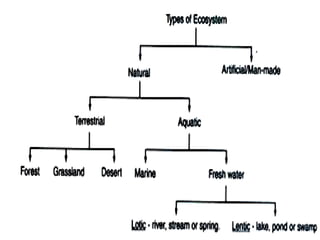
This document discusses ecosystems, defining them as units consisting of interacting living and non-living components. It describes the key components and structures of ecosystems, including abiotic factors, producers, consumers, and decomposers. Examples of major ecosystem types are provided, such as forests, grasslands, deserts, ponds, oceans, and croplands. Ecosystems are classified as natural or artificial/human-engineered.