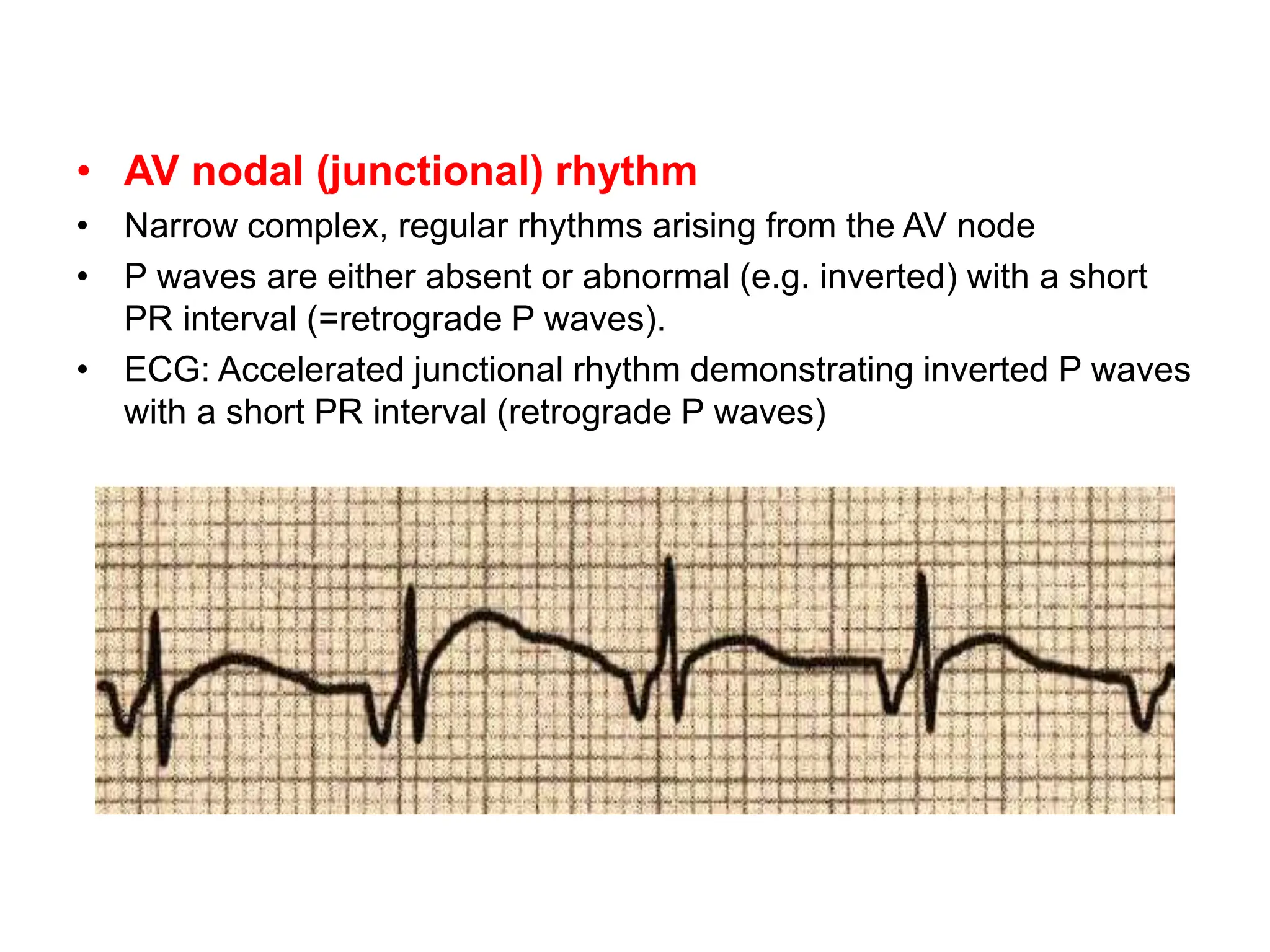
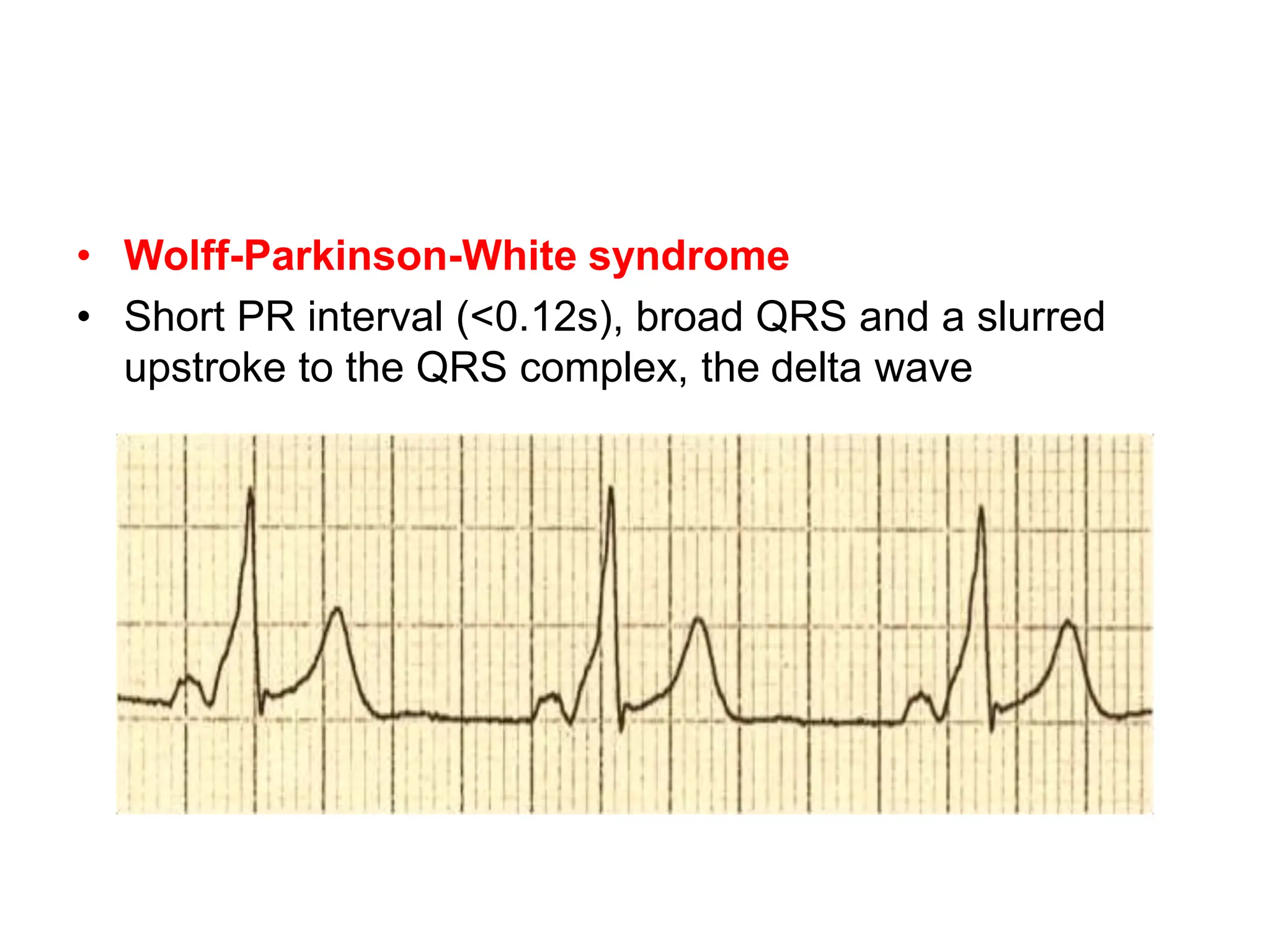
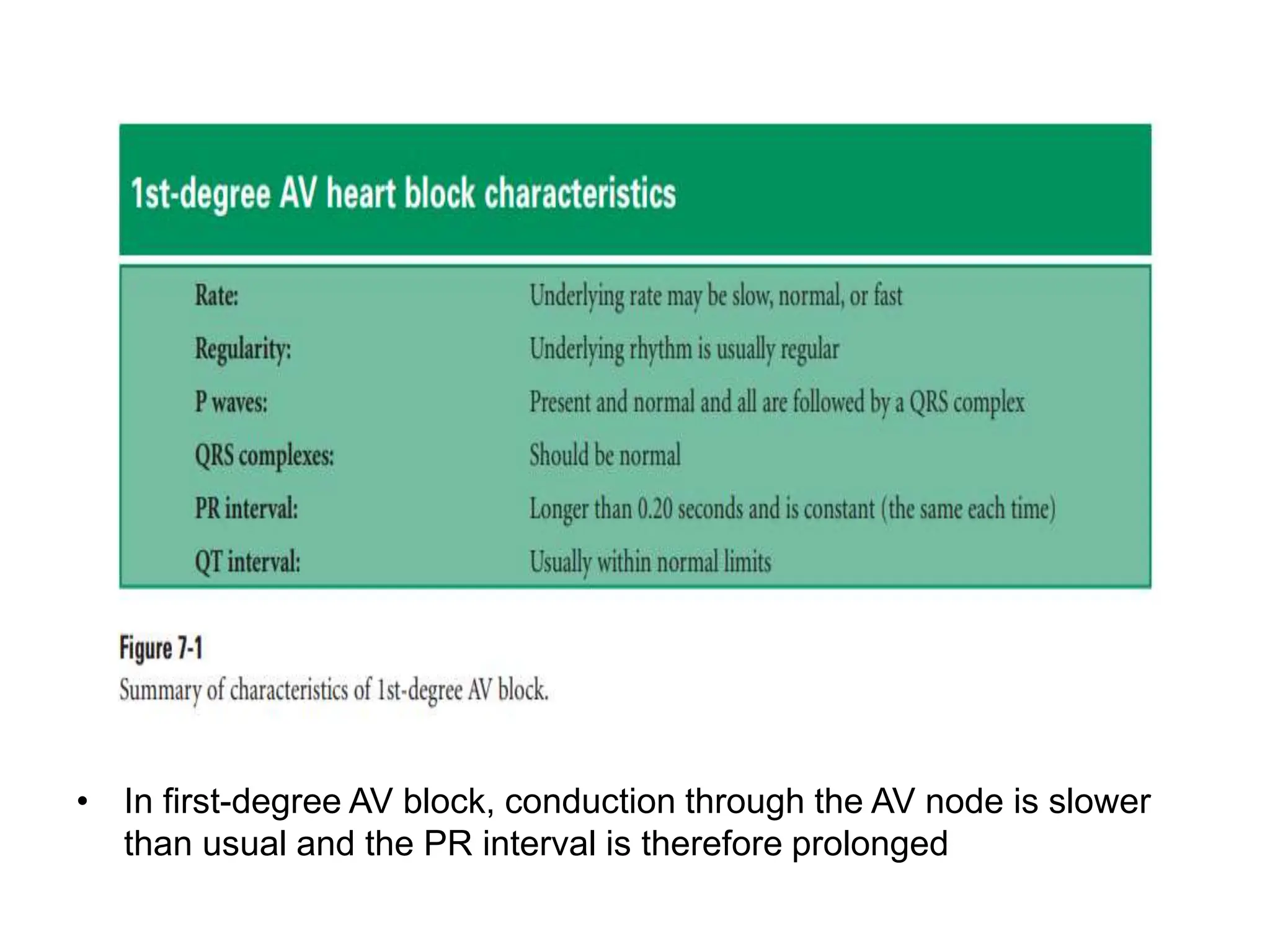
