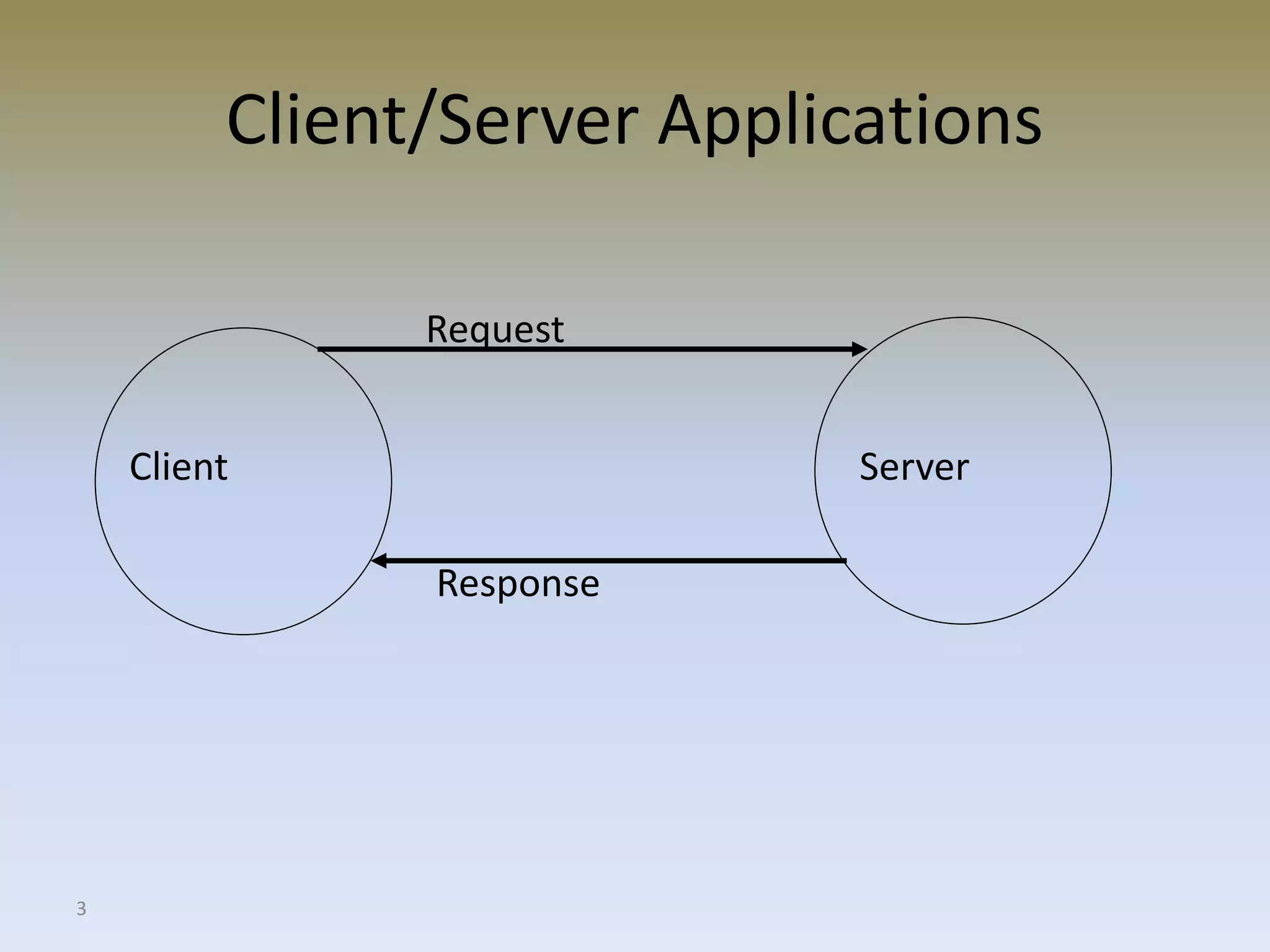
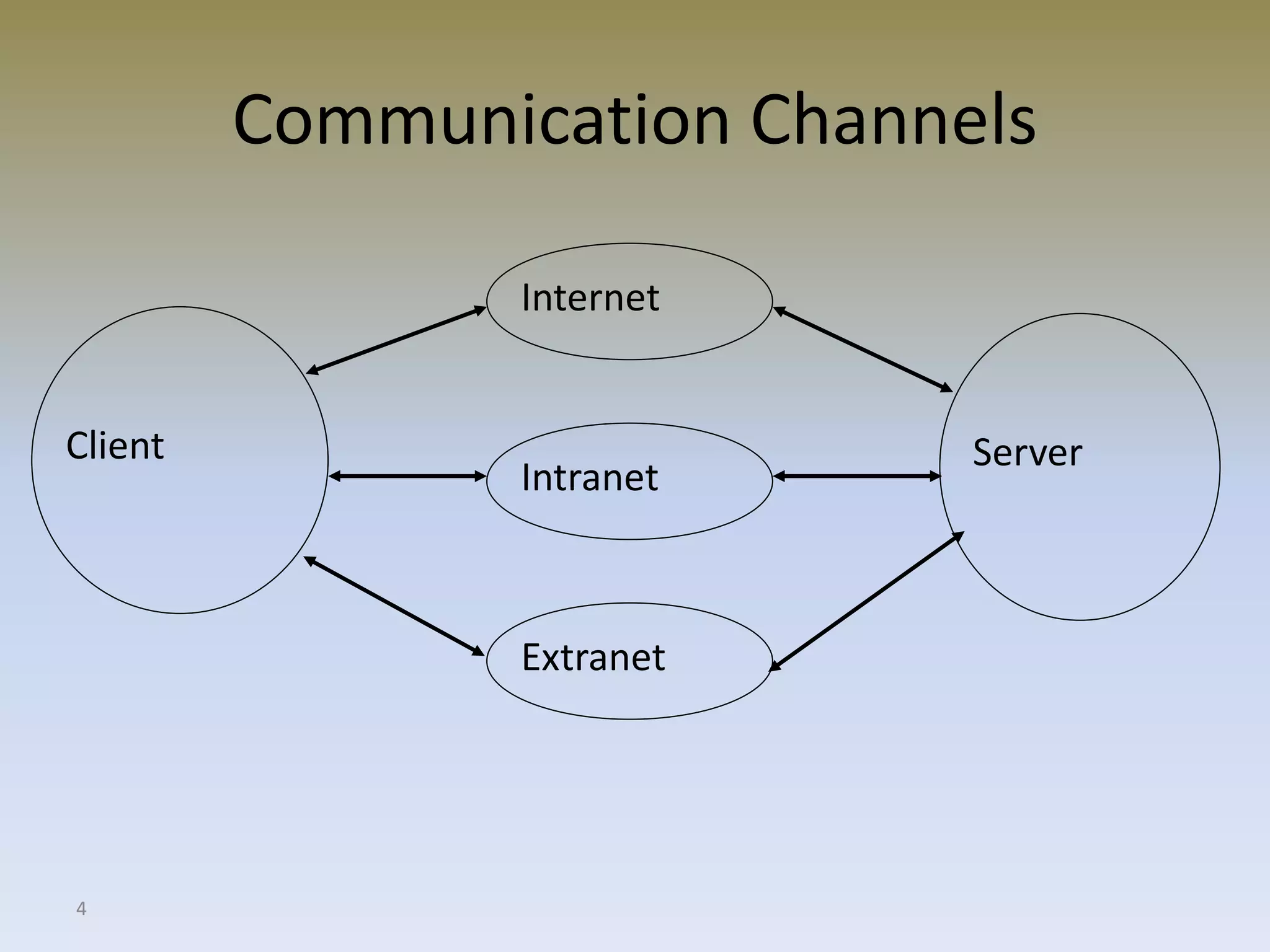
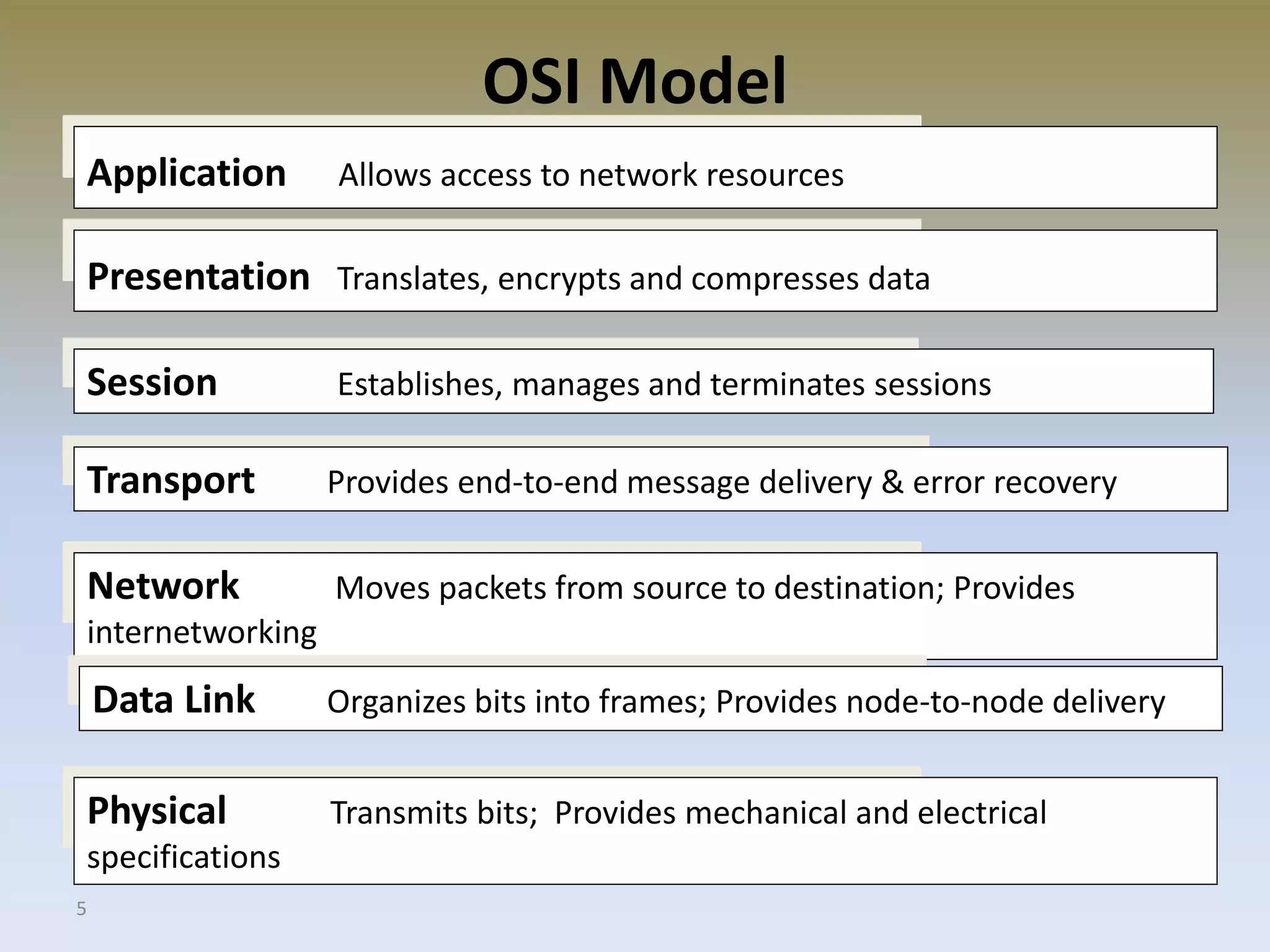
