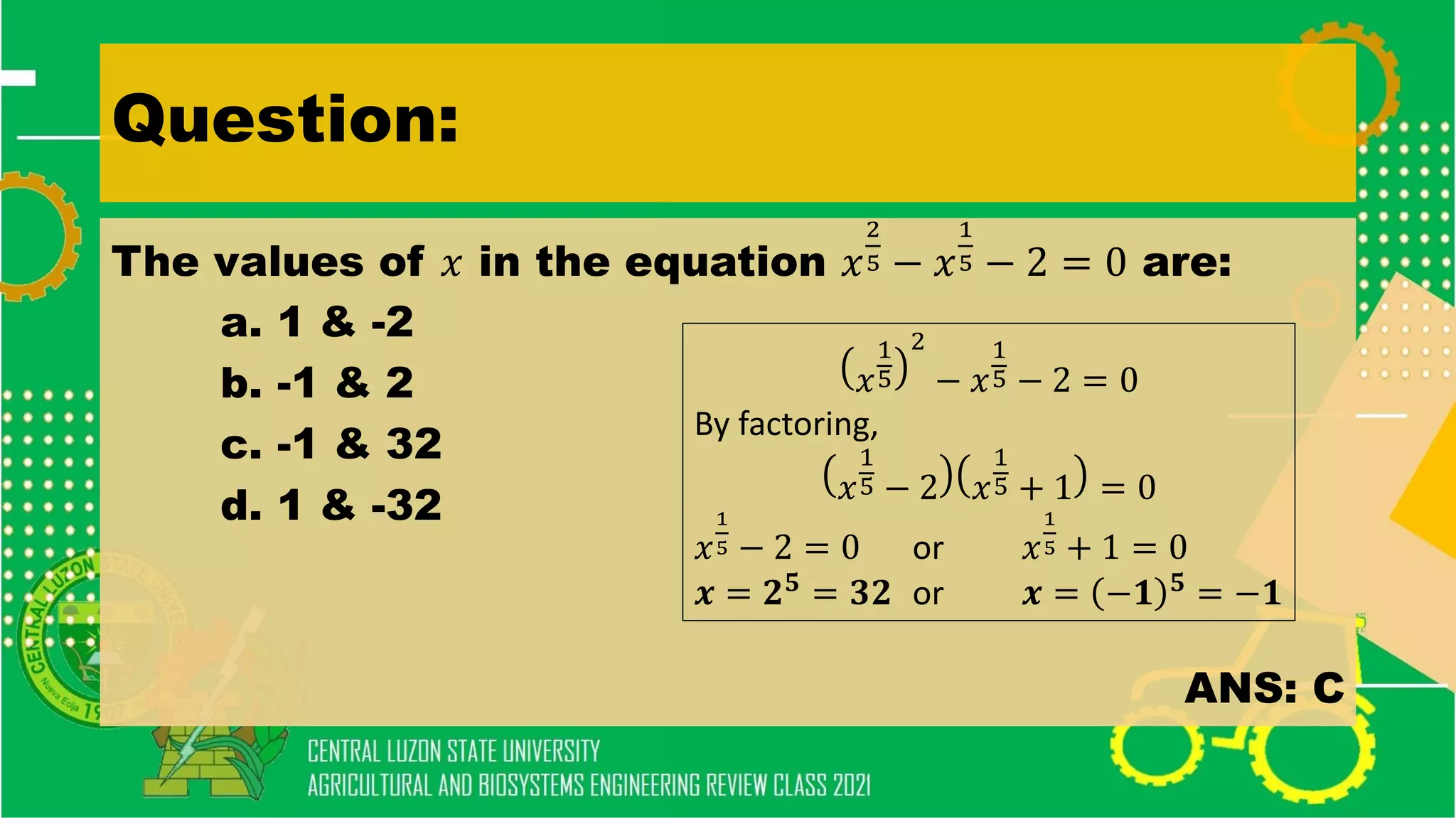
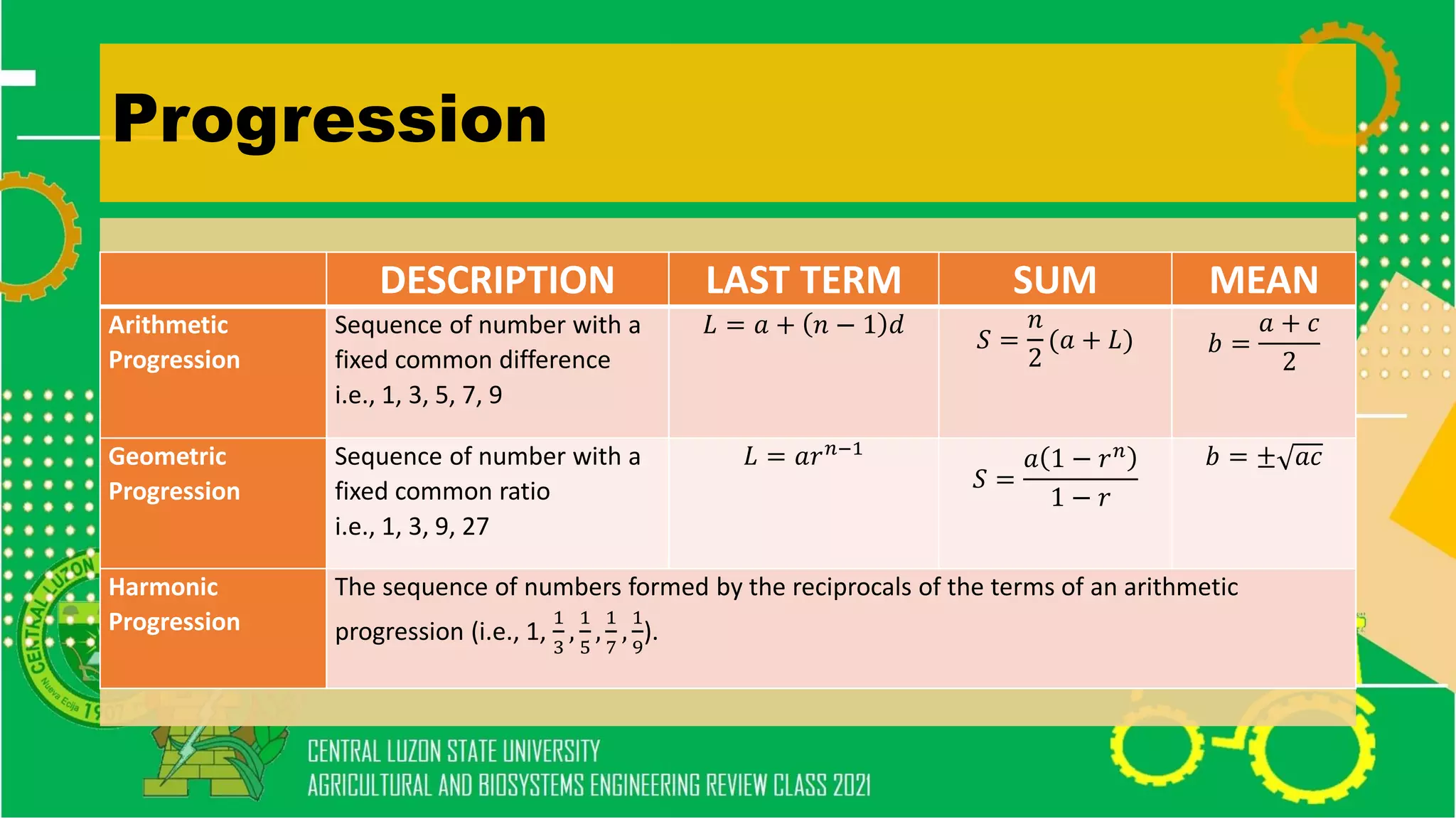
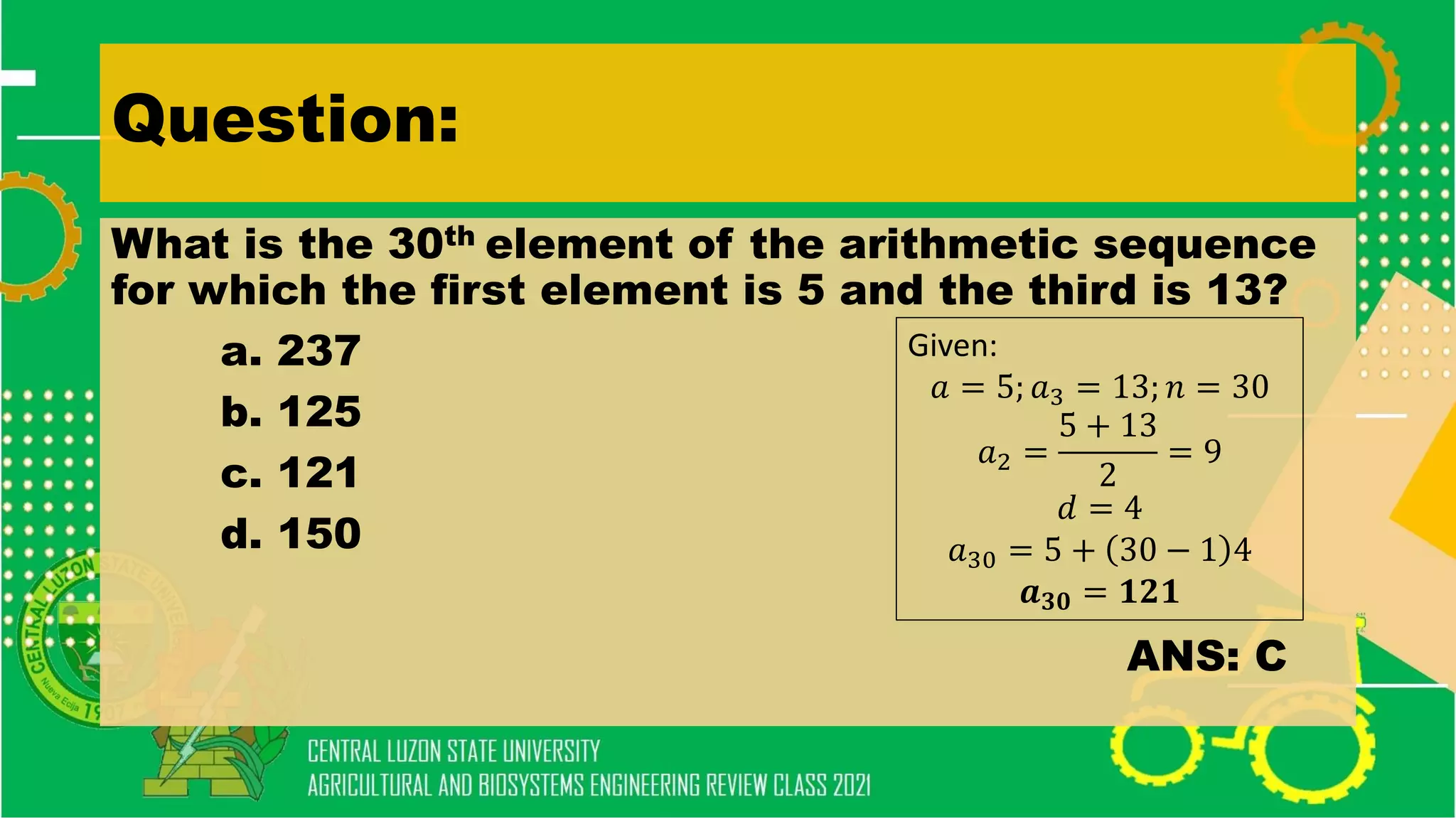
