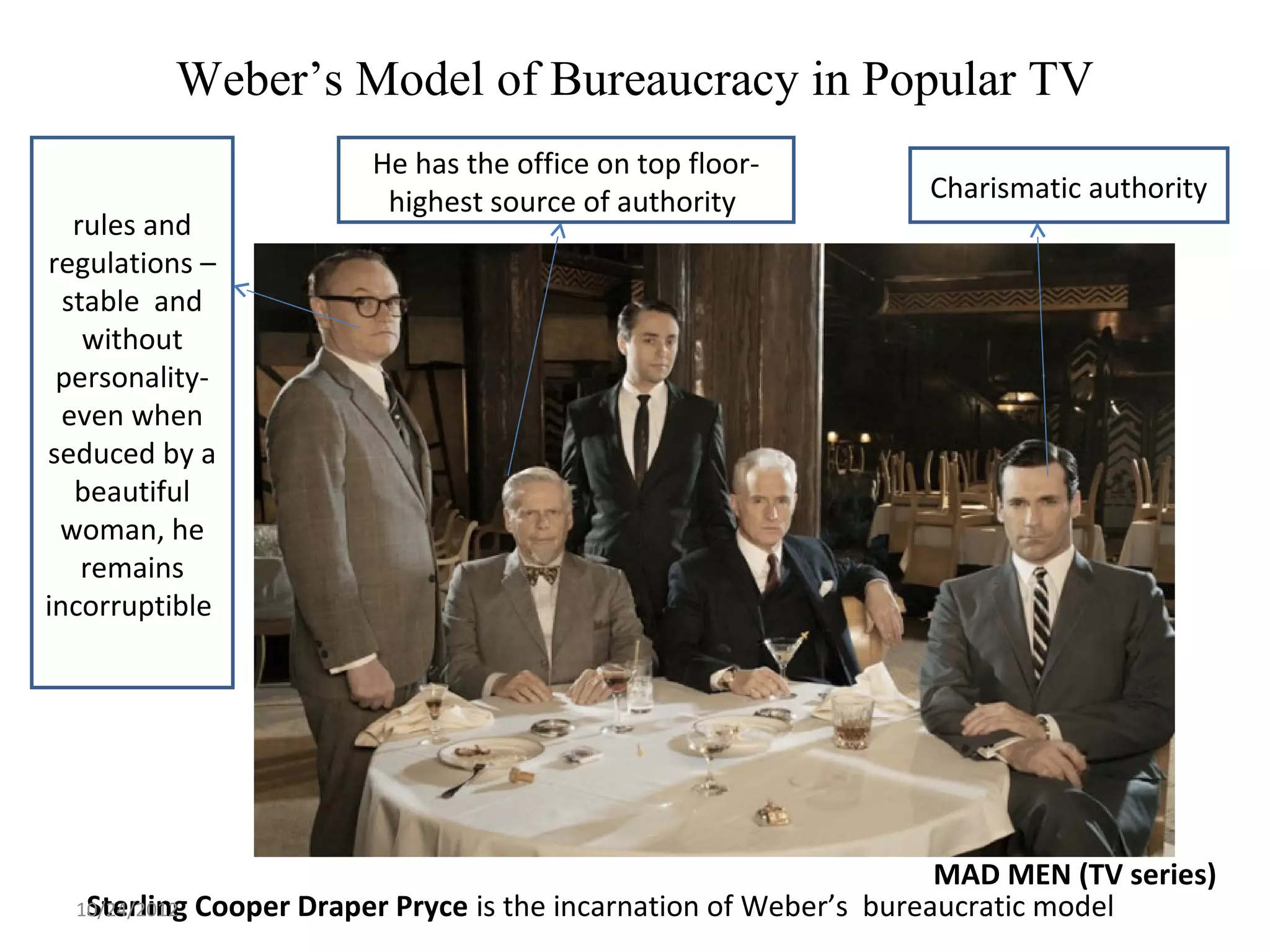
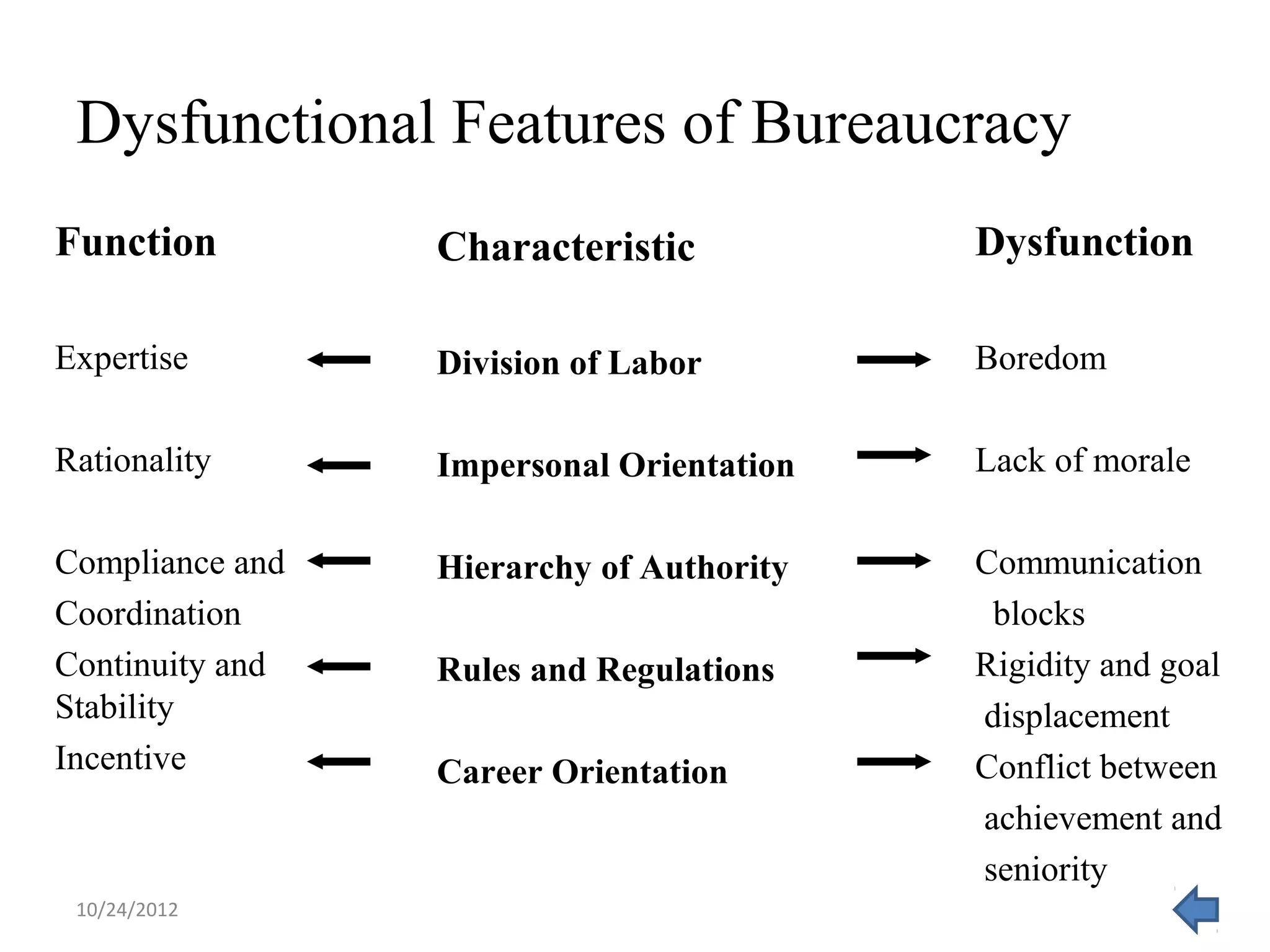
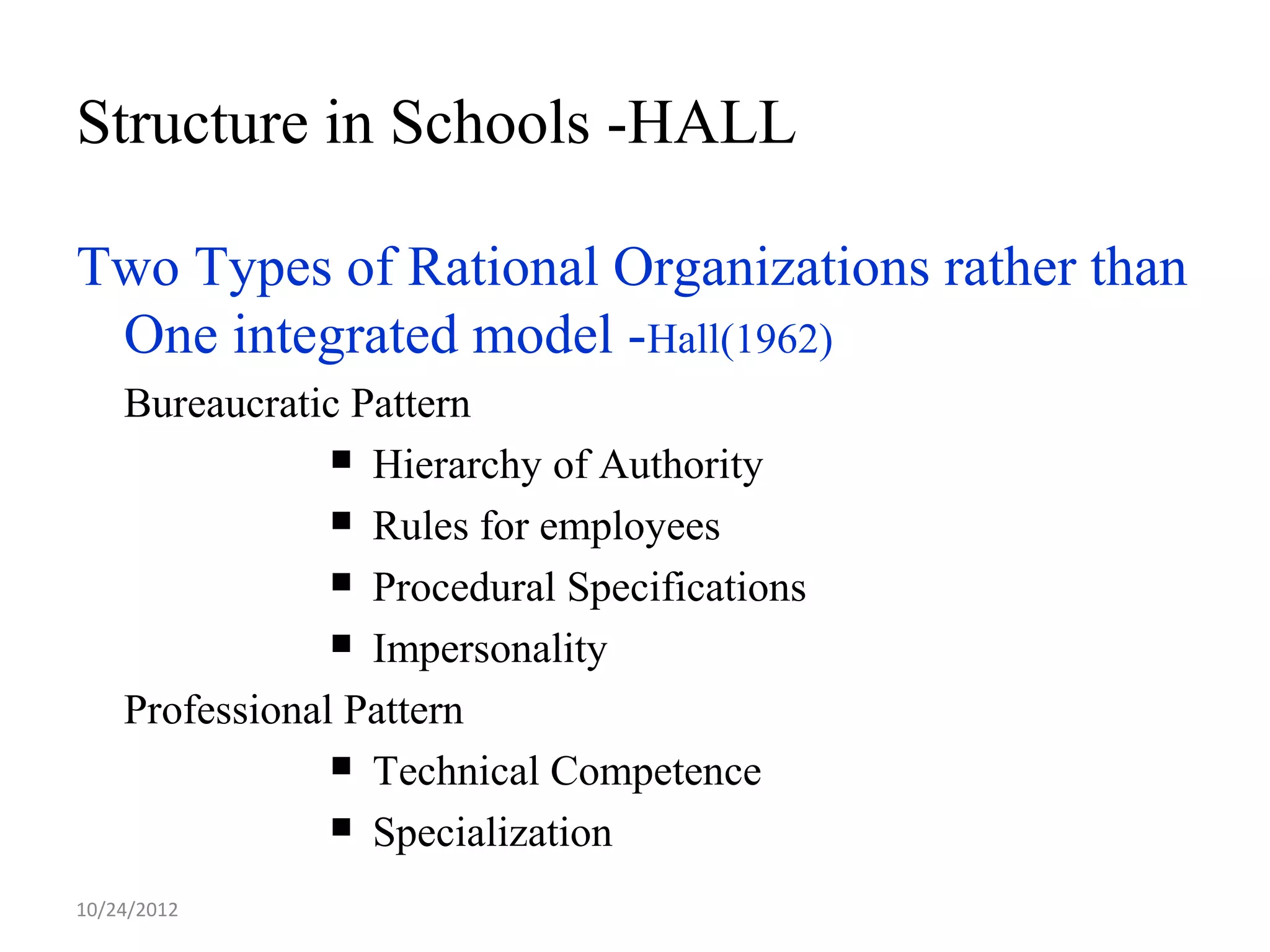
