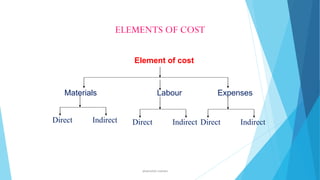
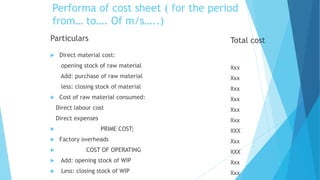
Cost accounting is concerned with recording, classifying, and summarizing costs to determine the costs of products or services. It also involves planning, controlling, and reducing costs, and providing information to management for decision making. Cost accounting includes elements such as direct and indirect materials, direct and indirect labor, and expenses. It utilizes methods like job costing, process costing, and standard costing. The objectives of cost accounting are cost ascertainment, estimation, control, reduction, determining selling prices, and facilitating financial reporting and operating policies.