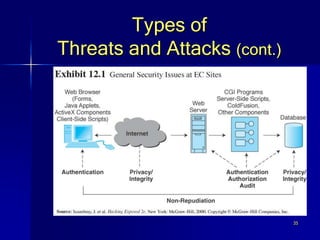
This document discusses electronic commerce (EC) security. It begins by outlining learning objectives on documenting security attacks, describing common security practices of businesses, and understanding basic EC security elements and types of network attacks. It then provides a story about a brute force credit card attack where over 140,000 fake charges were made. The document discusses solutions to brute force attacks and the accelerating need for EC security. It outlines common security issues for users and companies and requirements like authentication, authorization, and integrity. Finally, it details types of threats, managing security, and authentication and encryption methods.