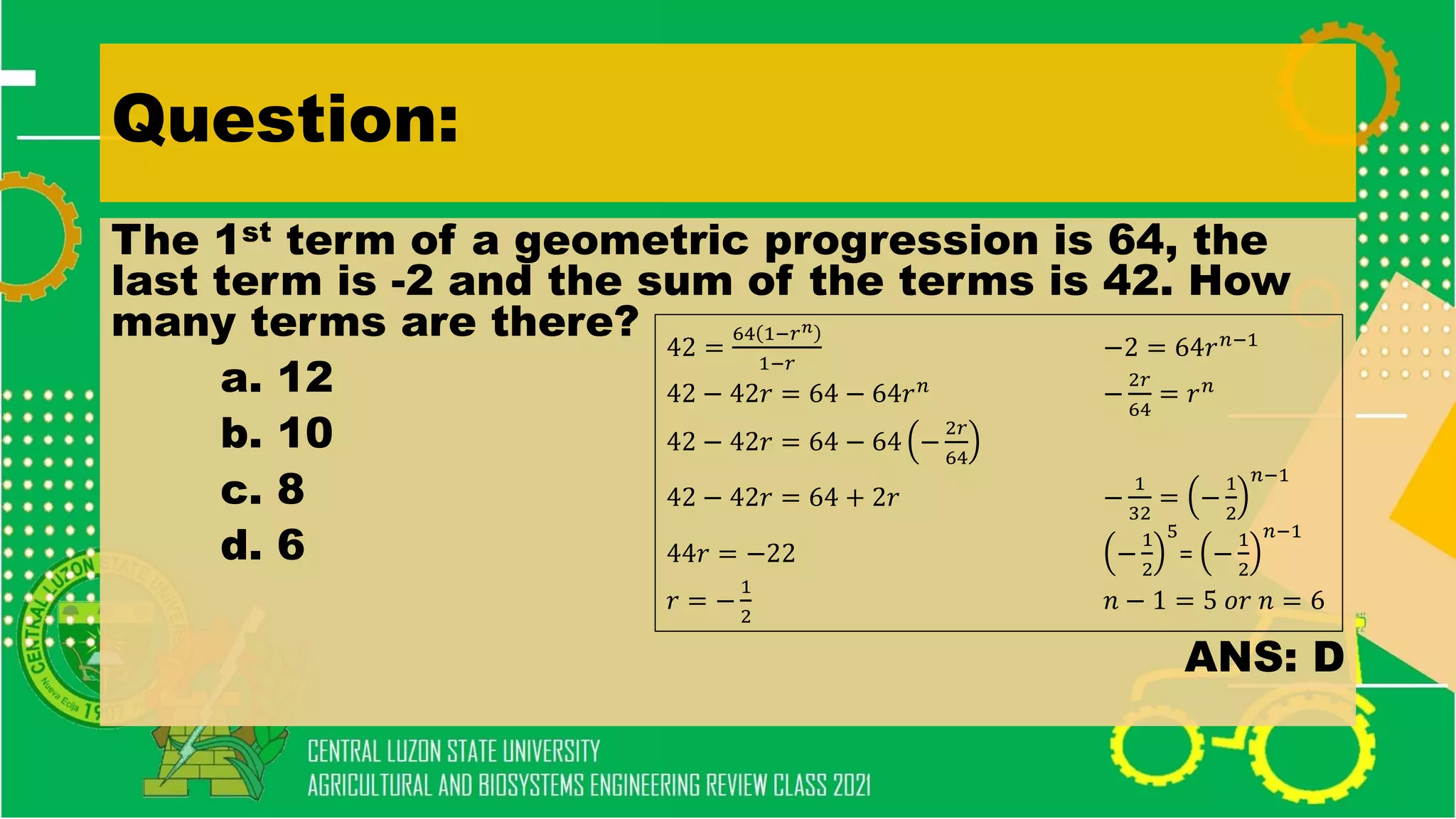
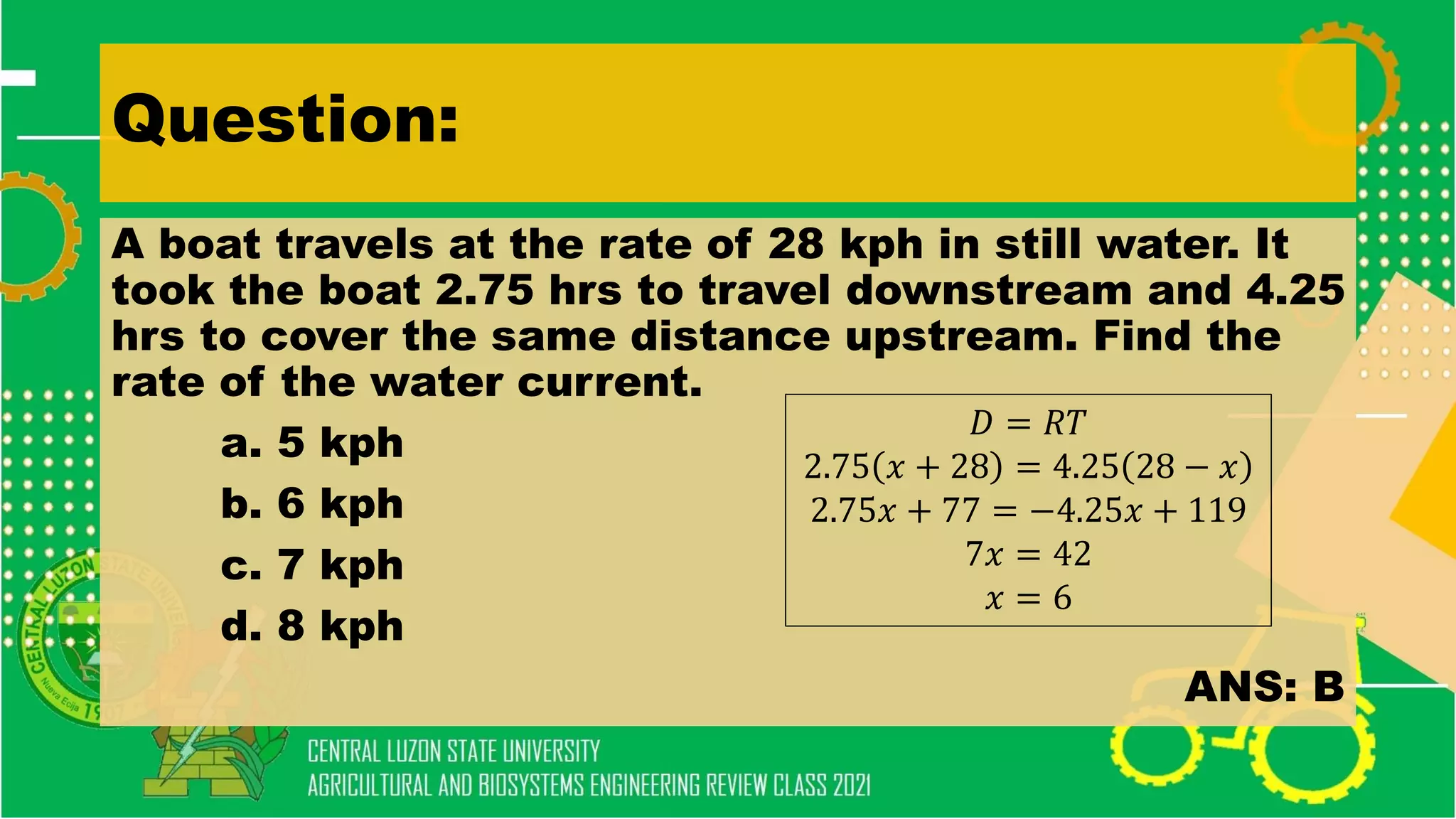
The document discusses elementary algebra