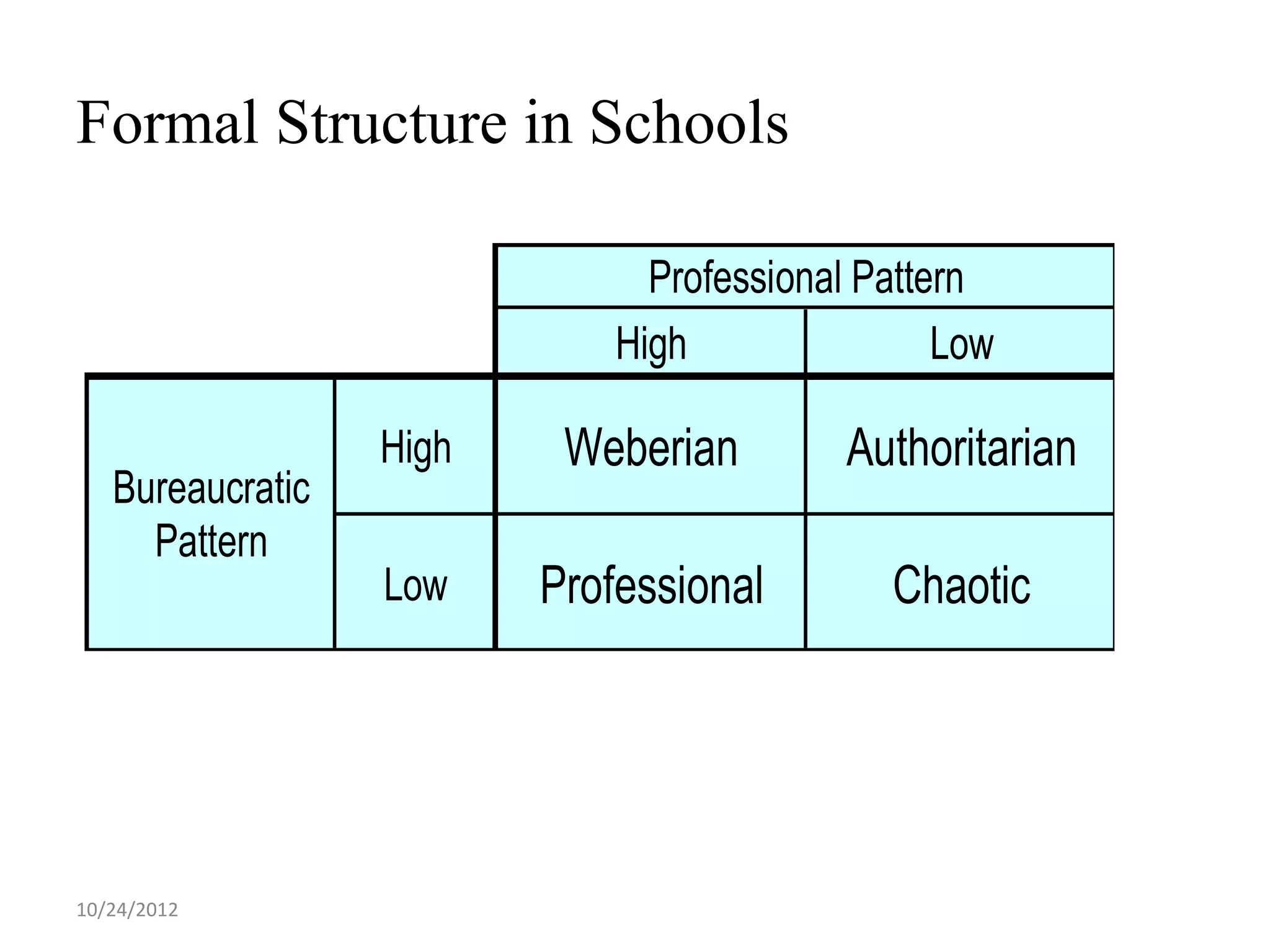
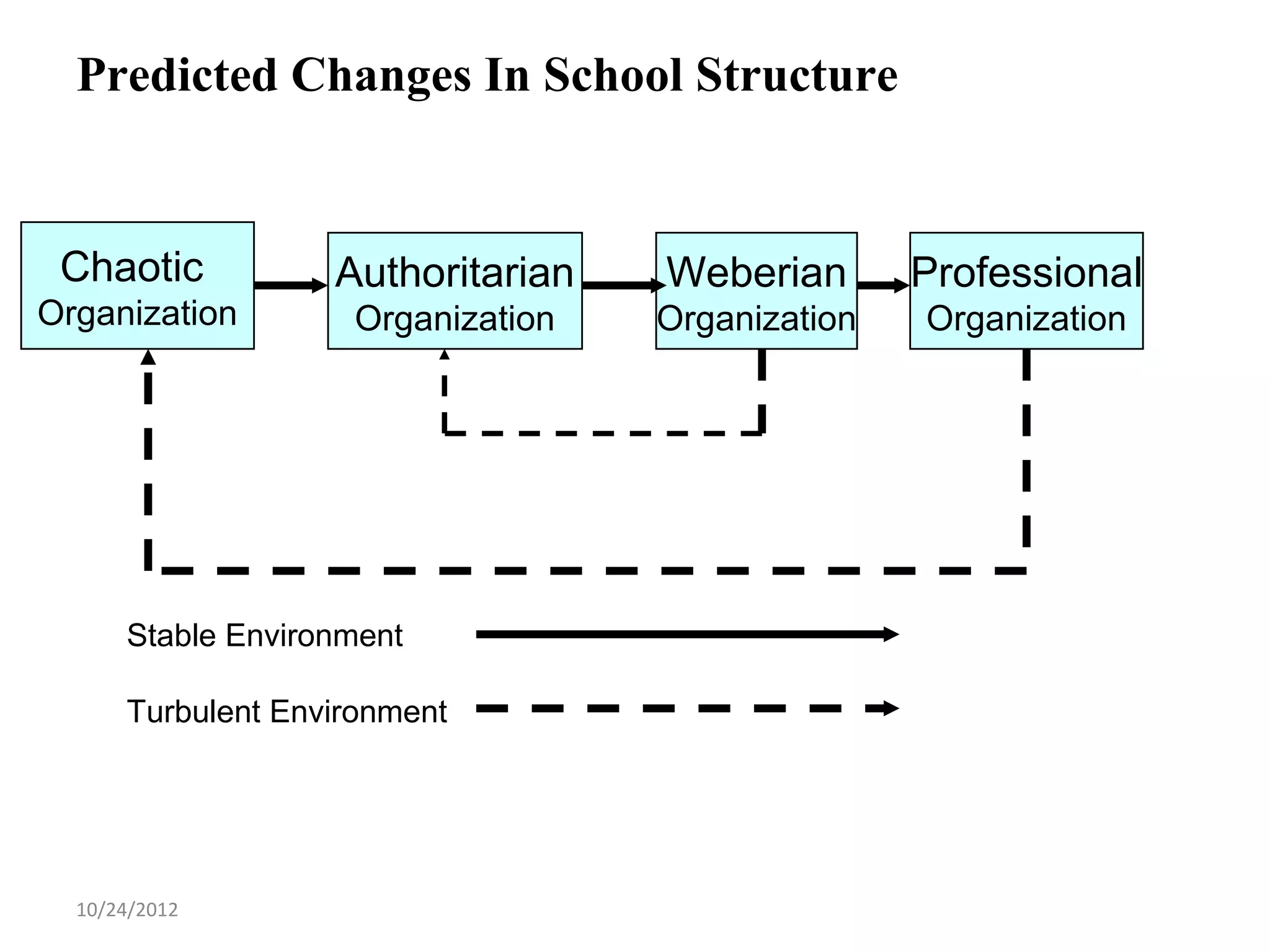
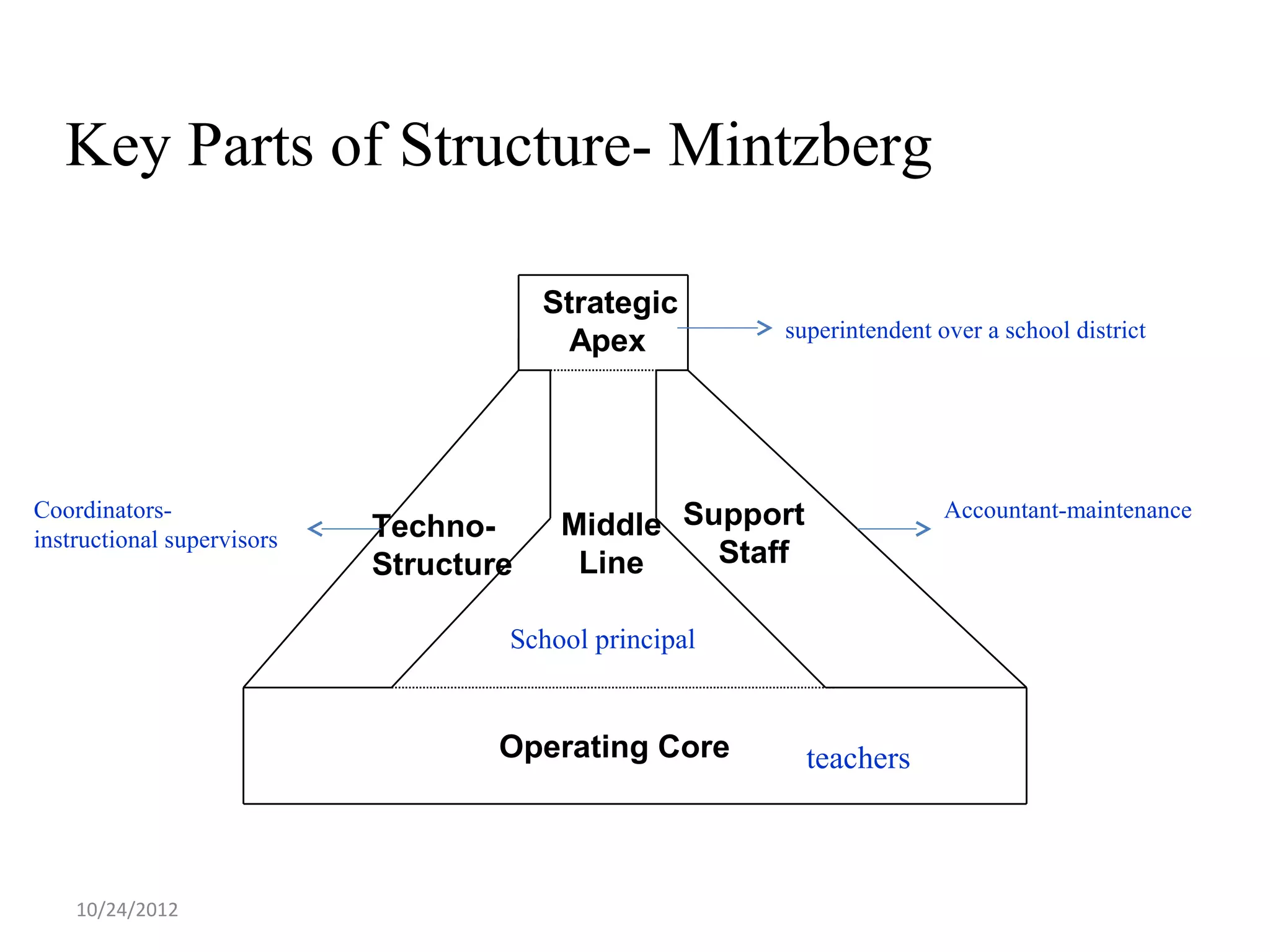
