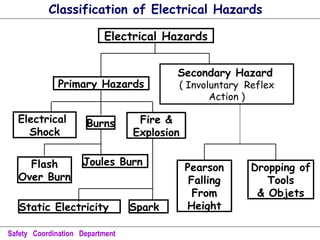
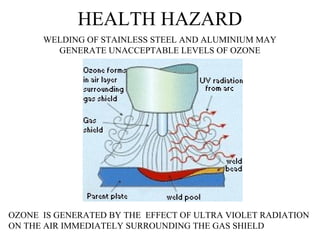
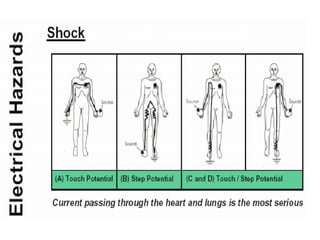
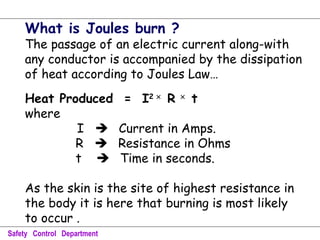
This document discusses various electrical hazards and safety measures related to them. It defines electric shock as the sudden stimulation of the body's nervous system by an electric current. The severity of shock depends on the amount of current, its path through the body, and duration of exposure. Currents between 1-20 mA can cause tingling to severe muscle contractions. Above 50 mA can cause ventricular fibrillation and death. It also describes flashover, flash burns and joules burns caused by electric arcs. The document outlines various shock protection methods like proper insulation, grounding, use of PPE etc. It discusses hazards of static electricity and importance of maintaining proper grounding to prevent failures.