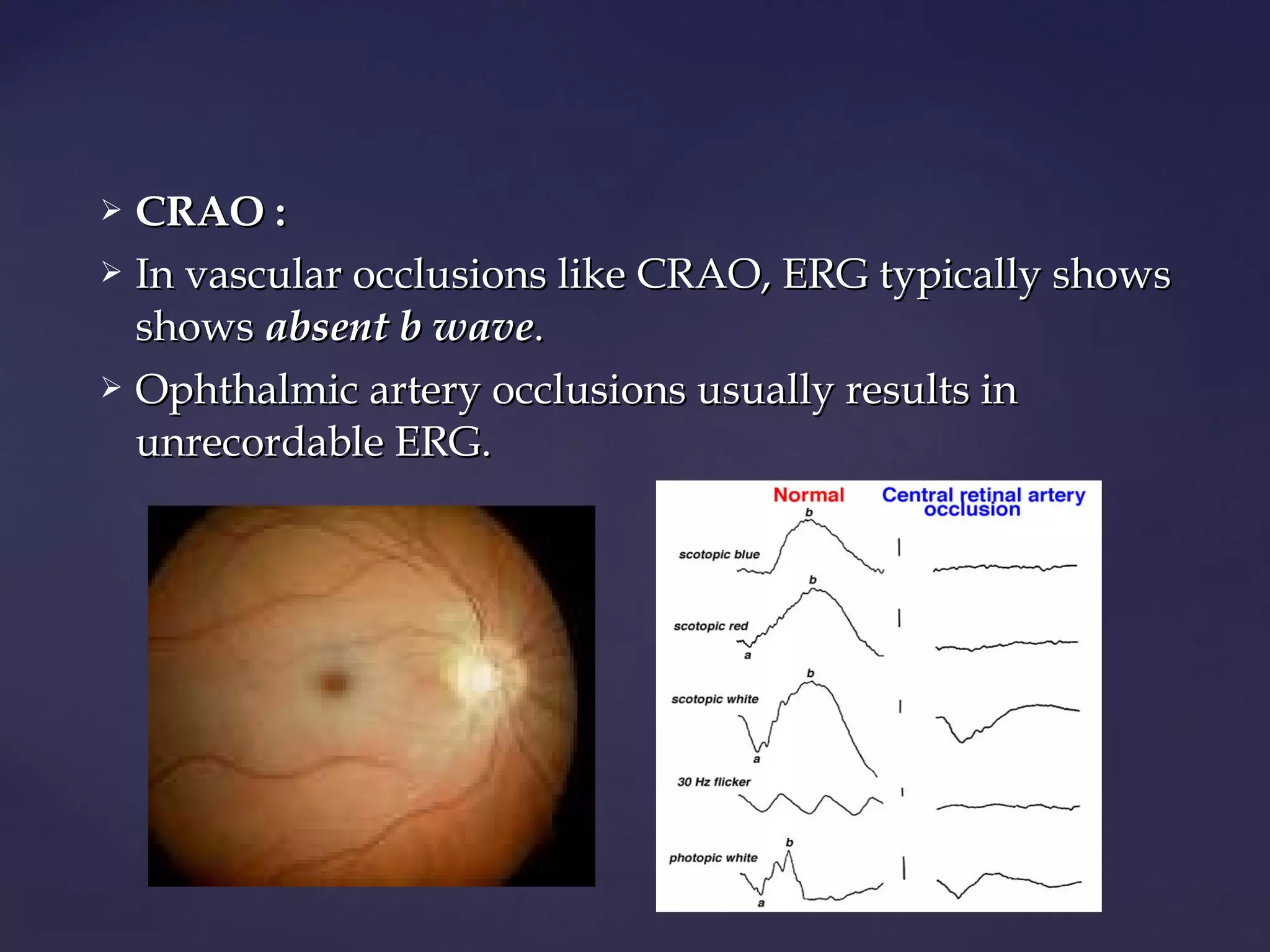
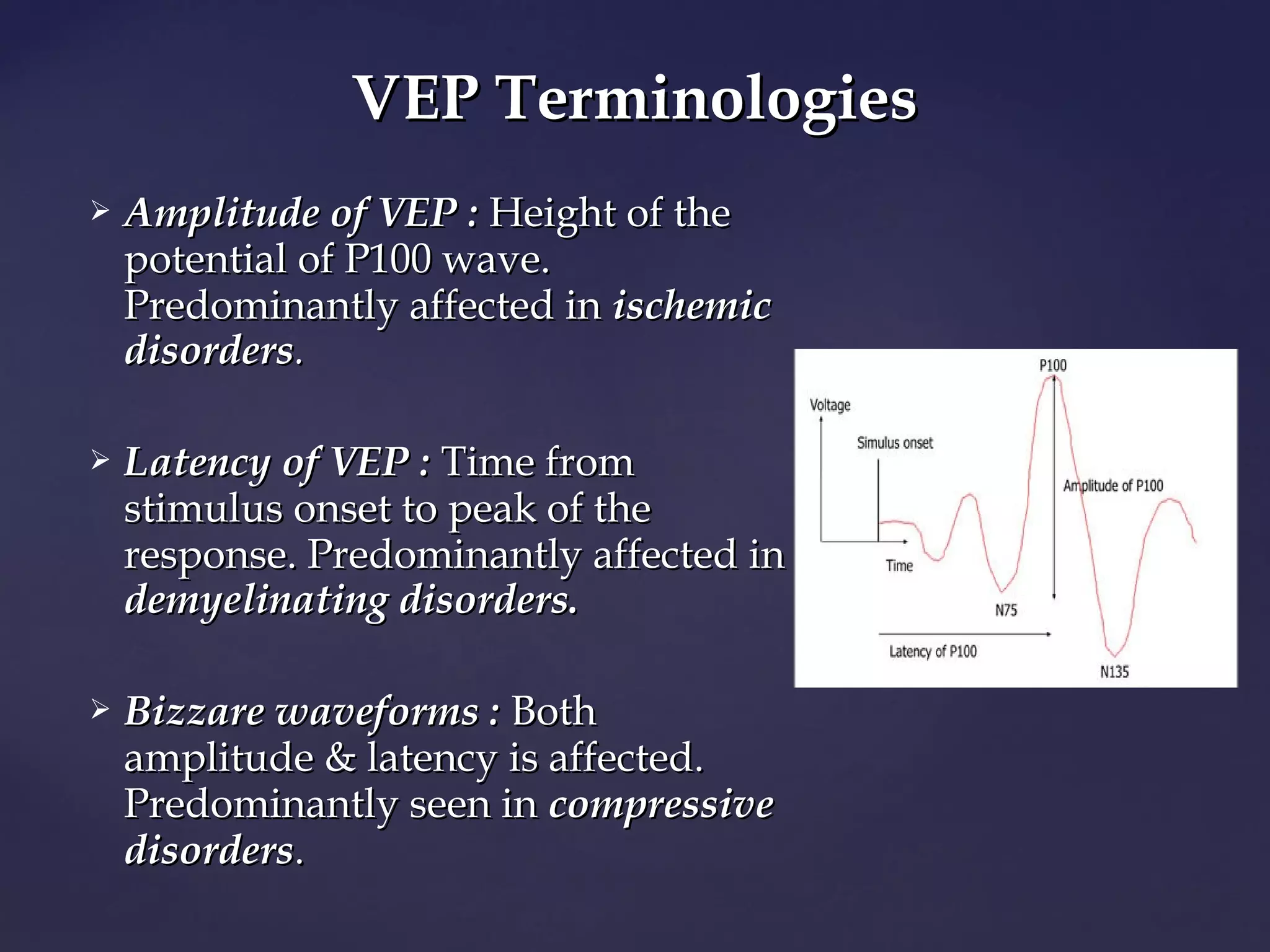
This document discusses various electrophysiological tests used to objectively assess visual pathway function, including the electroretinogram (ERG), electrooculogram (EOG), and visually evoked potentials (VEP). It focuses on the ERG test, describing the basic principles, waveforms, responses, electrodes, and specialized forms (e.g. bright flash ERG, focal ERG, multifocal ERG, pattern ERG). Clinical uses include evaluating retinal diseases like diabetic retinopathy, retinal detachment, retinitis pigmentosa, and more. Abnormal ERG findings typically include reduced amplitude and delayed peak times, varying with the specific disease.