concepts including:
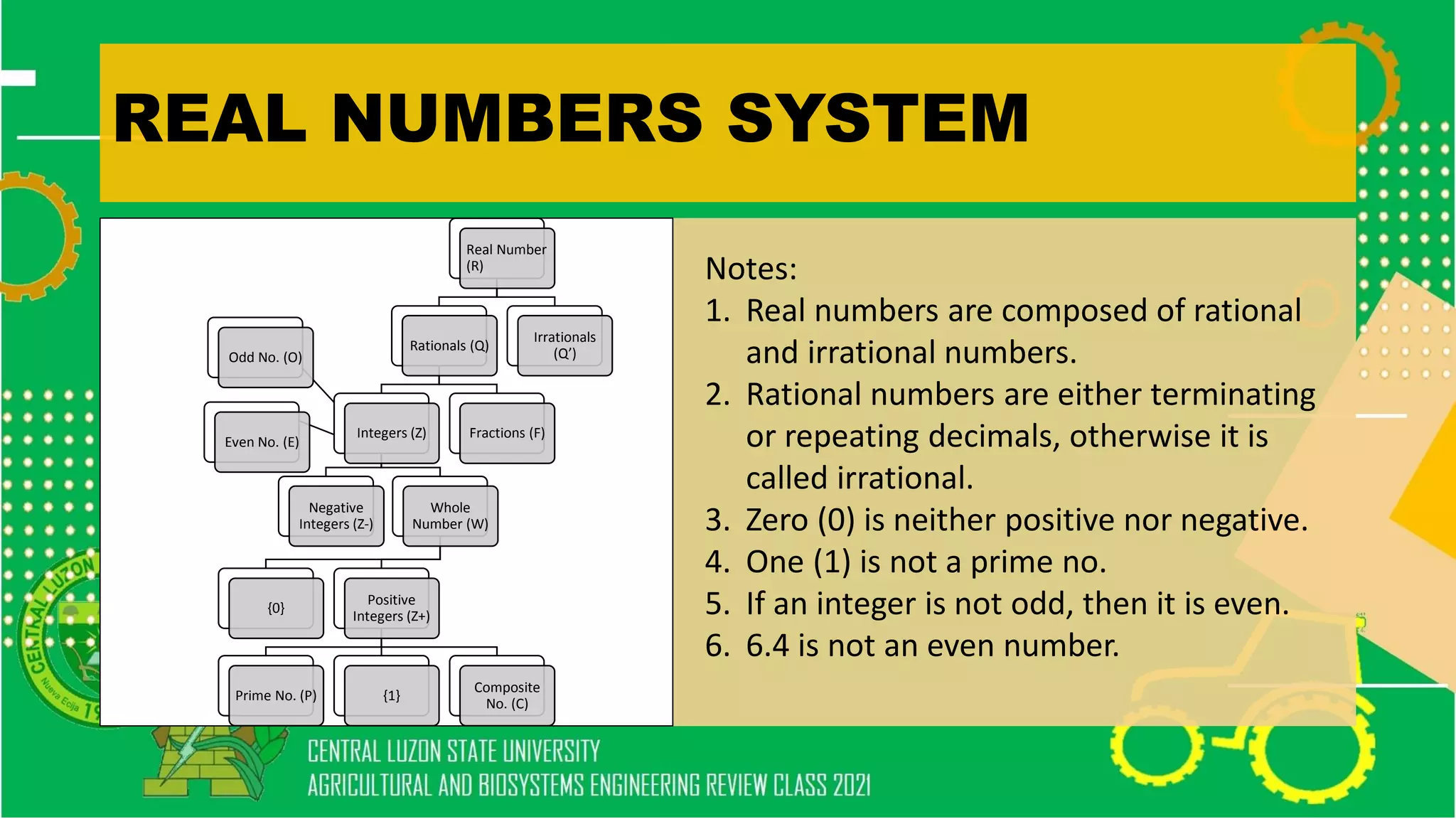
- Real number systems and their properties
