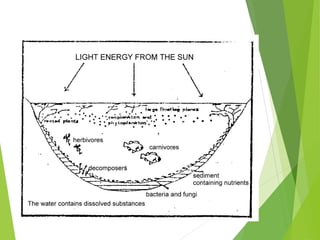
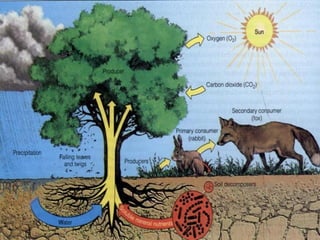
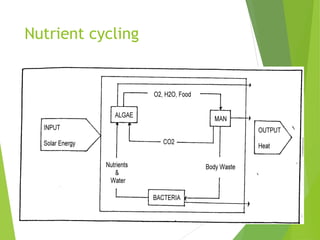
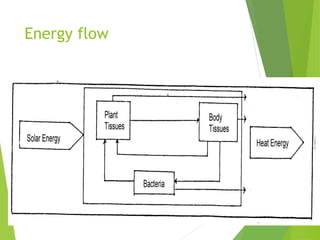
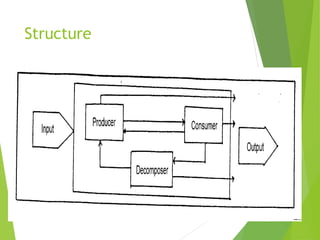
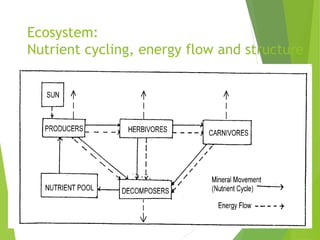
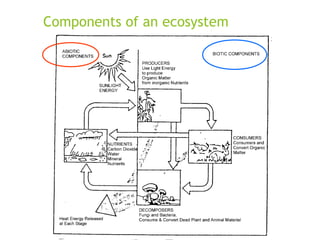
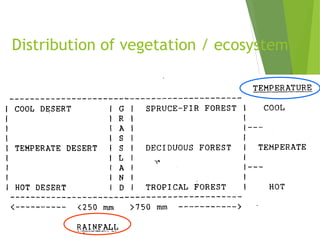
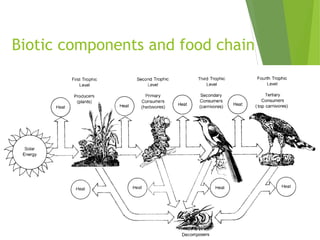
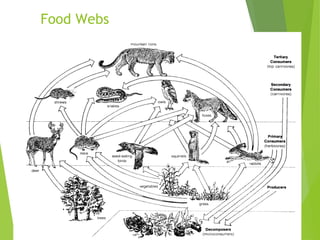
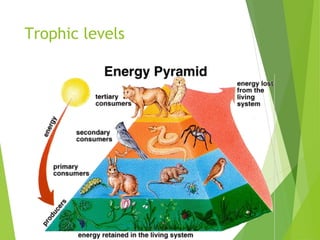
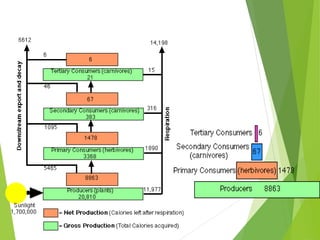
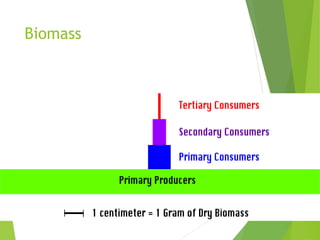
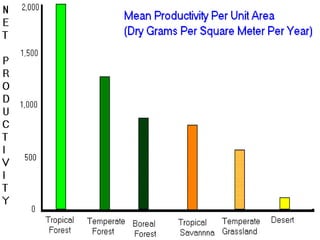
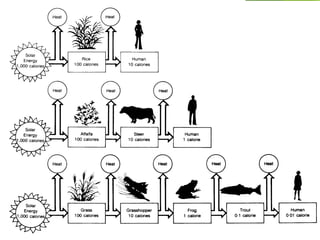
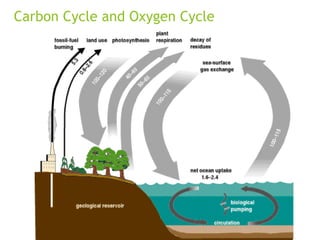
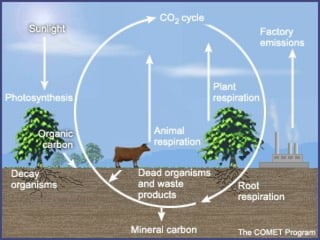
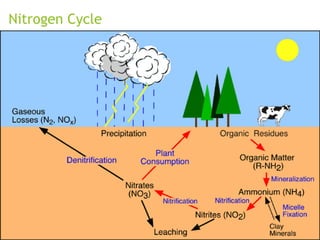
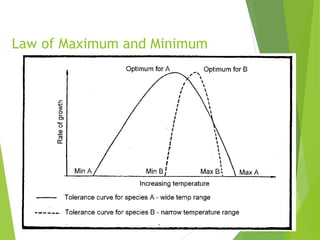
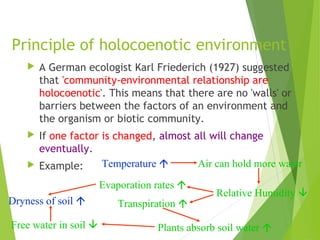
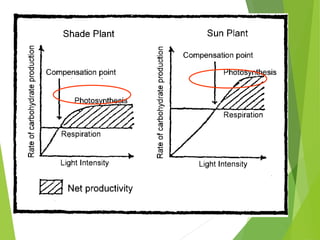
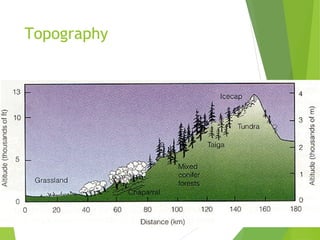
An ecosystem consists of biotic and abiotic components that interact through nutrient cycling, energy flow, and structure. The key biotic components are producers, consumers, and decomposers, which interact through food chains and webs. Energy and nutrients transfer between trophic levels, with biomass decreasing at higher levels. Ecosystems are influenced by various environmental factors like temperature, water, soil properties, and biotic interactions, with different species having specific tolerances. Ecosystems strive for balance, but human activities can disrupt natural nutrient cycles and environmental conditions.