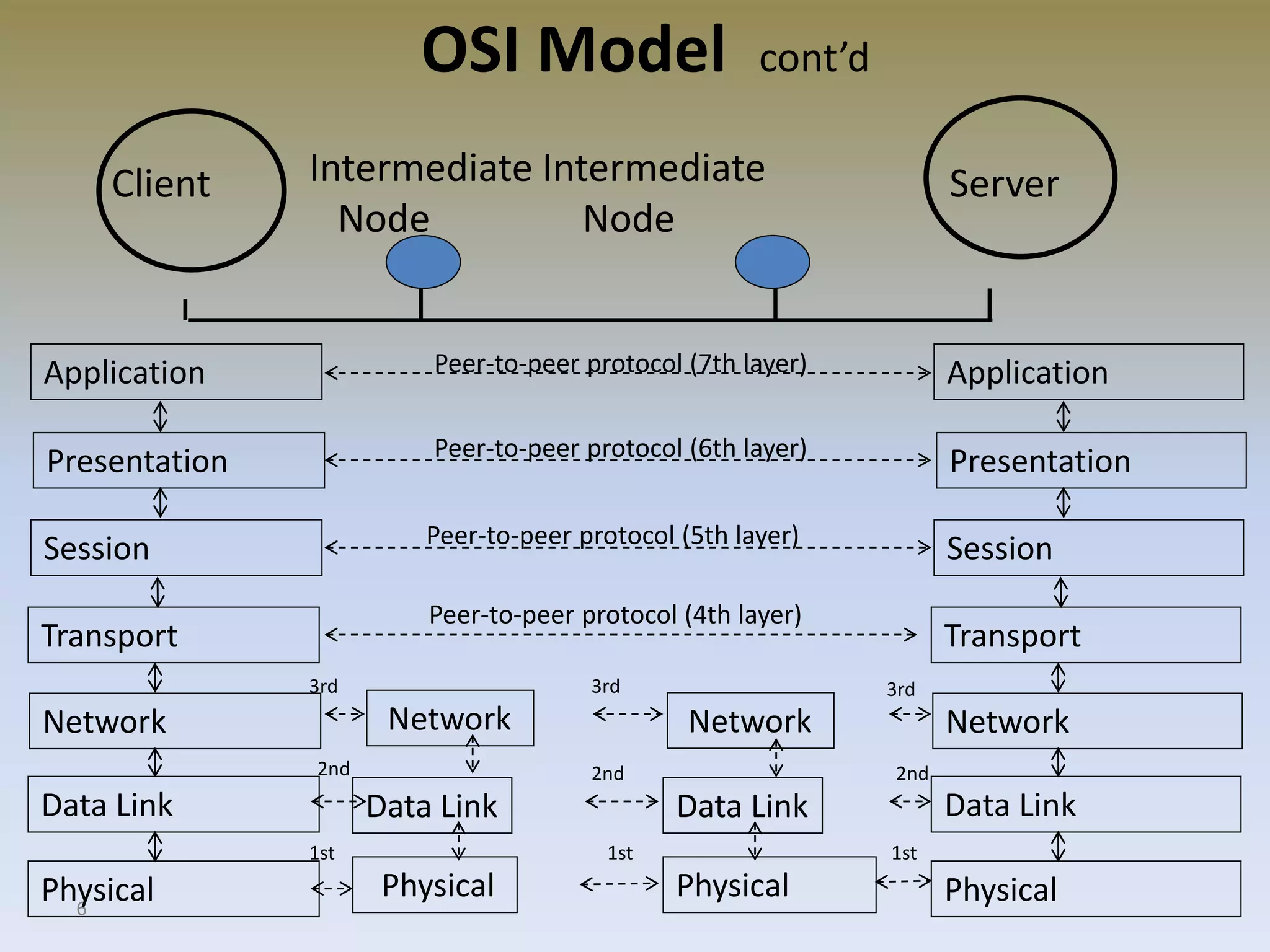
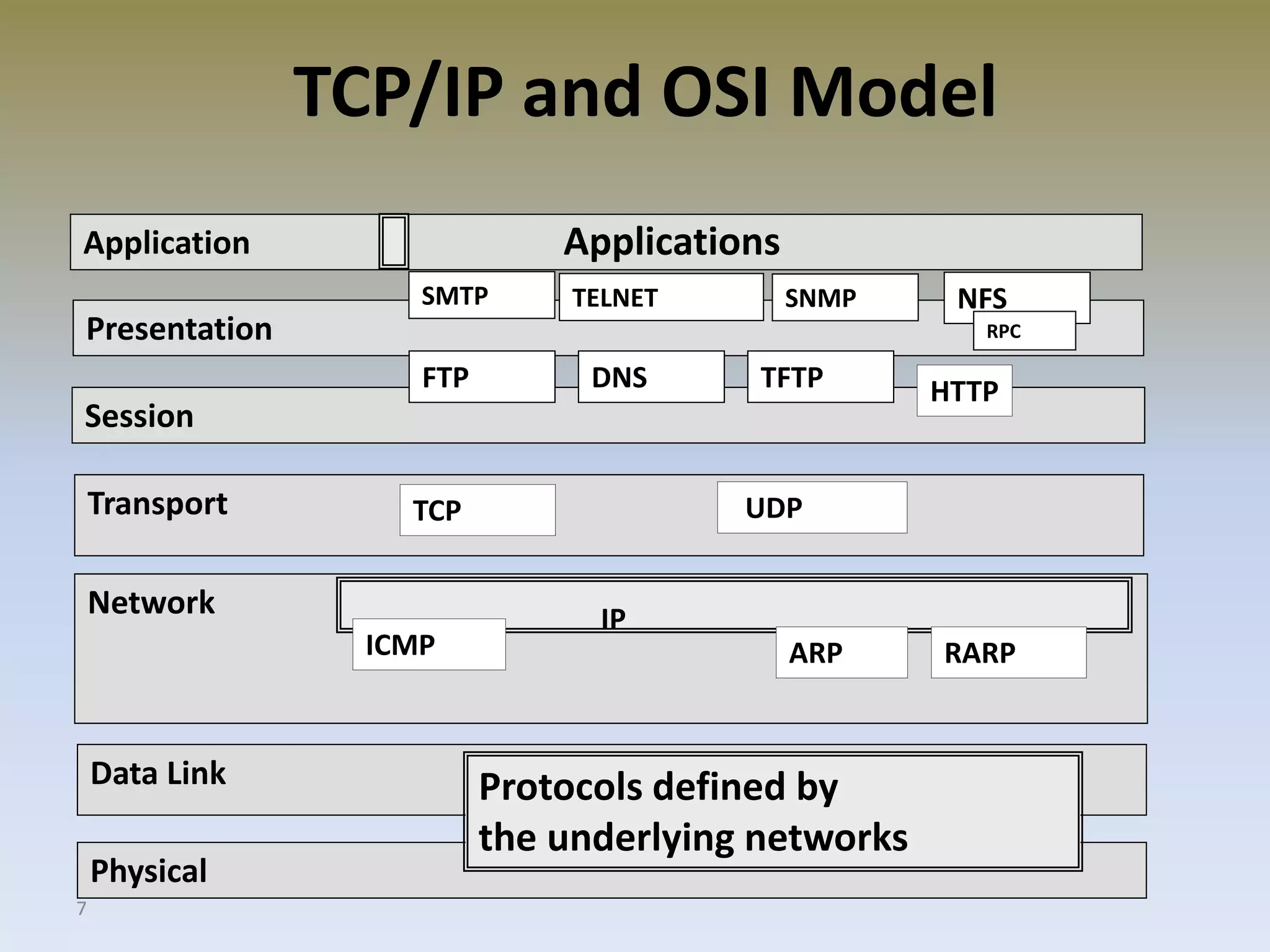
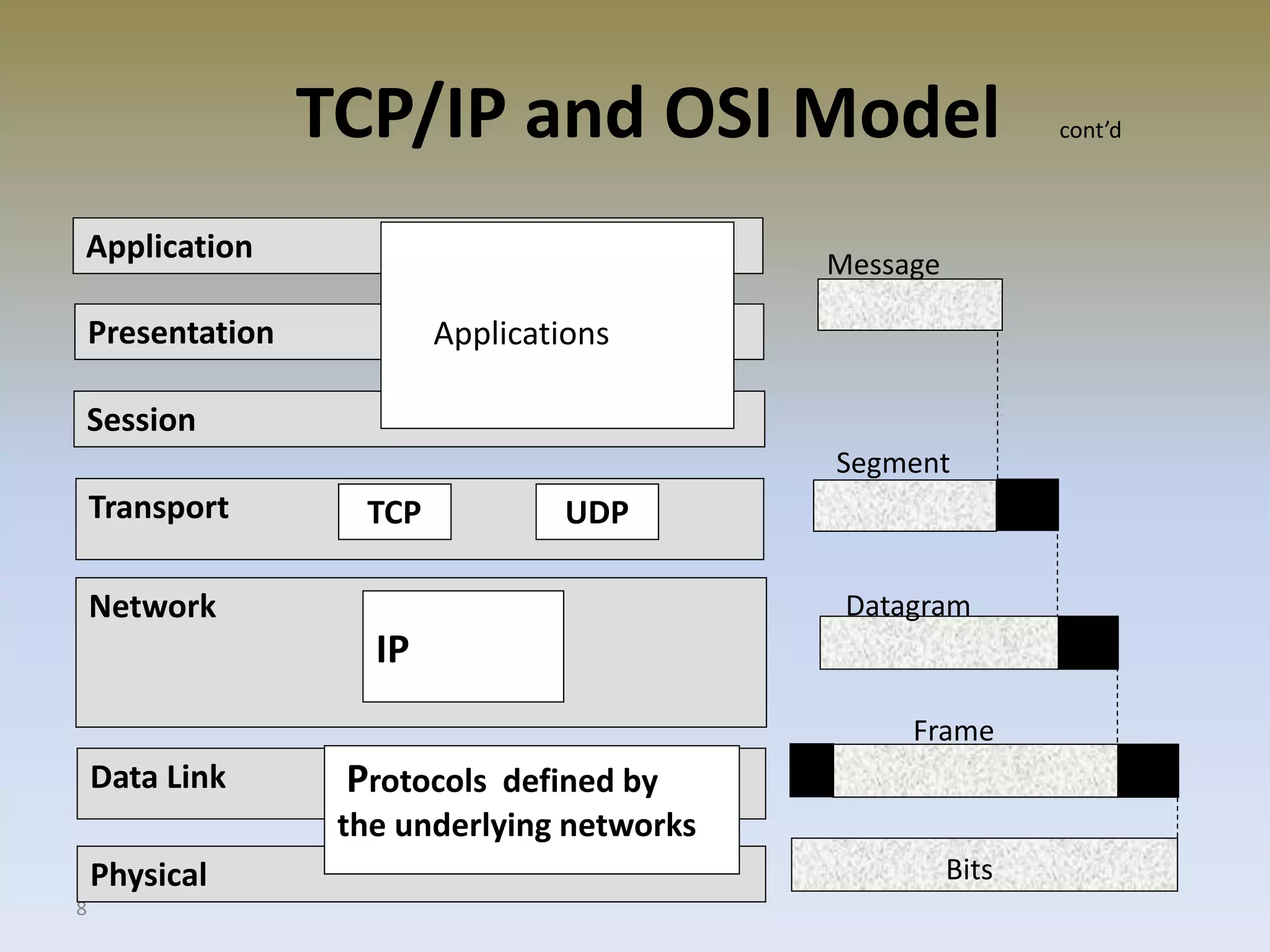