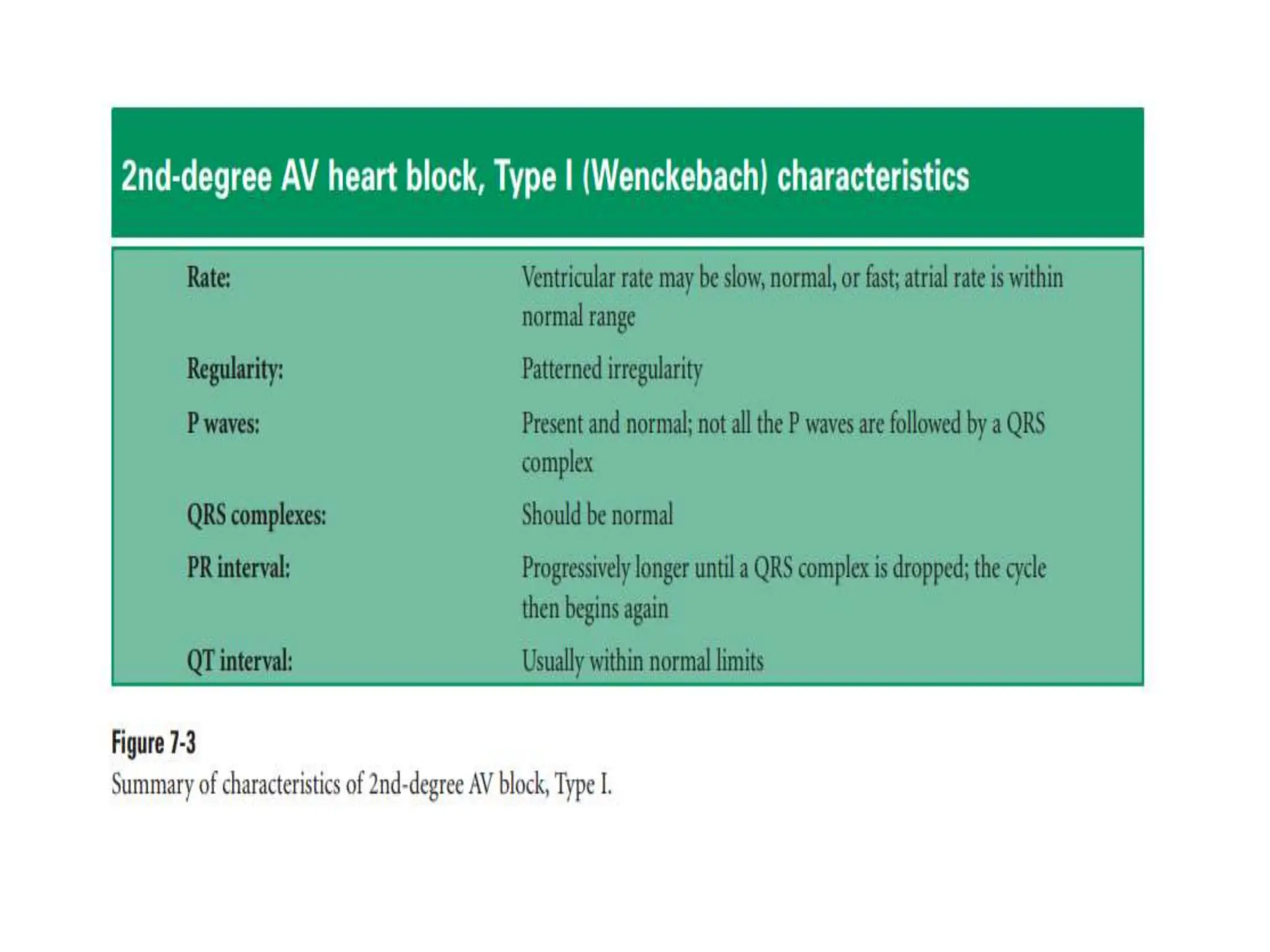
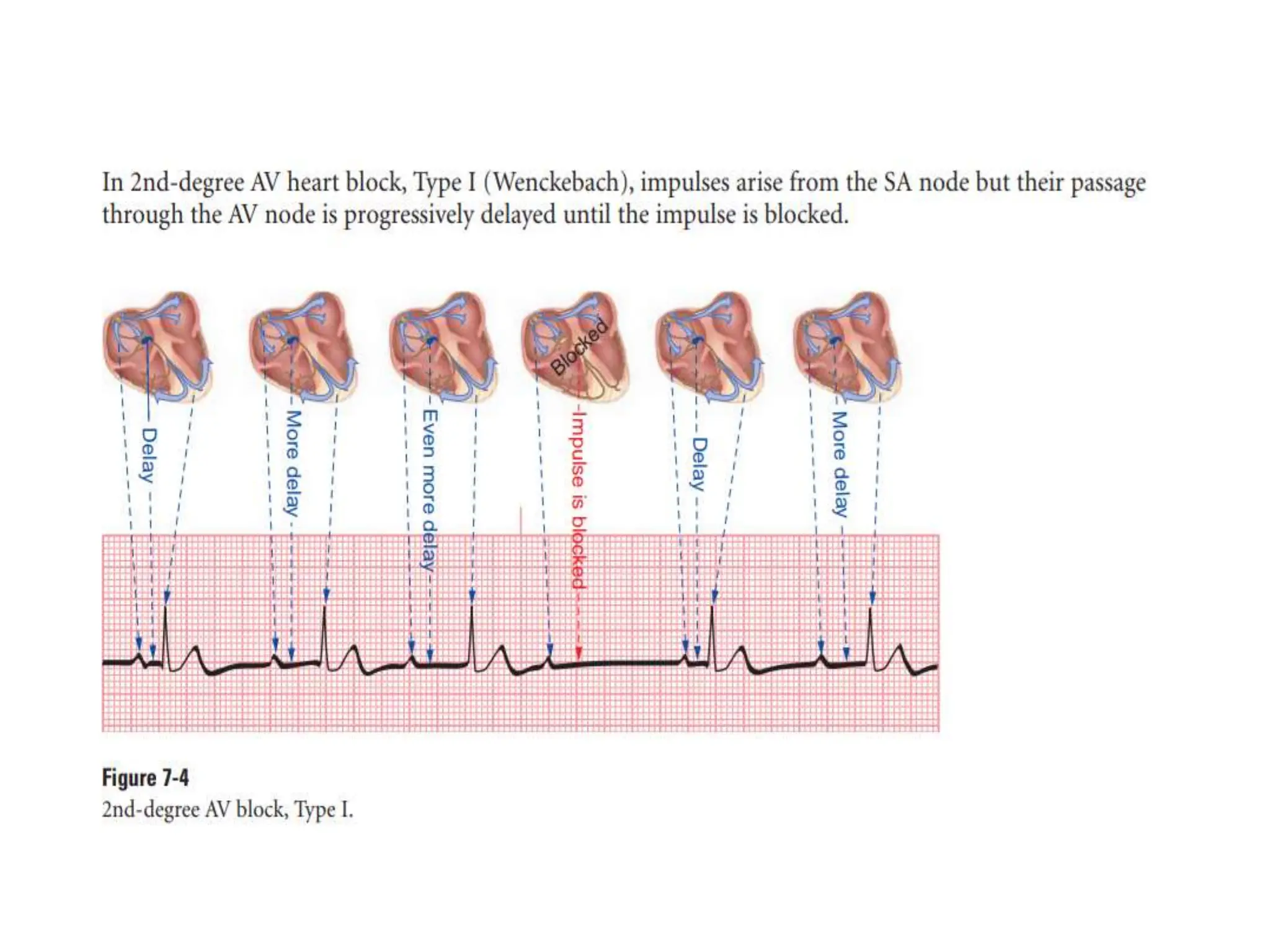
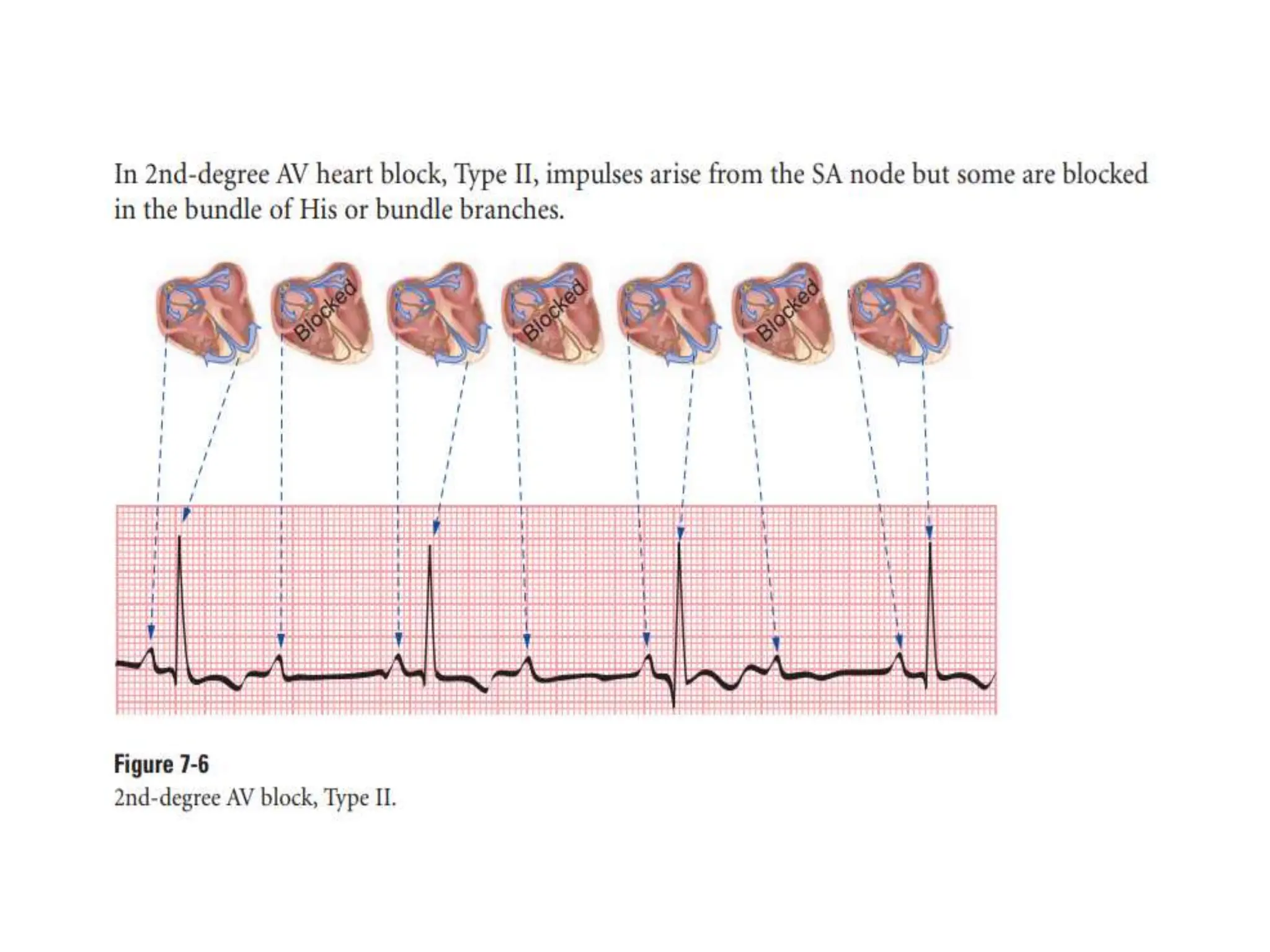
