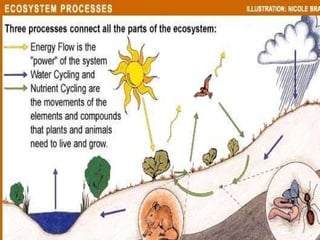
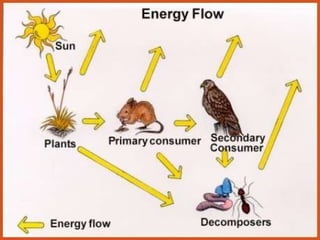
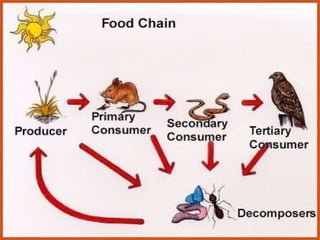
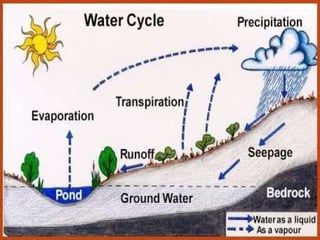
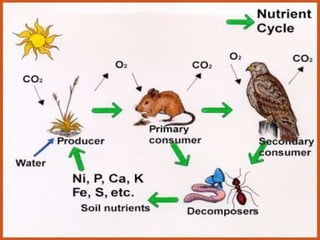
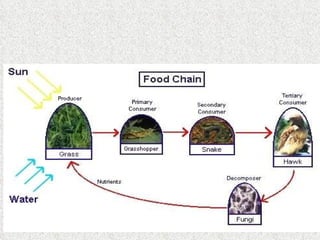
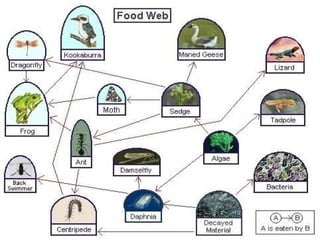
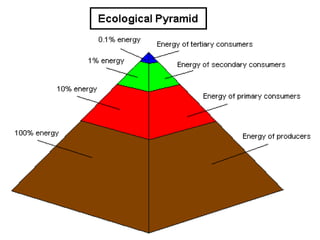
The document provides an overview of various ecosystems, including forest, desert, grassland, and aquatic ecosystems, detailing the roles of producers, consumers, and decomposers within these environments. It discusses the significance of each ecosystem type, their characteristics, components, and the relationships between organisms and their habitats. Additionally, it explores the threats to ecosystems and the essential services they provide to the environment.