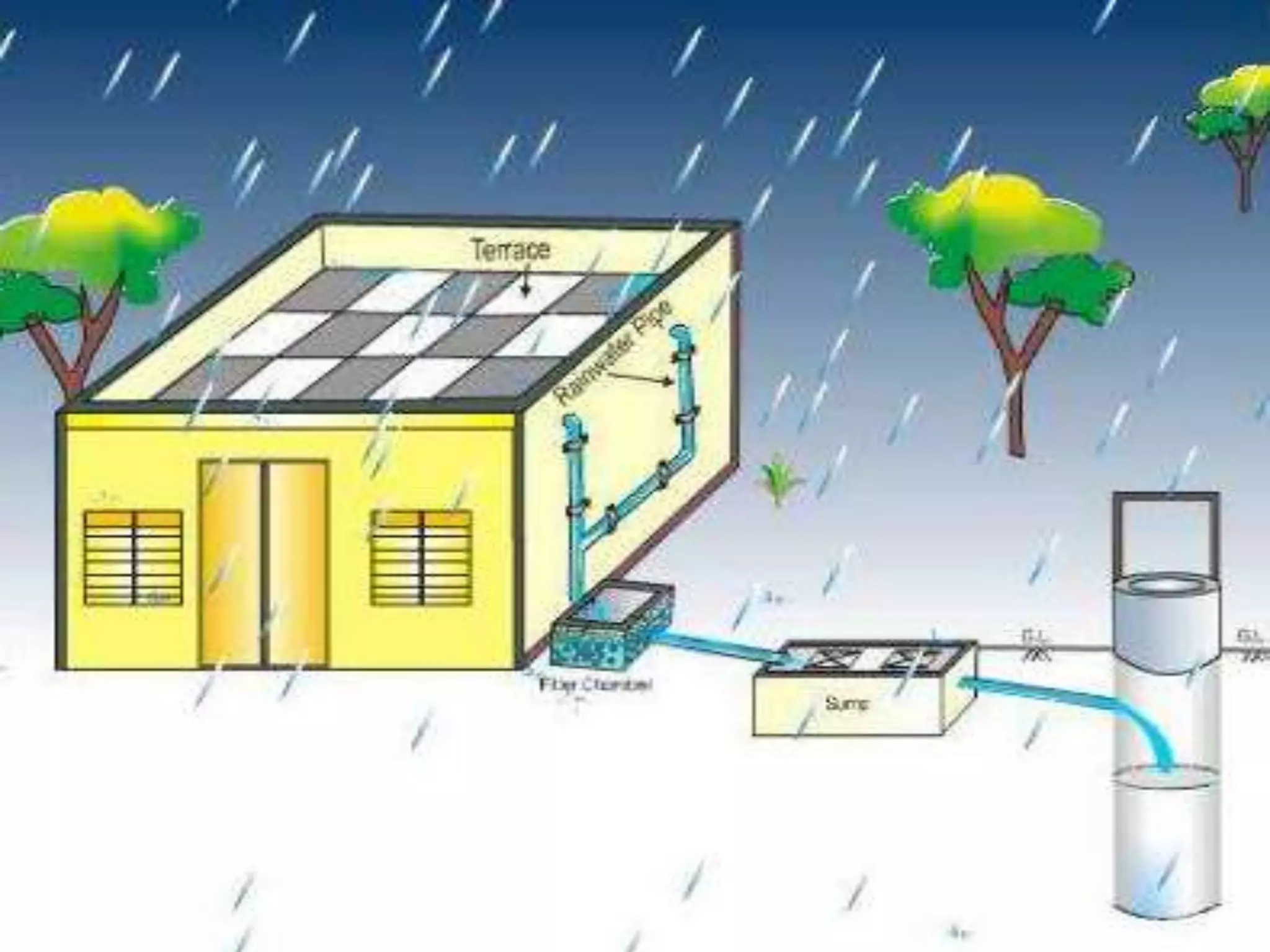
The document discusses various types of natural resources and conservation. It defines renewable and non-renewable resources, with examples such as plants and animals being renewable while coal and petroleum being non-renewable. It then covers different types of conservation efforts, including water, soil, wetland, plant, and wildlife conservation. Energy conservation is also discussed as a way to balance energy needs with environmental impacts through solutions like alternative fuels.