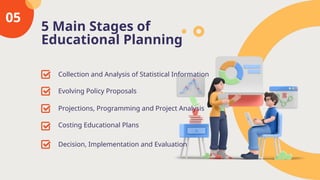
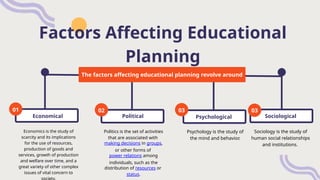
The document discusses the principles of educational planning, highlighting its definition, types, and the five main stages involved. It covers factors affecting educational planning such as economic, political, psychological, and sociological aspects, as well as the importance of community needs and resources. It emphasizes the necessity for clear educational policies, the involvement of stakeholders, and suggests solutions to improve the planning process.