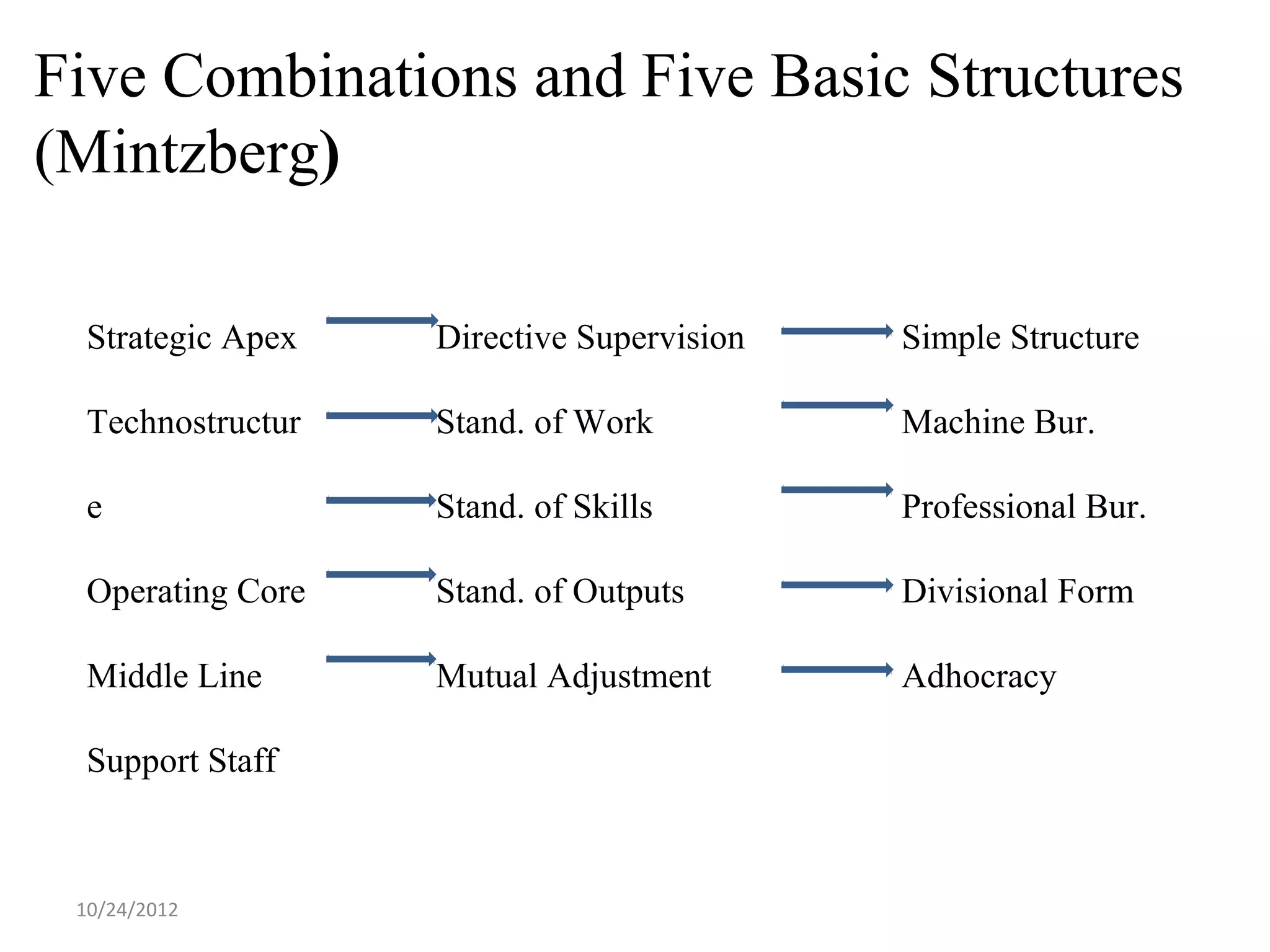
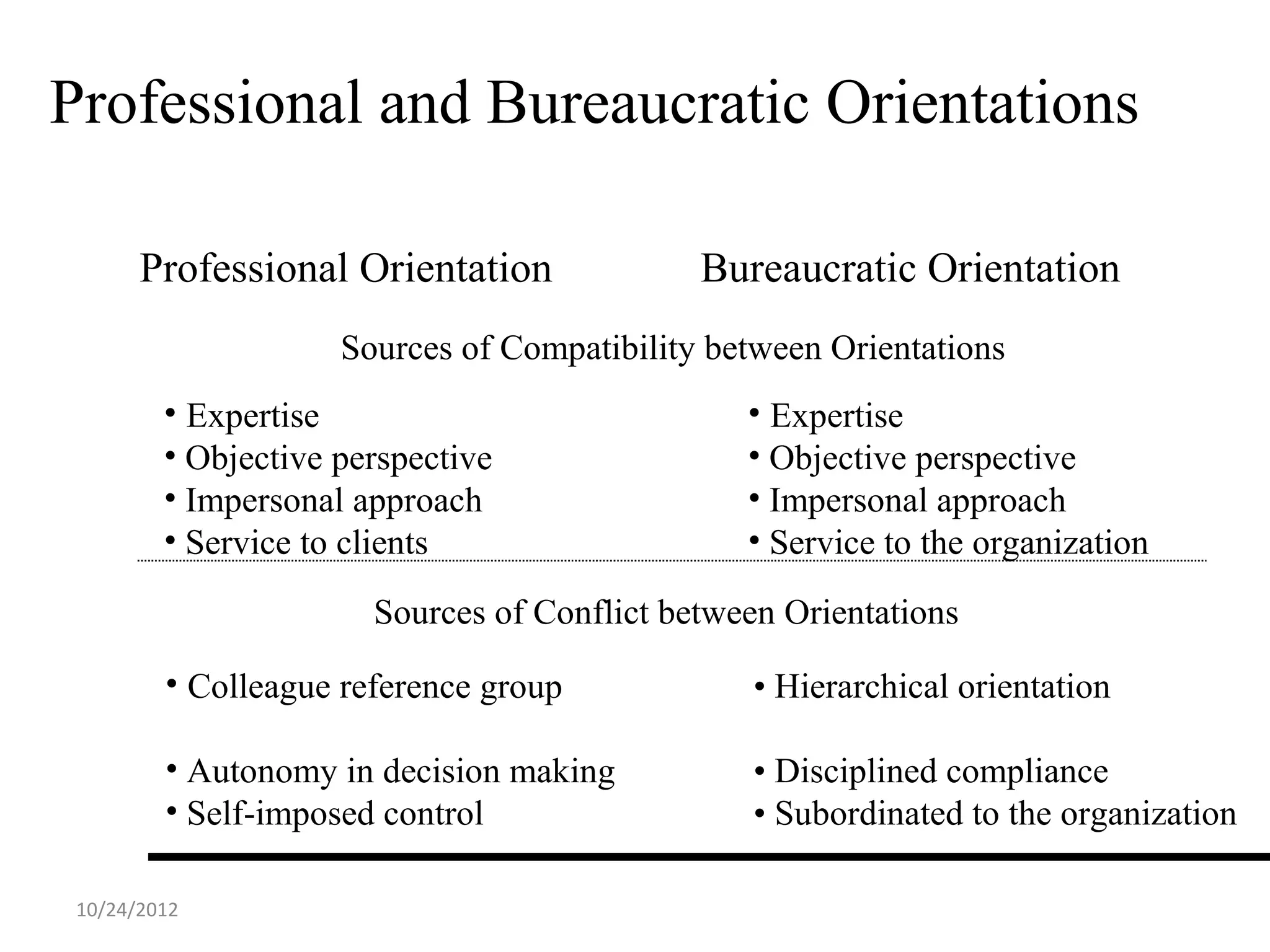
This document discusses different models and perspectives on organizational structure in schools. It covers Max Weber's model of bureaucracy, including its key elements like division of labor, impersonal orientation, and hierarchy of authority. It also discusses critiques of Weber's model, like its neglect of informal organization. Additionally, it outlines Hall's two types of rational organizations, Mintzberg's key parts of an organizational structure, and loose coupling perspective in schools. Overall, the document provides an overview of classic and contemporary theories for analyzing and understanding structure in educational organizations.