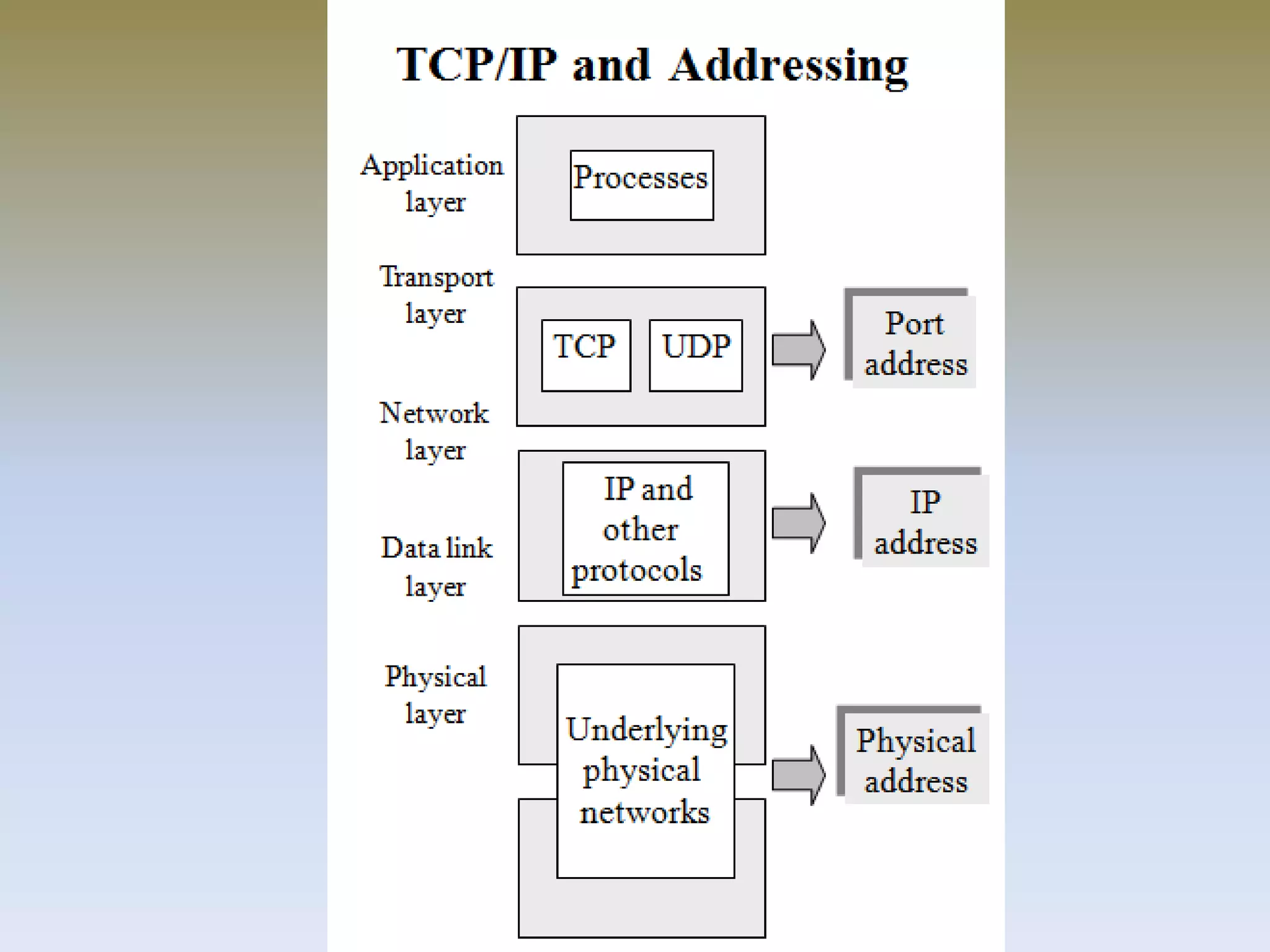
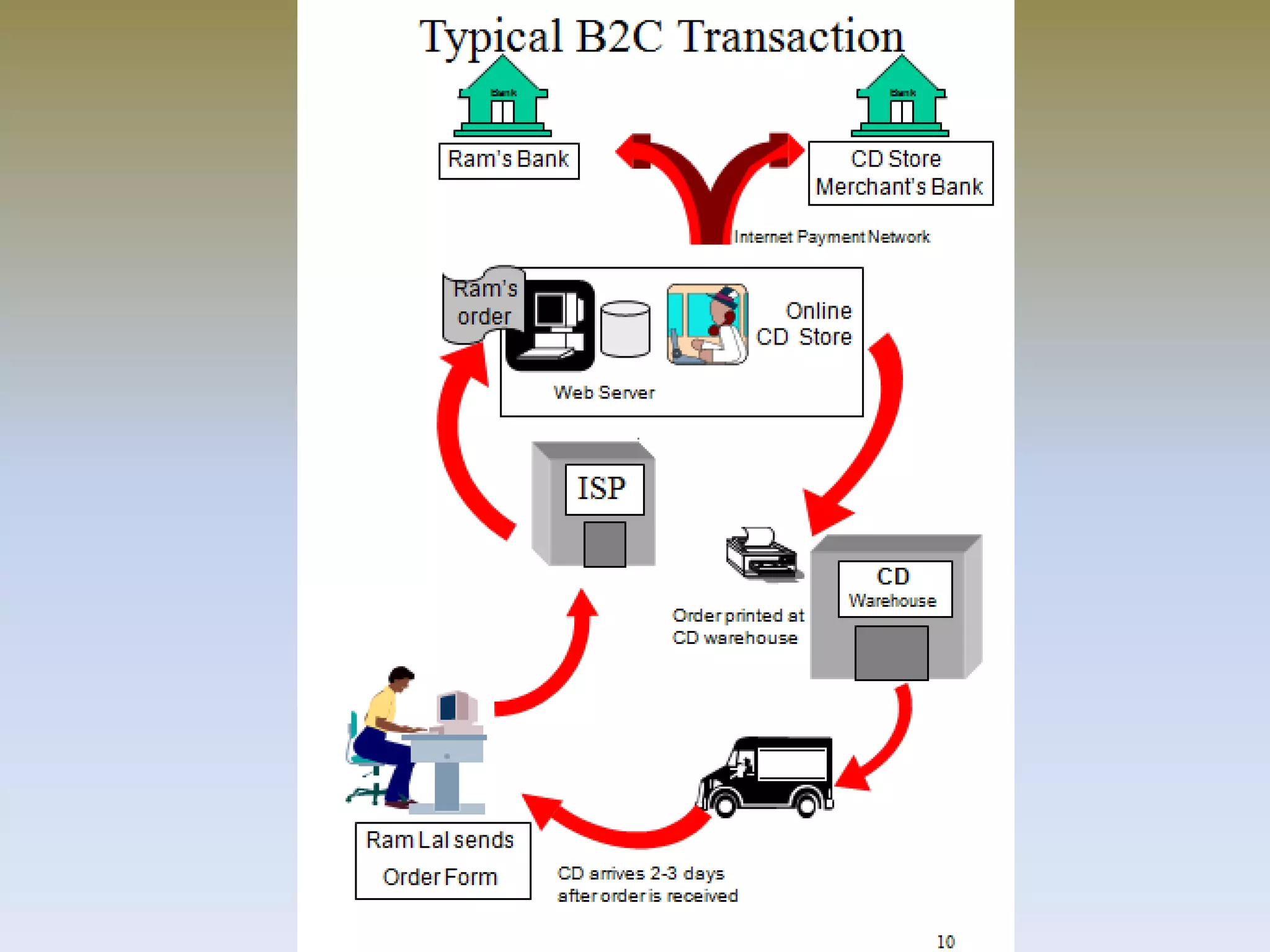
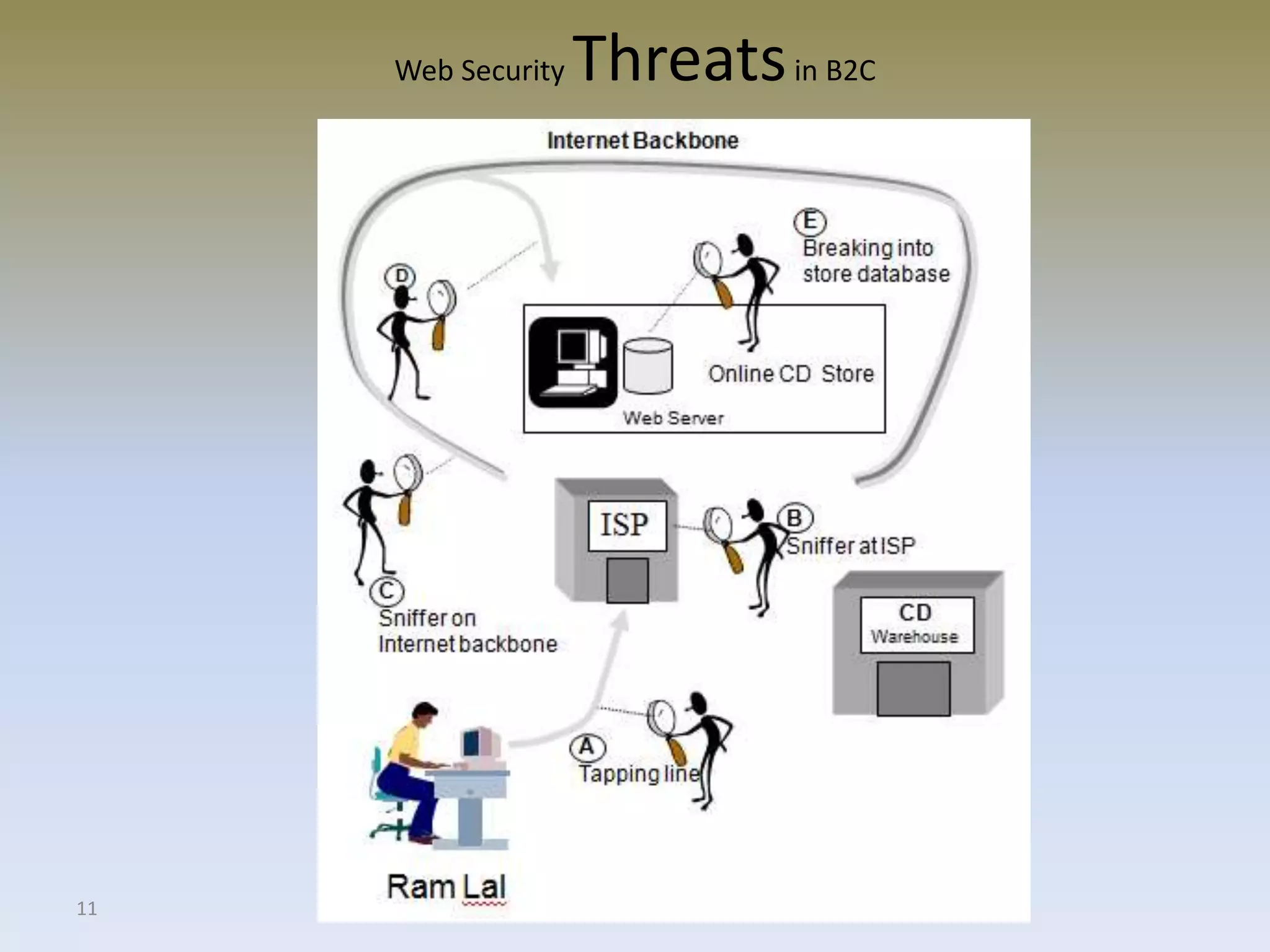
