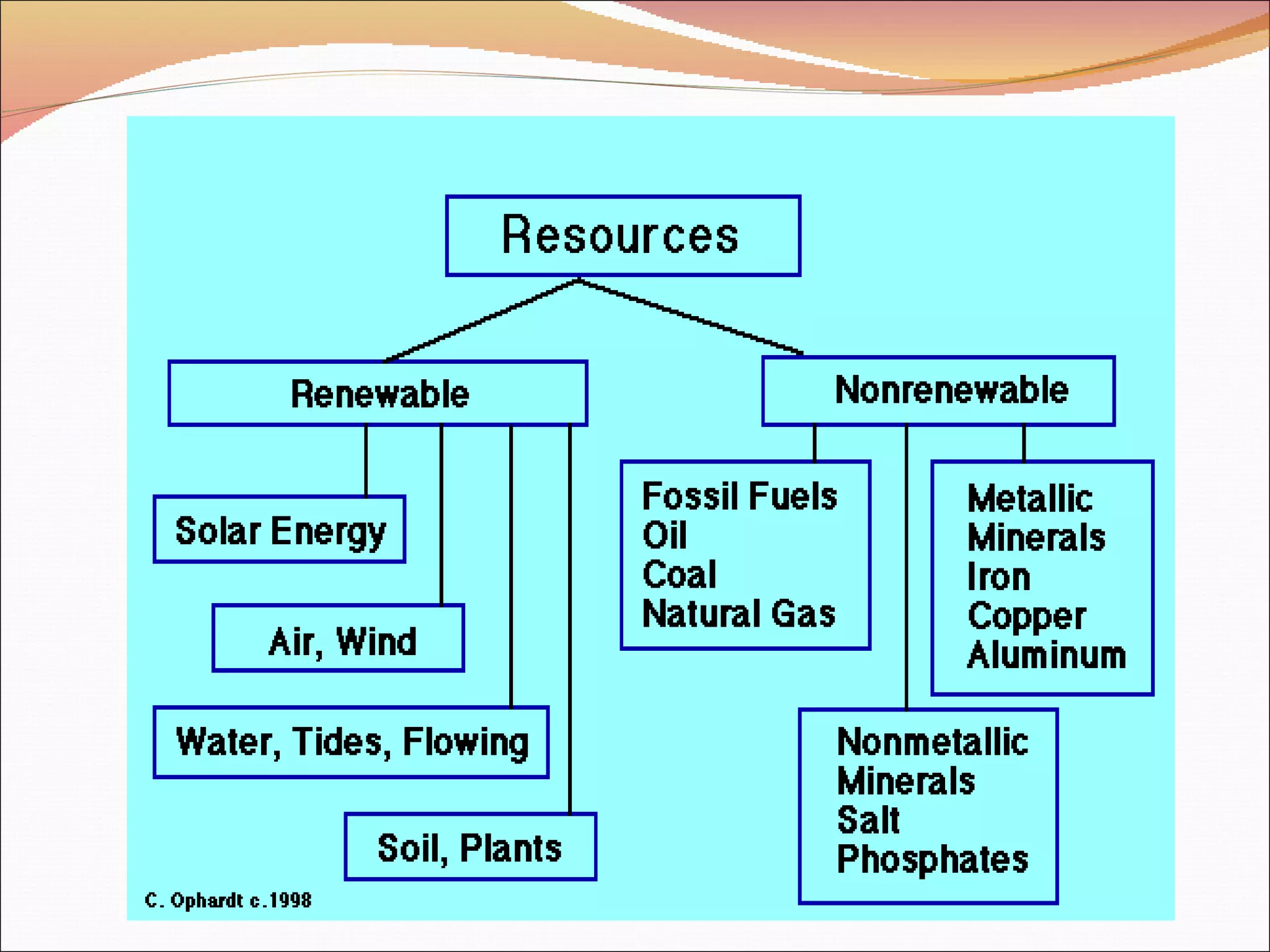
The document discusses resources, categorizing them as renewable and non-renewable, with examples and associated problems such as overexploitation and uneven distribution. It emphasizes the role of individuals in resource conservation through actions like saving energy and using eco-friendly products, while also highlighting the principles of sustainable development. Additionally, it touches on animal rights, advocating for the basic rights of non-human animals and their freedom from exploitation.