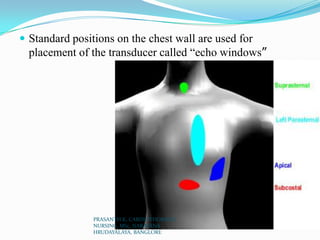
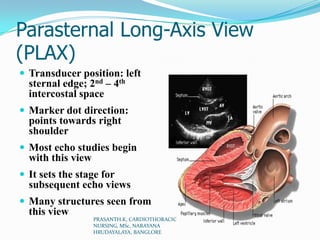
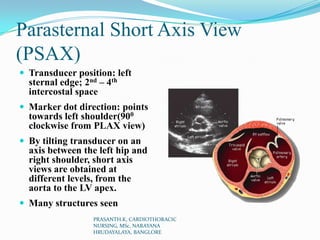
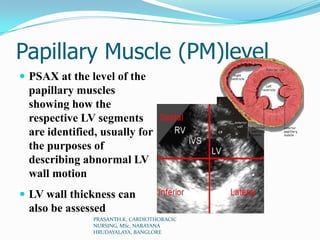
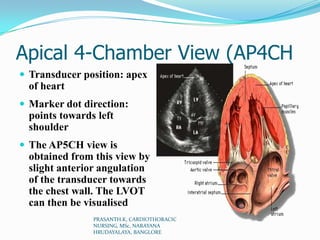
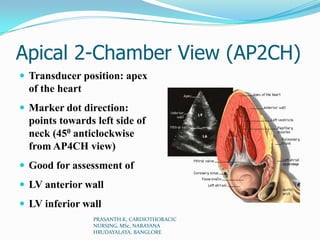
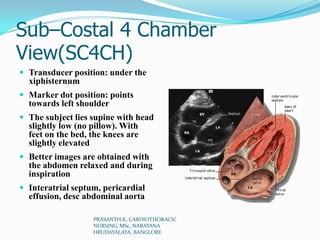
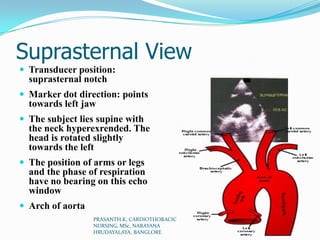
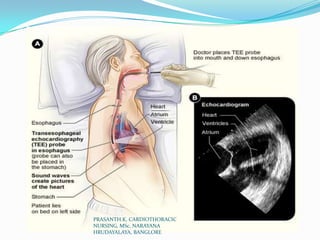
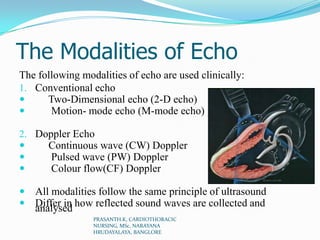
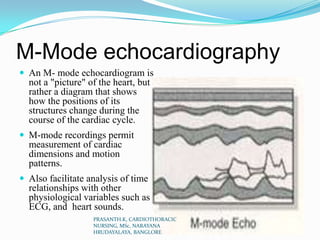
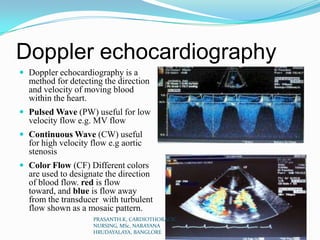
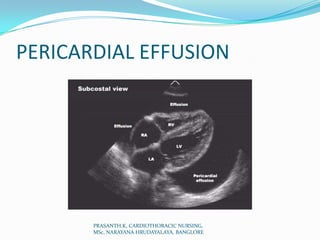
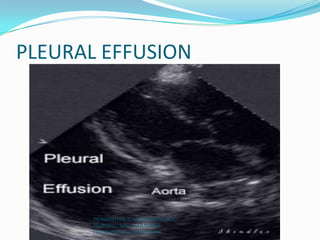
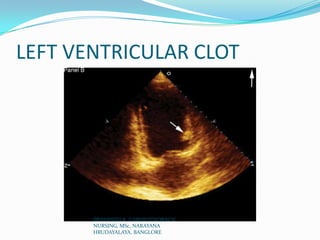
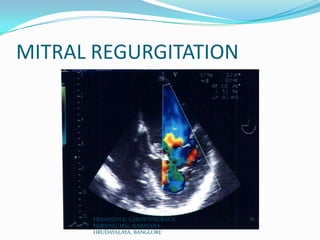
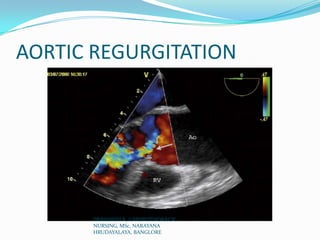
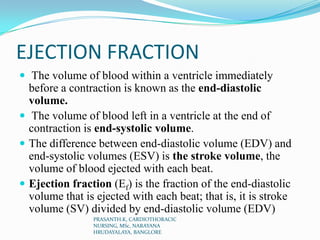
Echocardiography uses ultrasound to produce images of the heart. Sound waves are transmitted through a transducer and reflected off heart structures to create pictures. A standard echocardiogram begins with the parasternal long axis view and additional views are obtained by tilting the transducer. A transesophageal echocardiogram inserts the transducer down the throat for clearer images of posterior heart structures. Stress echocardiography images the heart during exercise to reveal lack of blood flow not seen at rest.