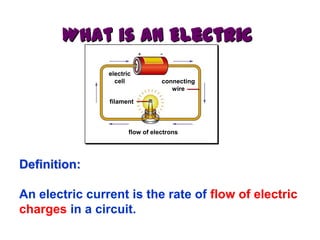
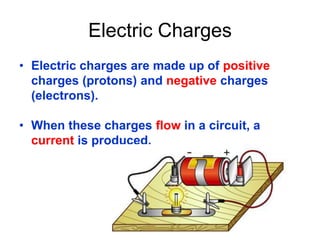
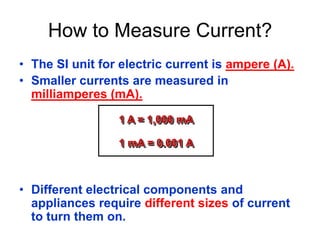
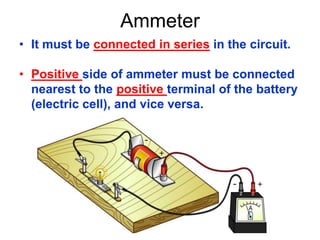
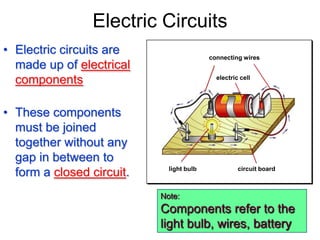
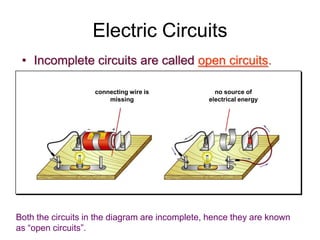
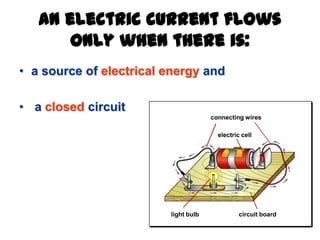
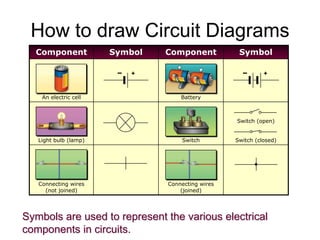
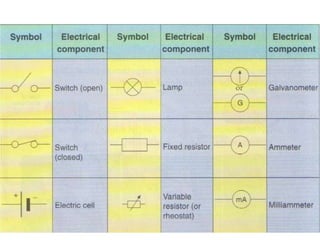
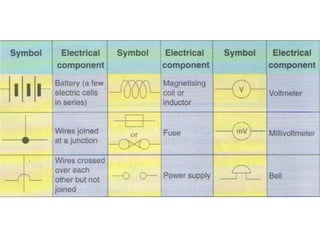
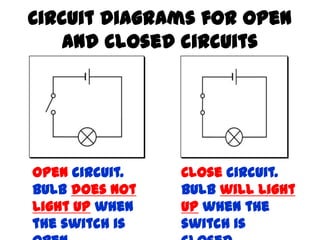
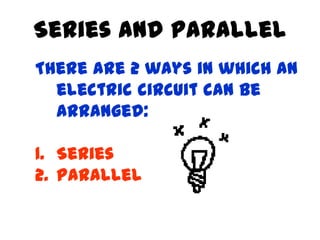
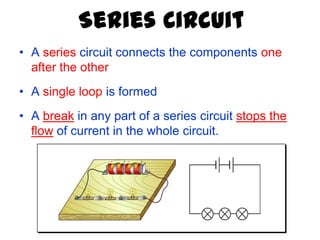
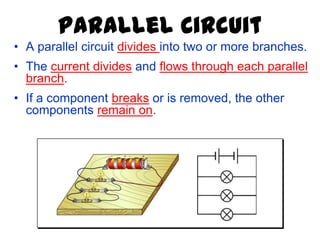
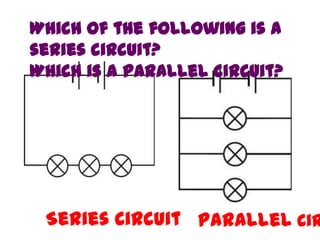
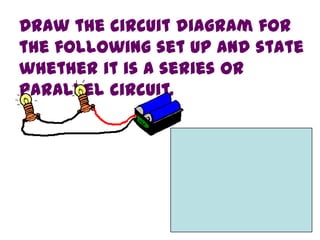
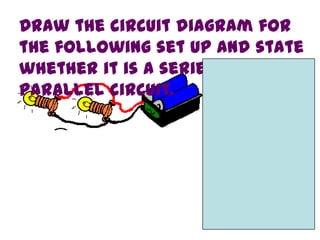
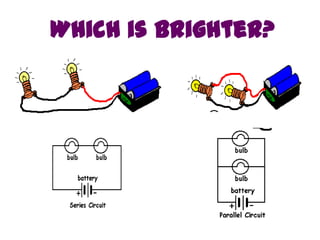
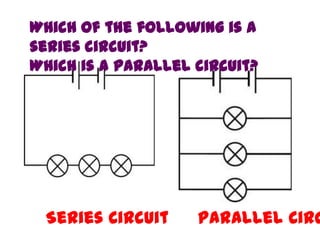
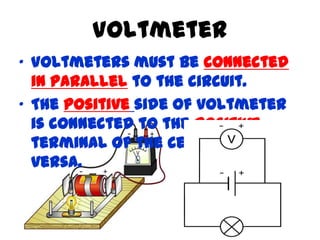
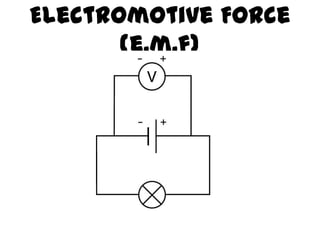
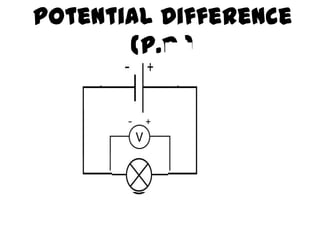
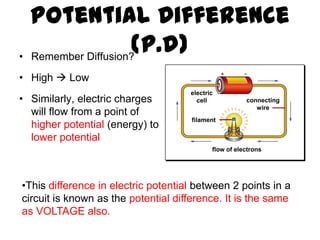
