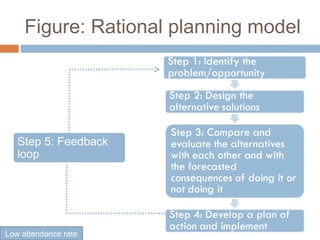
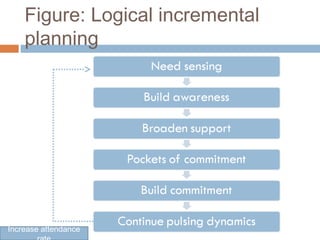
This document discusses the policy, planning, and program development process. It defines policy as a statement of goals, with plans developed to achieve those goals through specific programs and actions. The document then outlines Bangladesh's national education policy development process, which included forming a committee, setting goals of ensuring quality education for all, reviewing past policies and commissions, drafting the policy and soliciting public feedback, and finalizing the policy. It also discusses different models of planning, including rational planning, logical incremental planning, contingency planning, and crisis management planning.