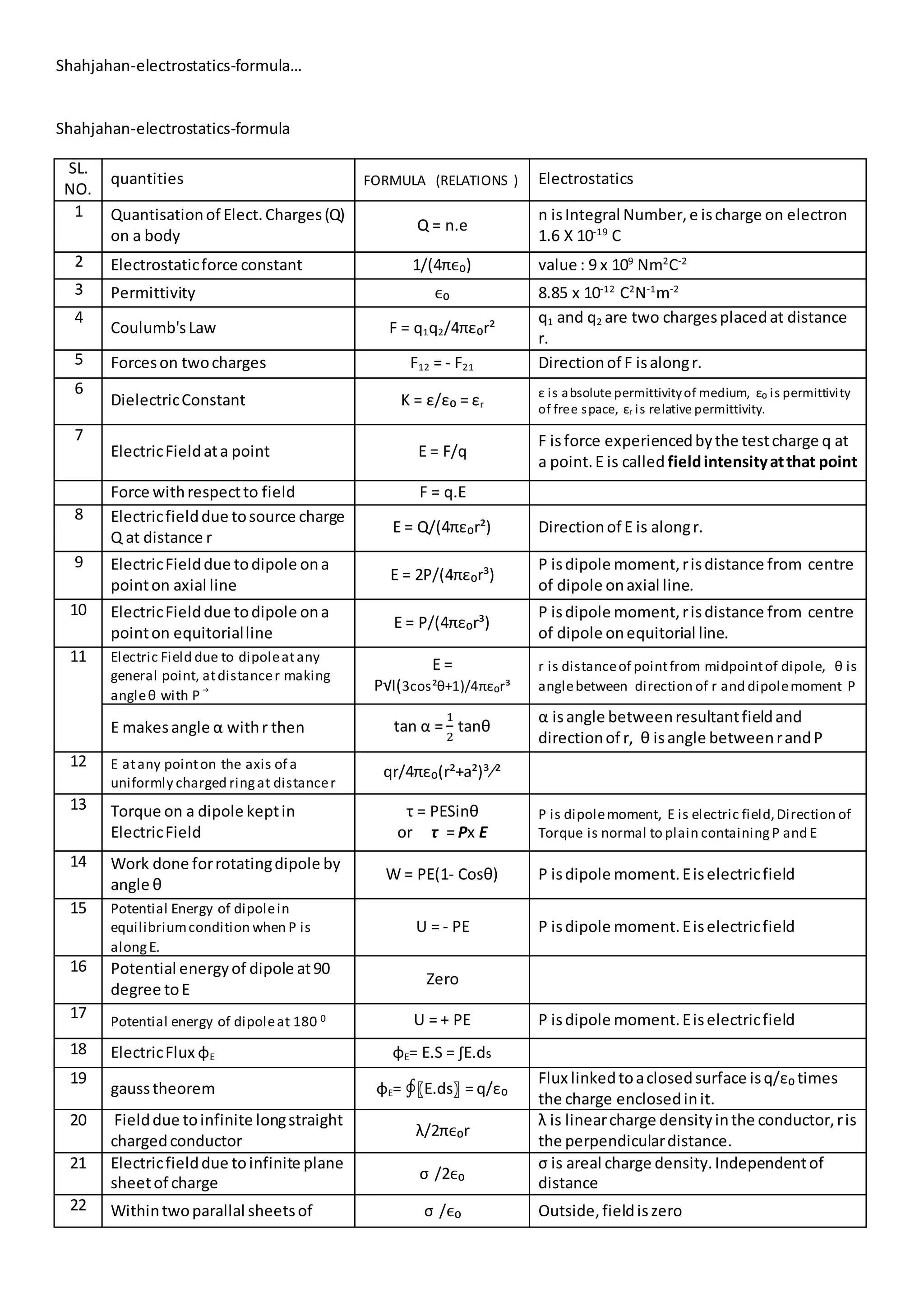
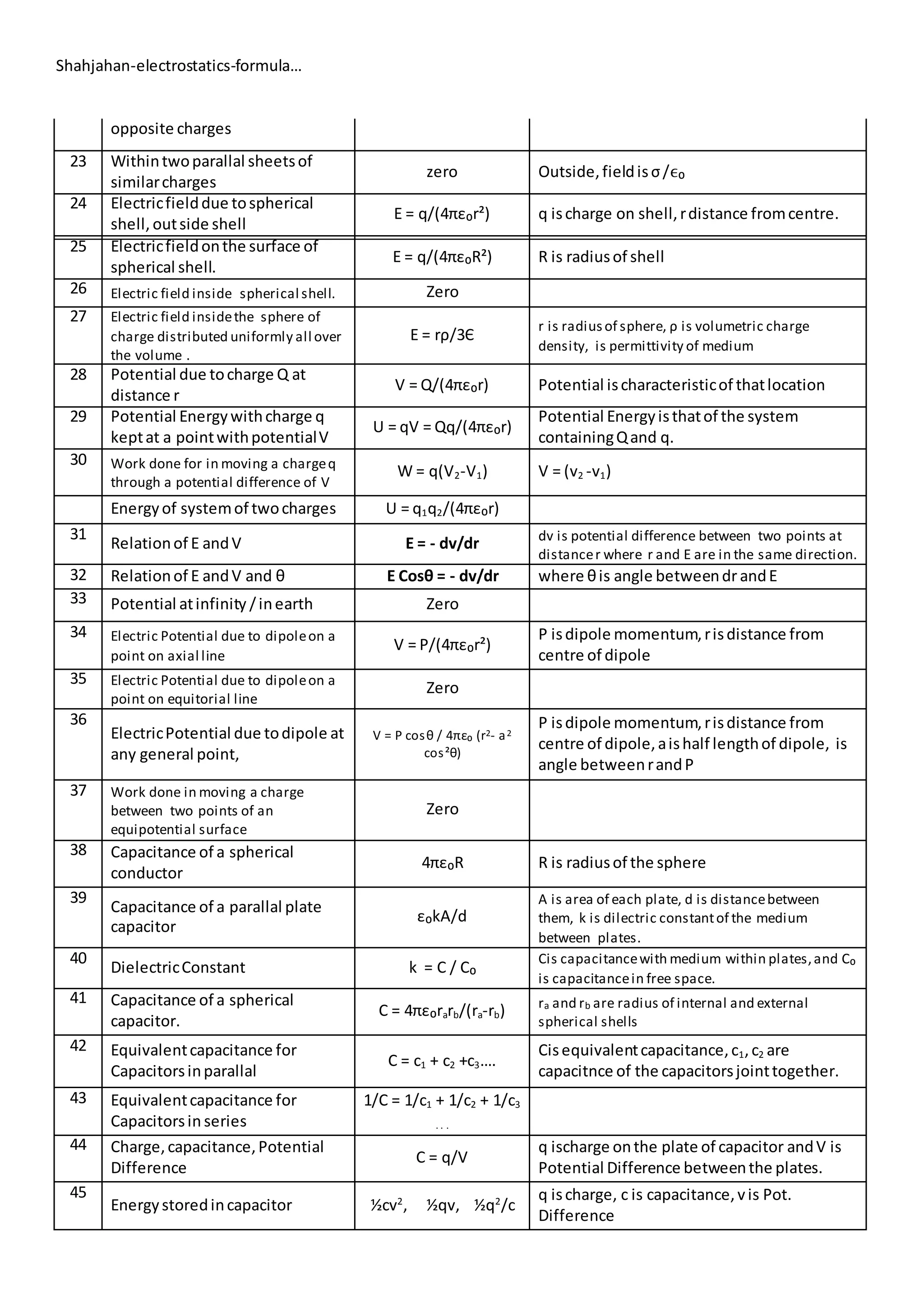
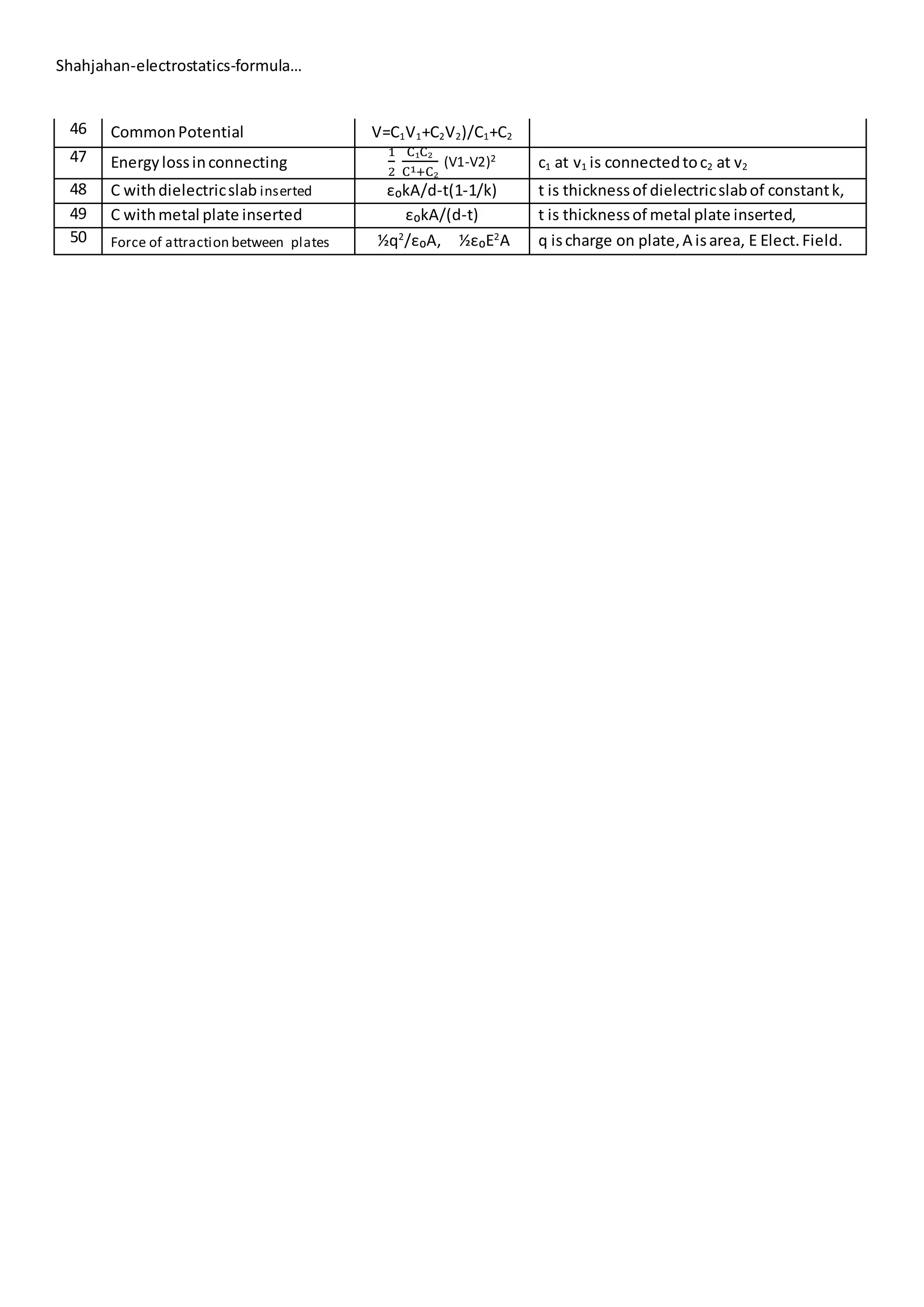
1. This document lists formulas related to electrostatics including:
2. Quantization of electric charge, Coulomb's law, electric field due to point charges, dipoles, and conductors.
3. It also includes formulas for electric potential, capacitance, work and energy related to electrostatic systems, and forces between charged plates.