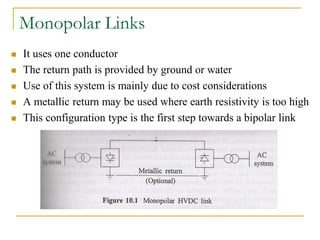
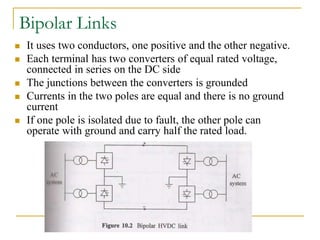
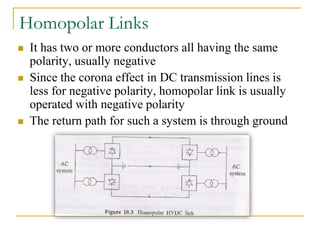
HVDC transmission was first used commercially in 1954 between Sweden and an island. It allows for bulk power transmission over long distances and undersea cables. HVDC systems use converters to change AC to DC and back. Components include smoothing reactors, filters, and electrodes. Configurations include monopolar, bipolar, and back-to-back links. Control is done by firing angle adjustment and tap changing. Advantages are long distance transmission and connecting unsynchronized grids, while disadvantages are costly converters and circuit breakers.