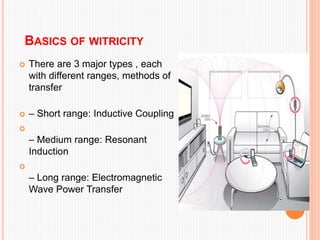
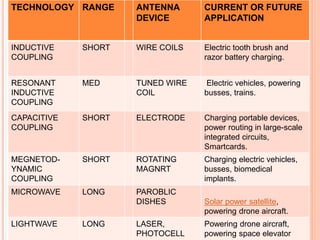
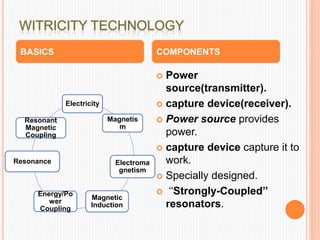
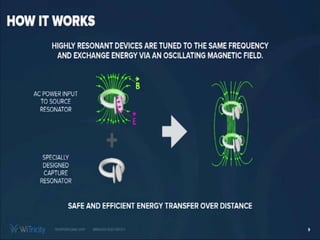
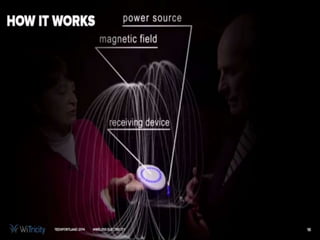
This document summarizes wireless power transmission called WiTricity. It describes how Nikola Tesla first proposed wireless power in 1899 using electromagnetic waves, but it had low efficiency. In 2007, MIT scientists revived the idea and named it WiTricity. There are three types of WiTricity with different ranges - inductive coupling for short range using coils, resonant induction for medium range using tuned coils, and electromagnetic waves for long range. It works by using a power source transmitter and receiver capture device with strongly-coupled resonators. While it could be used for applications like charging electric vehicles and devices, it has limitations like short transmission distances and decreased efficiency over longer distances.