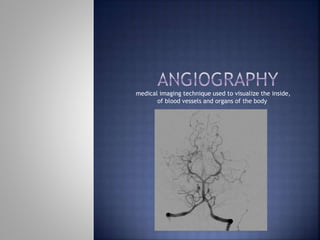
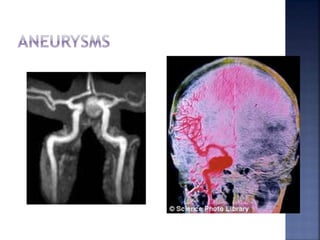
Angiography is a medical imaging technique that uses radiography to visualize blood vessels and organs after injecting a contrast medium. It can detect diseases of the arteries and veins like atherosclerosis, aneurysms, and internal bleeding. The procedure involves a team inserting a catheter into the blood vessels and injecting iodinated contrast dye before capturing x-ray images. Risks are generally low but can include minor bleeding, vessel damage, and allergic reactions to the contrast medium. Advances in digital subtraction angiography now make angiography the gold standard for assessing vascular diseases when other imaging modalities are inconclusive.