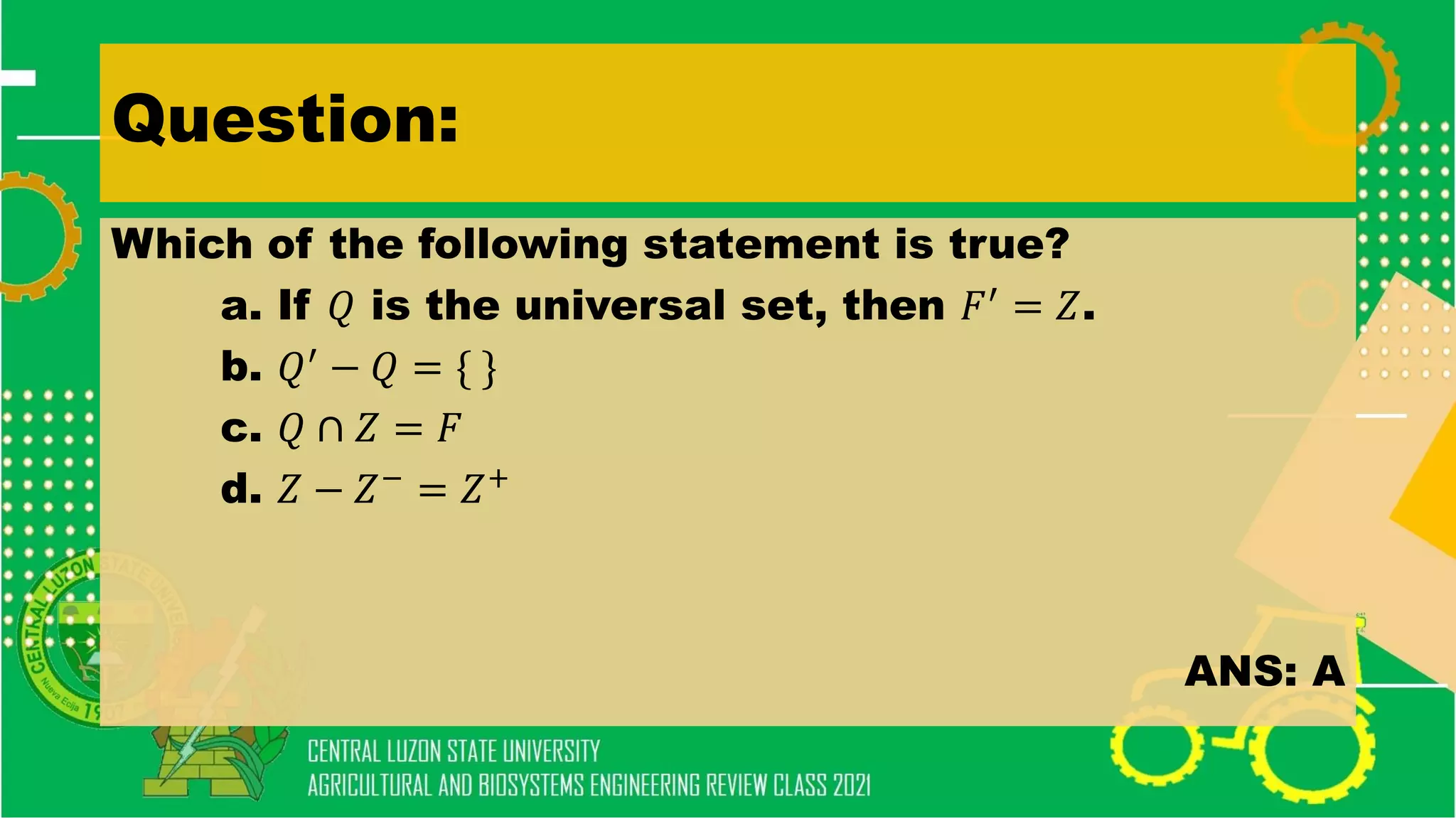
- Set operations like union, intersection, complement, and difference
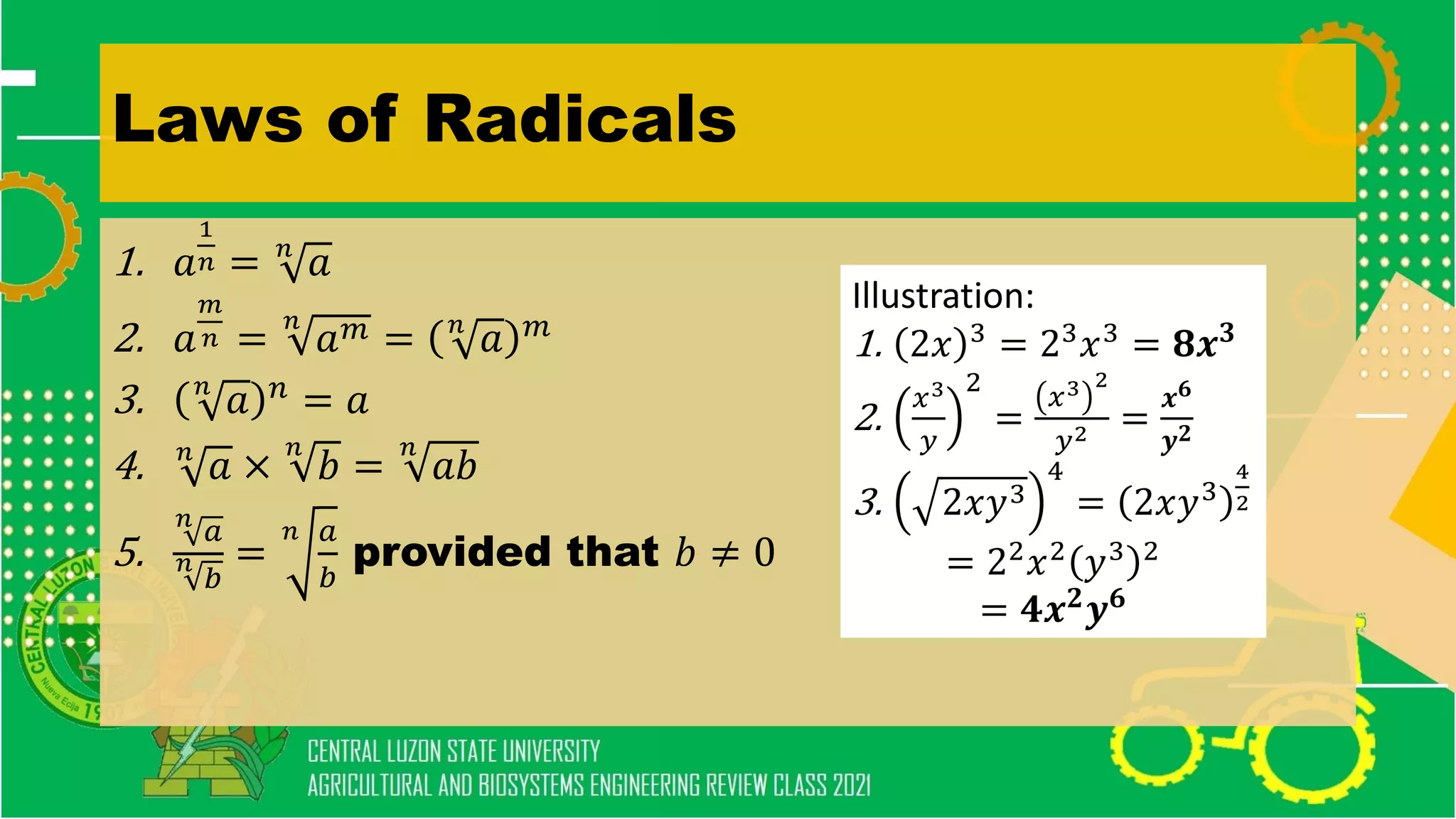
