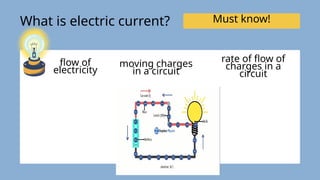
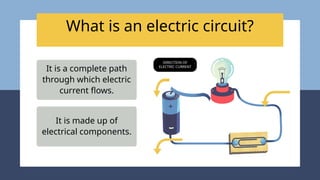
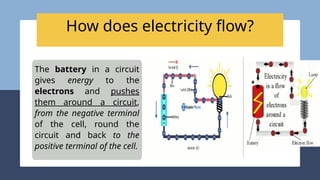
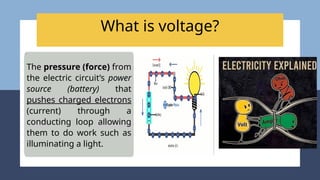
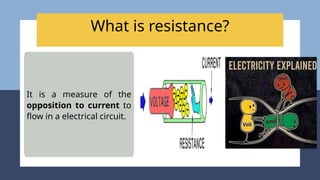
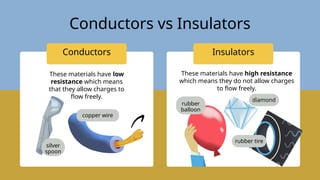
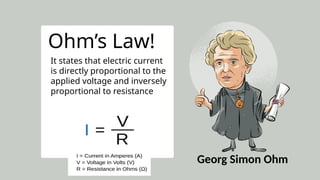
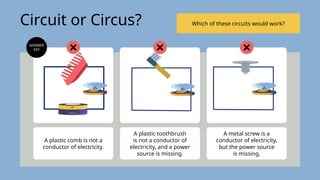
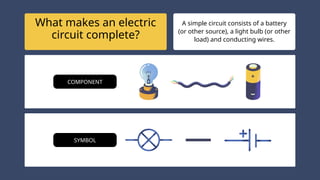
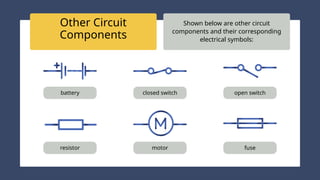
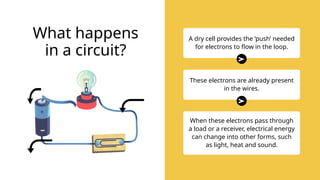
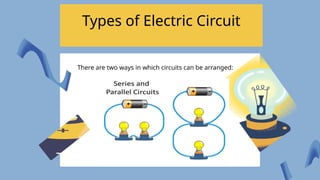
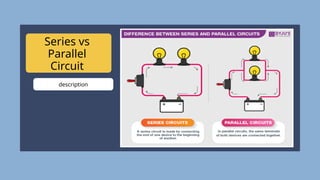
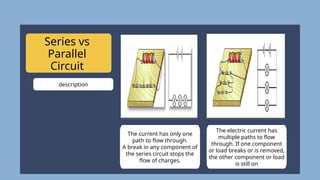
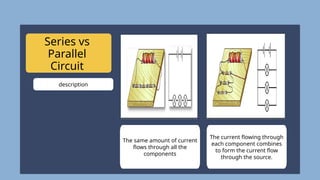
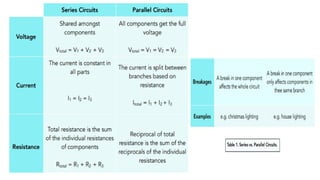
The document provides an overview of electricity concepts, including the relationship between current, voltage, and resistance, as well as the functions and differences between series and parallel circuits. It explains safety devices commonly used at home, such as fuses and circuit breakers, to prevent electrical hazards. Additionally, it covers practical applications and methodologies for testing circuits and understanding electric flow, emphasizing Ohm’s law and electrical safety.