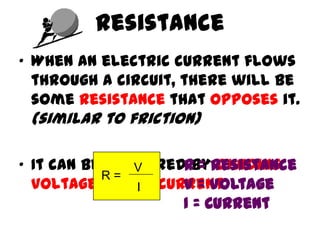
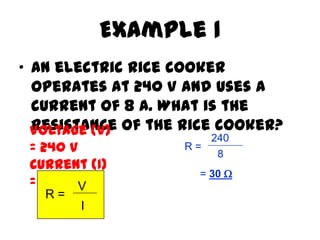
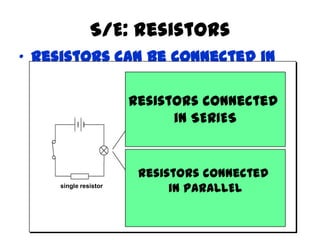
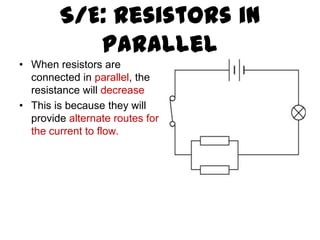
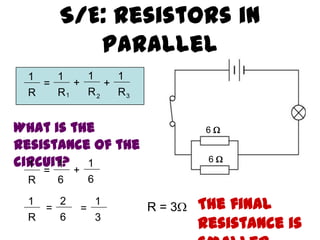
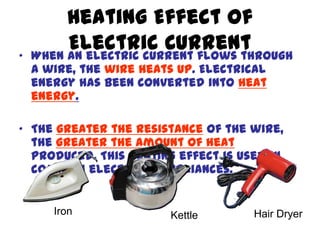
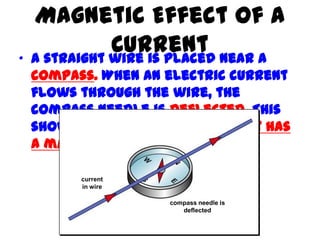
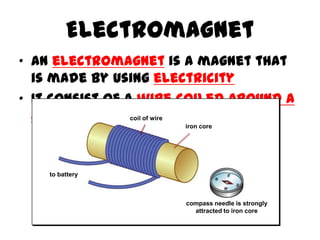
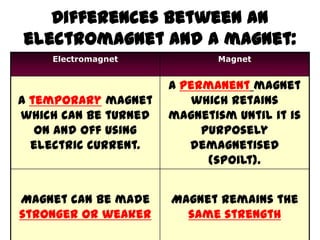
This document provides an overview of electricity, including definitions of key terms like electric current, voltage, resistance and circuits. It explains that electricity is a form of energy that can power appliances. Current is the flow of electric charges in a circuit. Voltage and electromotive force (EMF) refer to the "push" of electricity. Resistance opposes current flow. Circuits can be connected in series or parallel. Electricity has heating, chemical and magnetic effects. Common applications like lighting, heating and electroplating are discussed.