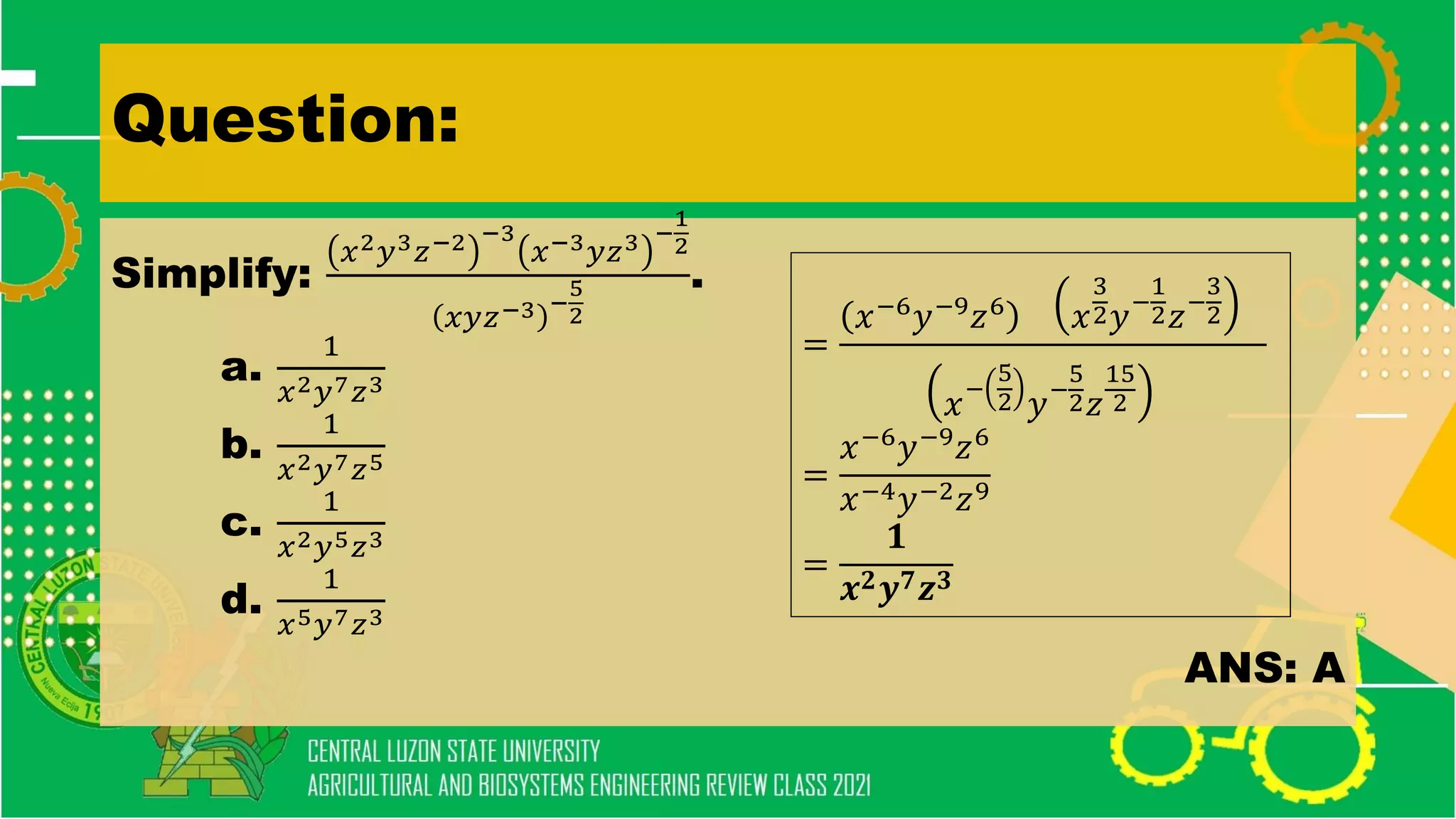
- Theorems on real numbers and exponents
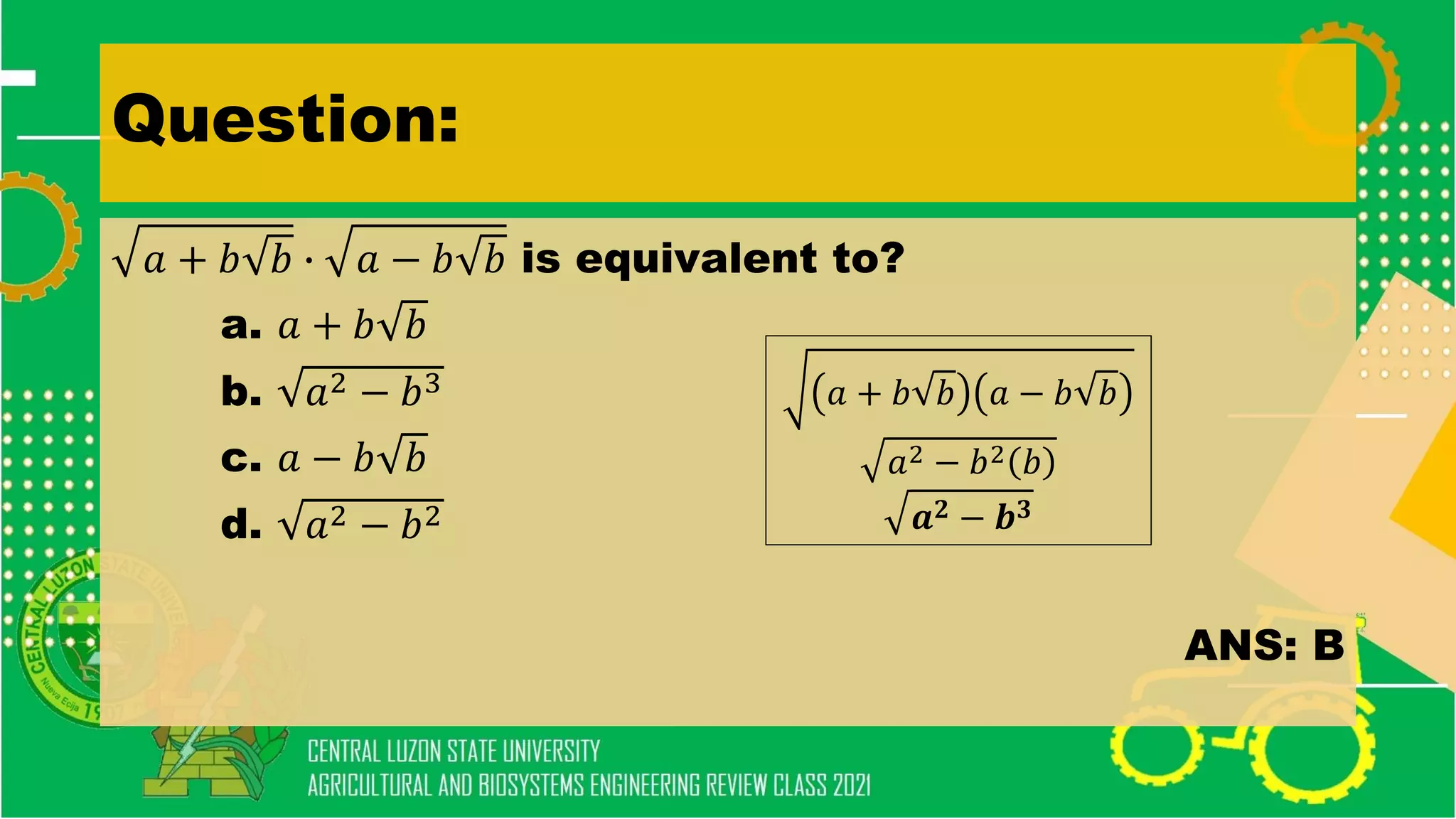
