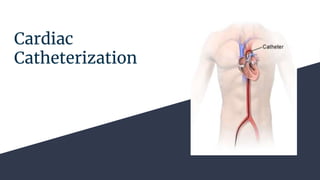
Cardiac catheterization is an invasive procedure used to visualize the heart chambers, valves, and vessels to diagnose and treat abnormalities. It can be done for both diagnostic and interventional purposes. The nurse's role is important in pre, intra, and post-procedure care. During the procedure, a catheter is inserted into the appropriate vessel and advanced under fluoroscopy while contrast dye is injected to image the heart and vessels. The patient is monitored closely for any complications like arrhythmias, bleeding, or reaction to contrast dye. After the procedure, the patient requires bed rest, monitoring of the insertion site, and observation for complications.