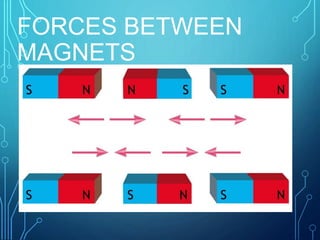
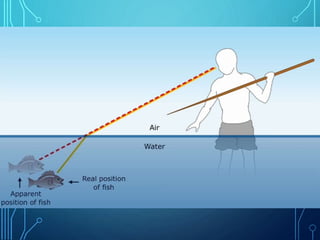
The document discusses electricity, light, and sound. It explains that electricity is generated by the movement of electrons forced along a path by humans. Materials like conductors can carry electrical energy in the form of moving electrons, while insulators cannot. Light is a form of energy made up of photons that can behave as both a particle and wave. Light travels very fast but bends when passing through different materials like water via refraction. Sound is a vibration that travels through matter as a wave and can be heard. It needs material to travel through as it moves molecules in a chain.