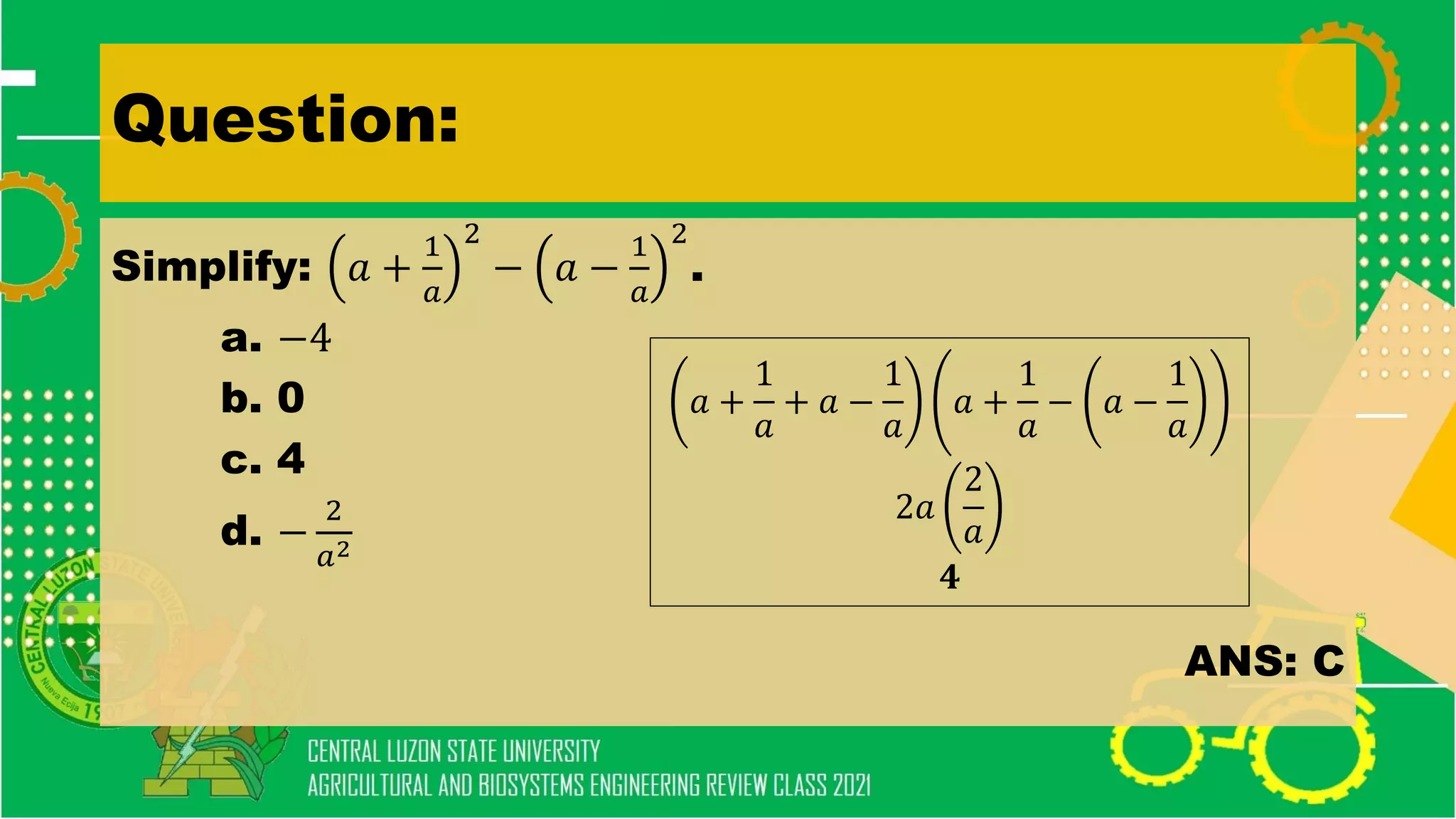
- Simplifying algebraic expressions using laws of exponents, factoring