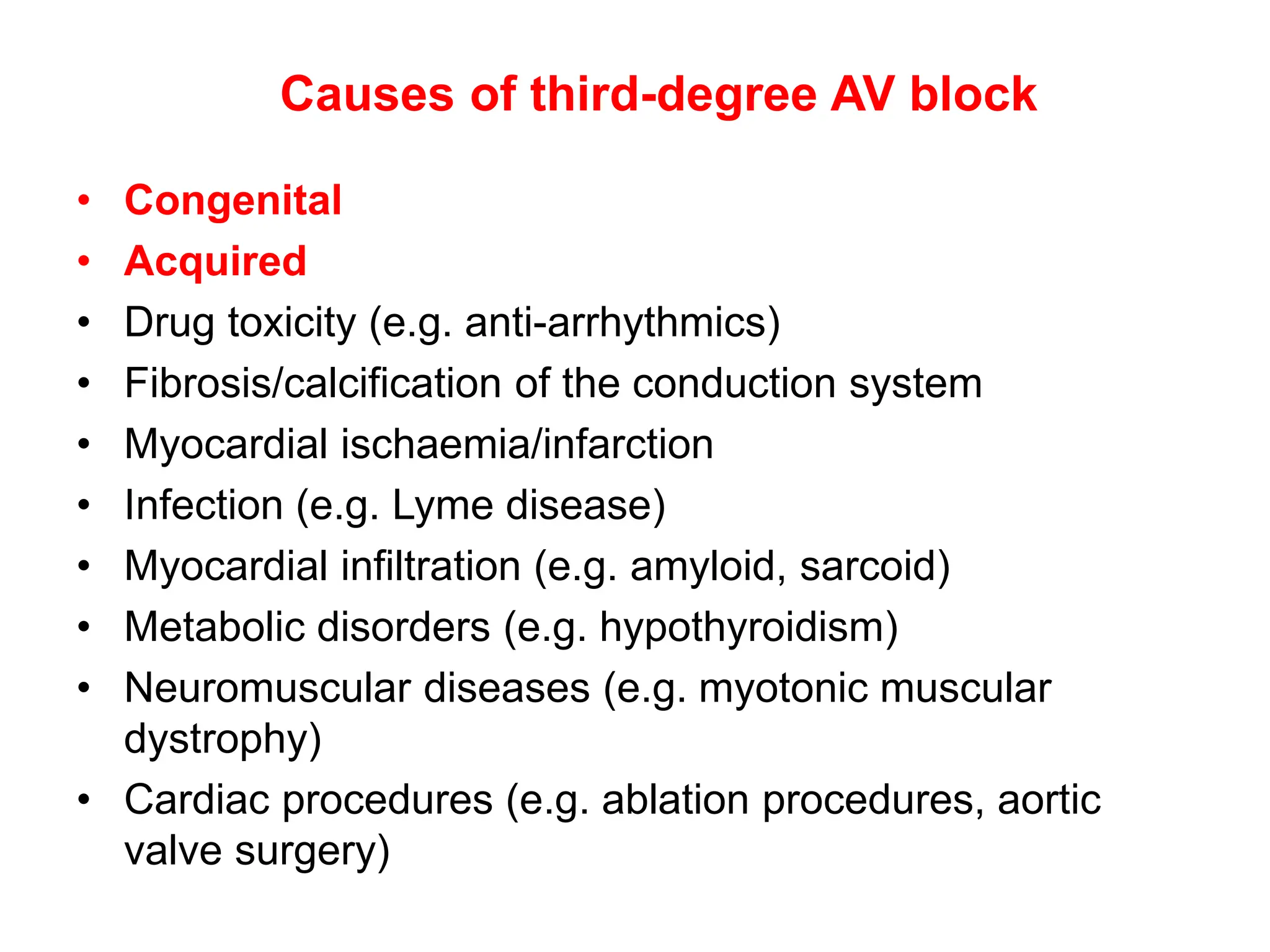
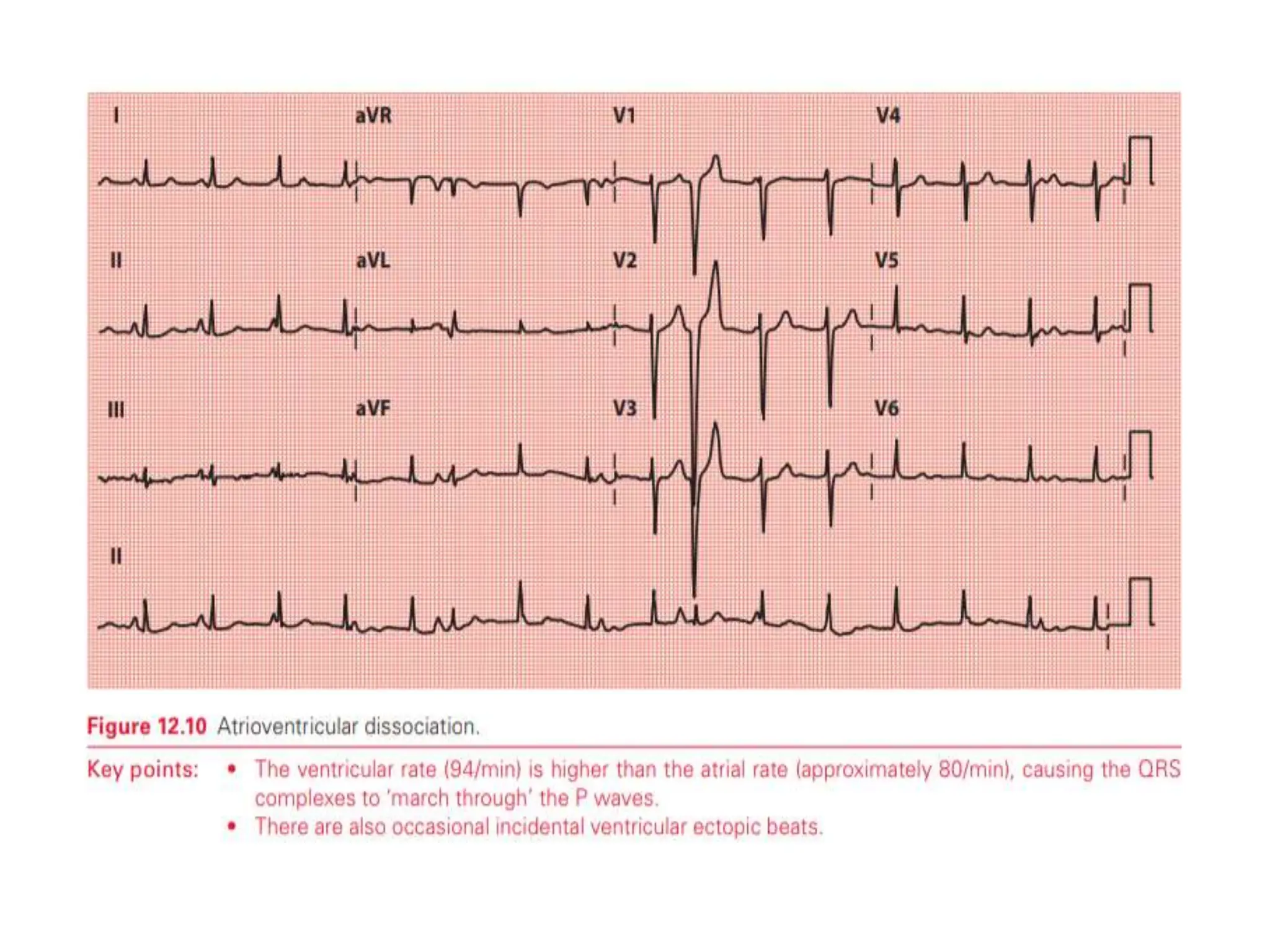
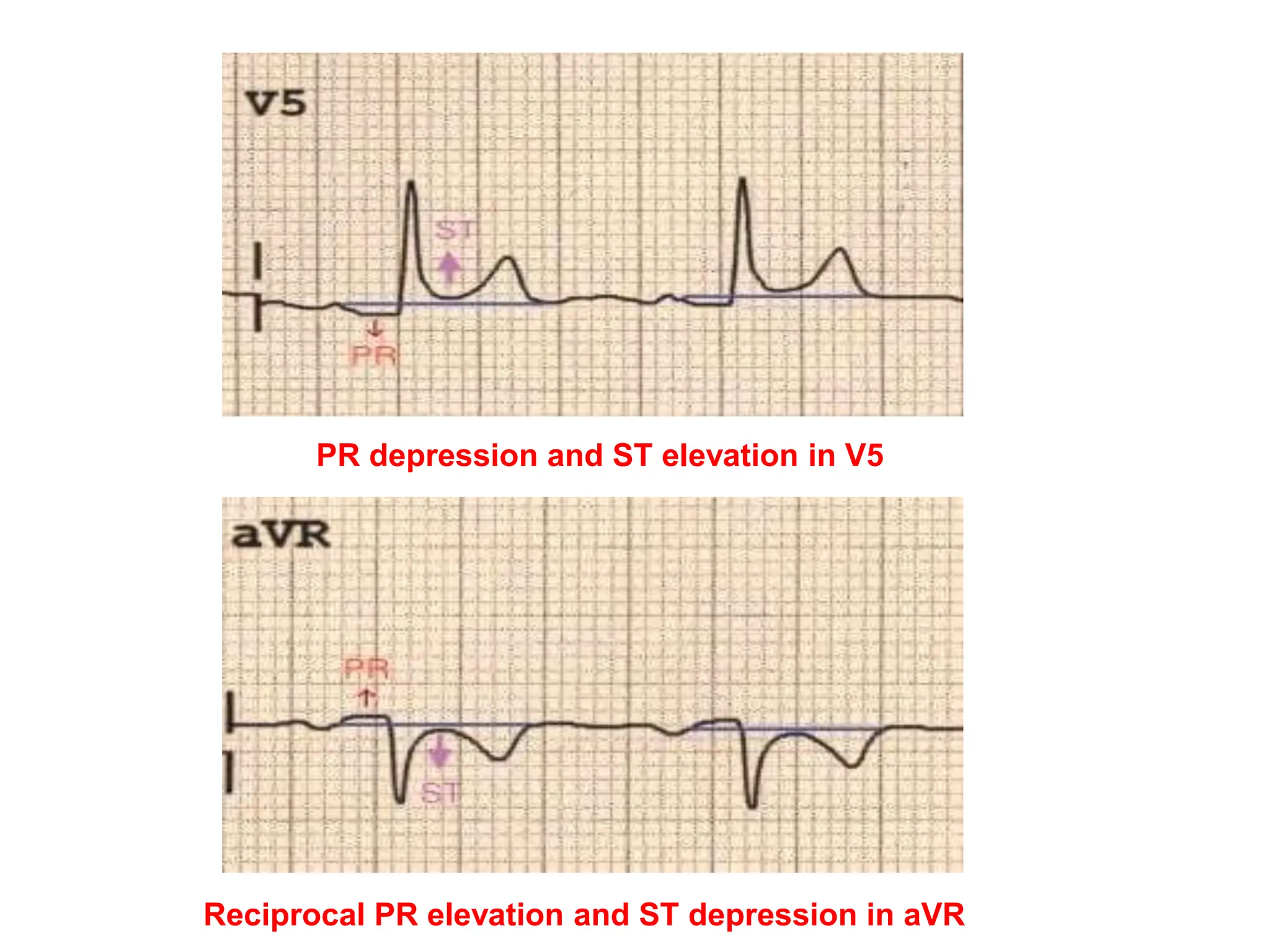
The PR interval represents the time taken for electrical signals to travel from the sinoatrial node through the atria and atrioventricular node to reach the ventricles. A normal PR interval is between 120-200 milliseconds. Short or long PR intervals can indicate various conduction abnormalities between the atria and ventricles. The document discusses various conditions that can cause short or long PR intervals such as first-degree heart block, Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, and complete heart block. It also describes what features of the PR interval such as variability, absence, or elevation/depression may indicate specific cardiac issues.