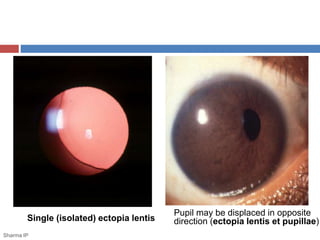
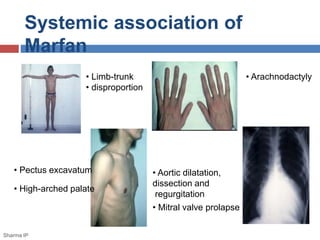
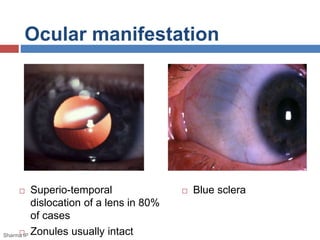
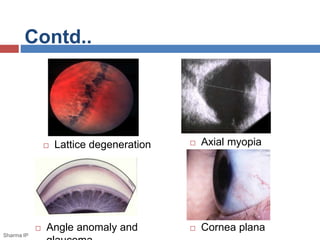
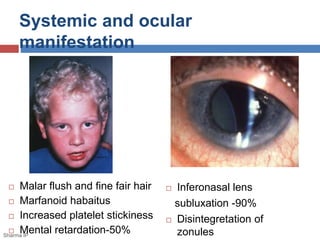
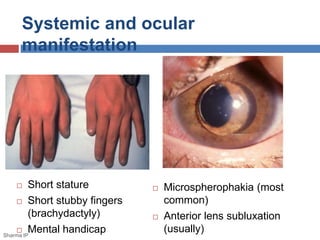
This document discusses ectopia lentis, or displacement of the crystalline lens. It begins with an overview of ectopia lentis, including definitions and pathophysiology. Signs and symptoms include visual impairment, fluctuating vision, poor near vision, and visual field defects. Causes of ectopia lentis include trauma, genetic conditions like Marfan syndrome, and other systemic diseases. Evaluation involves assessing vision, external eye exam, imaging, and lab tests if a systemic condition is suspected. Treatment options include refractive correction, surgery like lensectomy, and low vision devices. Low vision management aims to improve distance and near vision through high-power lenses, telescopes, magnifiers and other optical and non-optical aids.