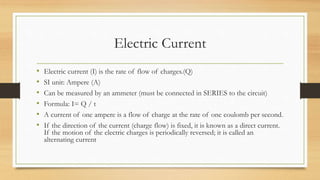
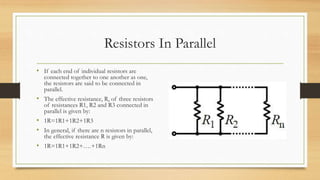
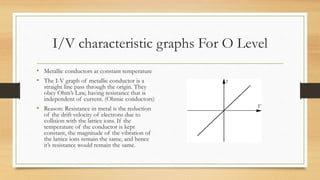
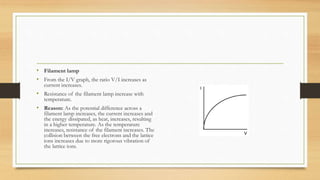
Electric current is the flow of electric charge. It is measured in Amperes and can be measured using an ammeter. The rate of electric current is equal to the total charge passed divided by the time taken. There are two types of electric current: direct current which flows in one direction and alternating current which periodically changes direction. Electromotive force is the energy converted when a coulomb of charge passes through a source and is measured in Volts. Potential difference is the energy lost when a coulomb passes between two points in a circuit and is also measured in Volts. Components connected in series have their emfs add up while those in parallel do not. Resistance depends on the material and dimensions of a conductor. It is