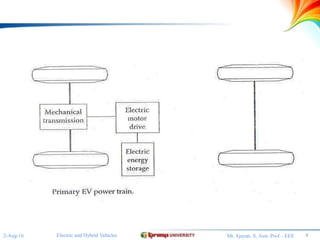
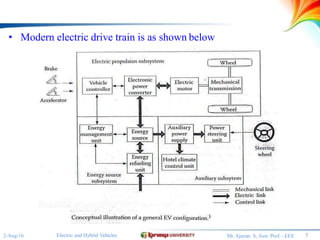
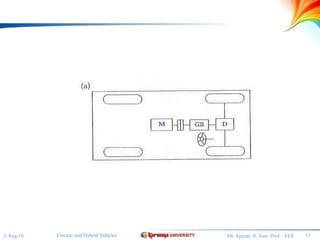
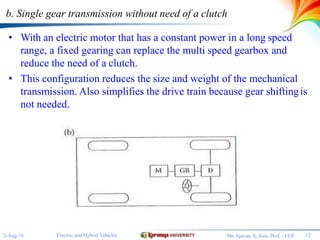
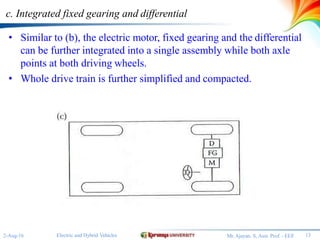
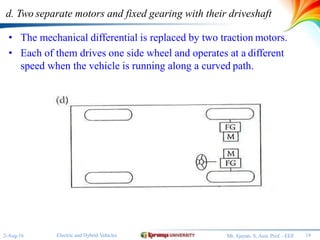
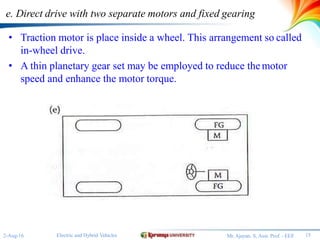
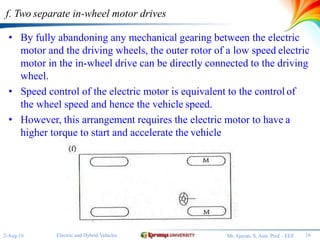
The document discusses different configurations for electric vehicles (EVs). It notes that early EVs converted internal combustion engine vehicles, which led to problems, while modern EVs are purpose-built. The key subsystems of a modern EV drive train are the electric motor propulsion system, the energy source, and auxiliary systems. The document then describes six possible EV configurations, including using a conventional drivetrain with gearbox and clutch, a single fixed gear transmission without clutch, integrated fixed gearing and differential, two separate motors with fixed gearing, direct drive with two motors and gearing, and two separate in-wheel motor drives.