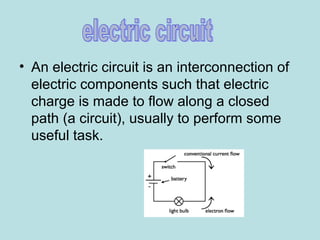
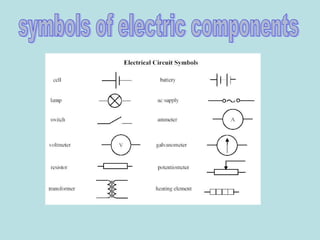
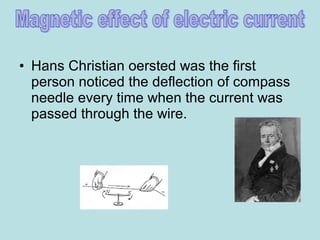
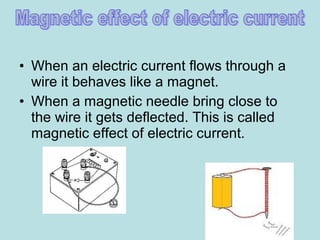
1. Electric current is the flow of electrically charged particles, typically measured in amperes.
2. James Joule discovered that electric current generates heat when passing through a wire, known as the heating effect.
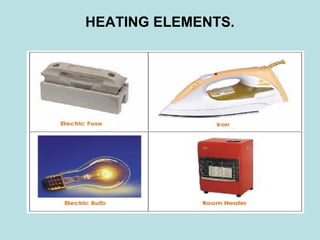
3. The heating effect has many applications, including heating elements in appliances that produce heat when current flows through coils inside.