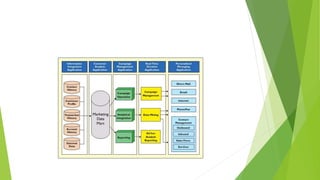
E-CRM involves using digital technologies like databases, email, and social media to maximize sales to existing customers and encourage ongoing customer relationships. It focuses on customer selection, acquisition, retention, and extension. E-CRM allows companies to gather unified customer information, respond faster to customers, build loyalty, and gain competitive advantages like increased income and reduced costs. Examples of e-CRM include using customer data to send personalized emails, recommendations, loyalty programs, and call center CRM software to improve customer service.