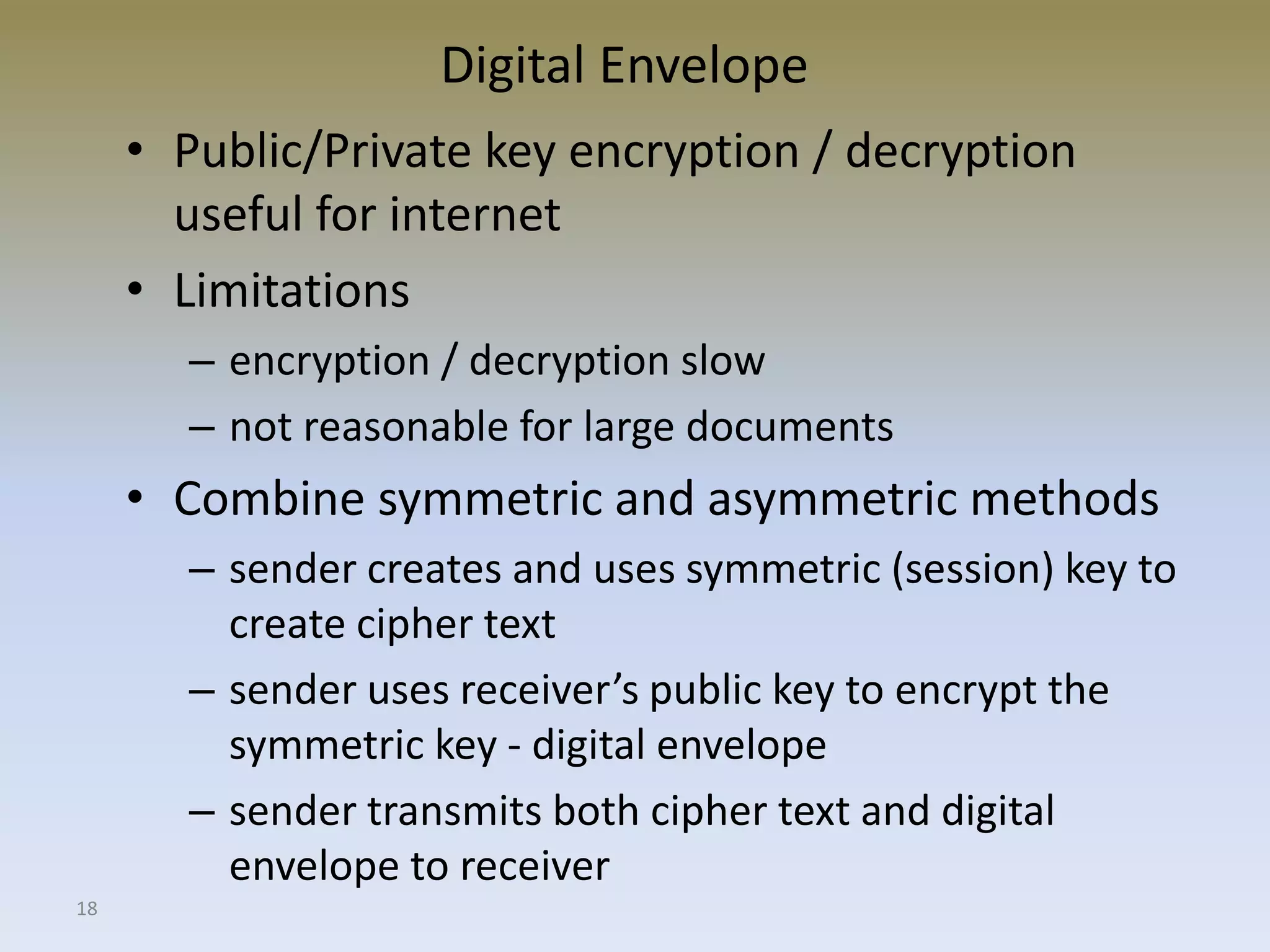
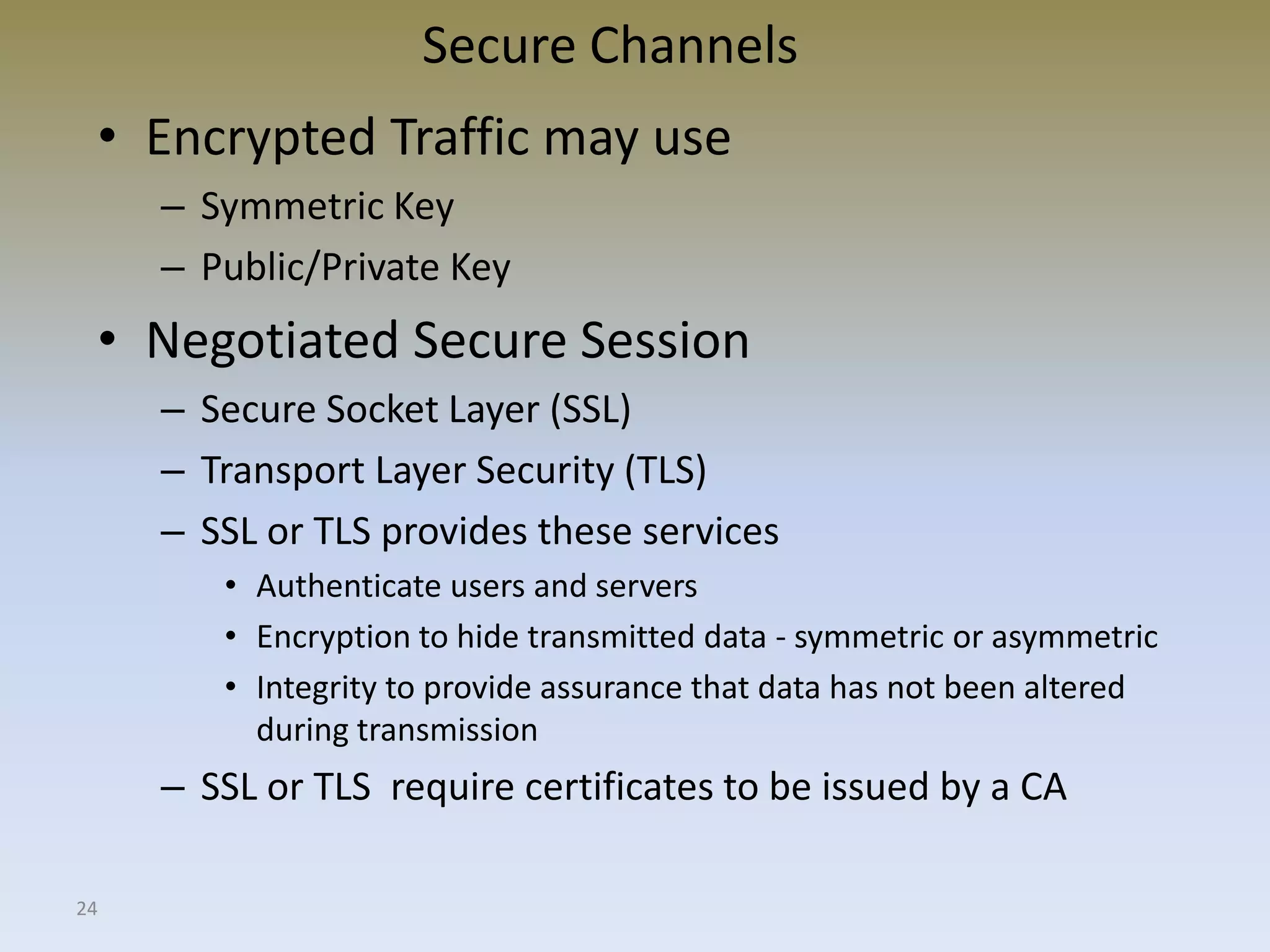
The document discusses web security for e-commerce and describes various threats such as insecure transmission and unauthorized access. It explains methods for protecting online businesses including cryptographic techniques, transport and application layer security, and firewalls. Specific topics covered include client/server applications, communication channels, OSI and TCP/IP models, security threats, cryptography services, digital signatures, envelopes, certificates, and secure channels.