polynomials, and other algebraic operations
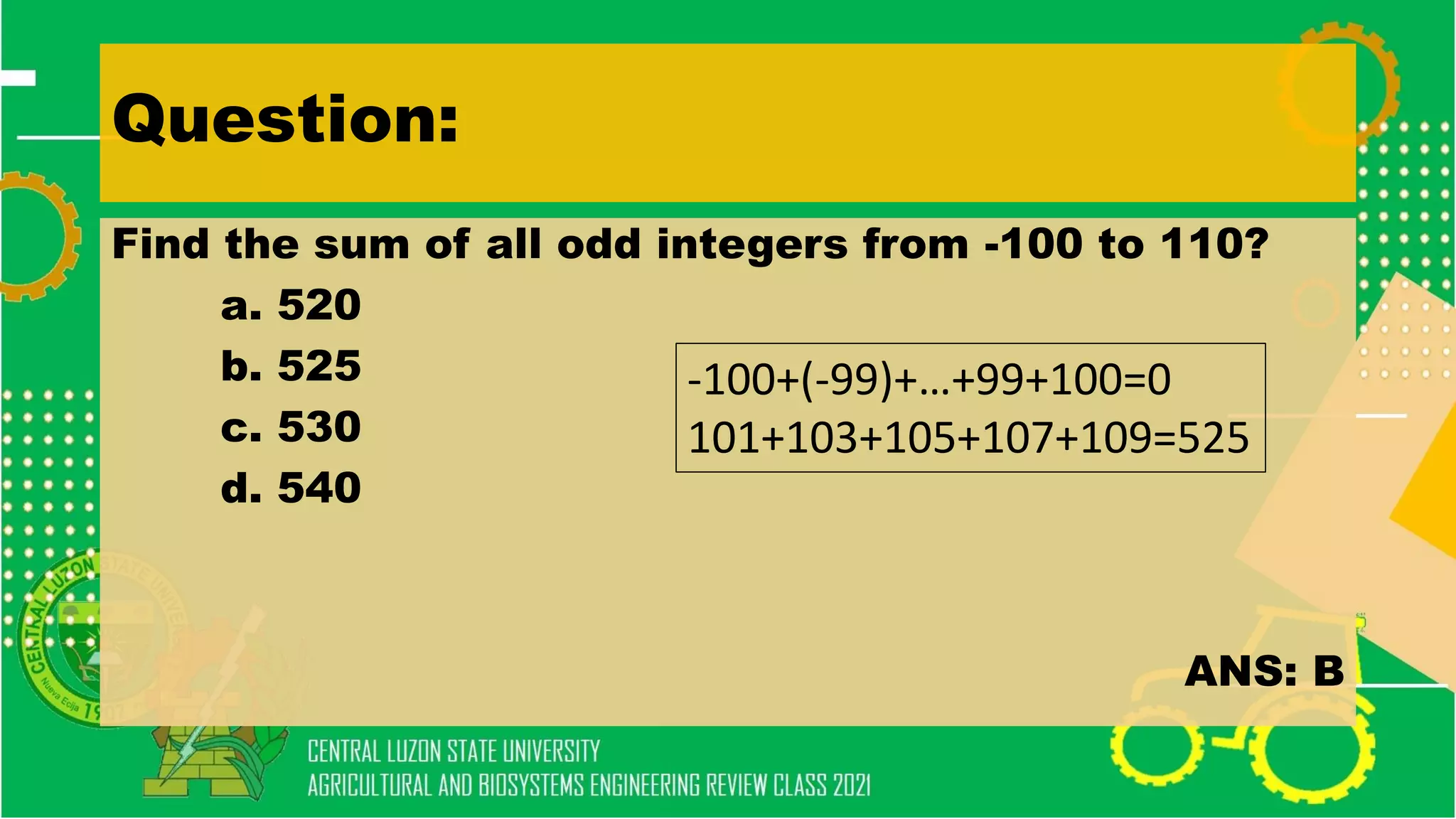
- Solving word problems involving algebraic concepts
The document provides examples and notes for understanding key algebraic topics at an elementary level.