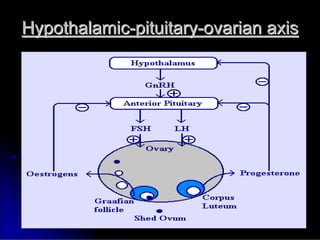
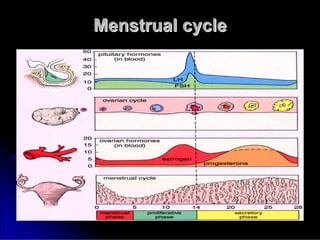
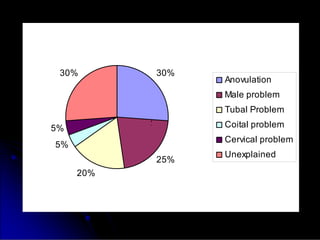
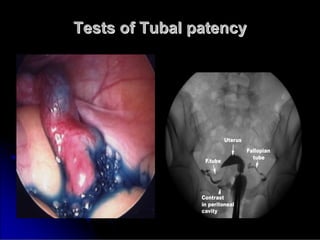
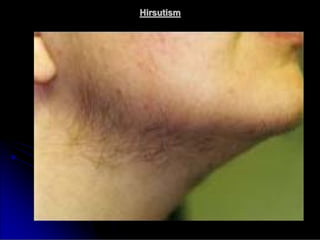
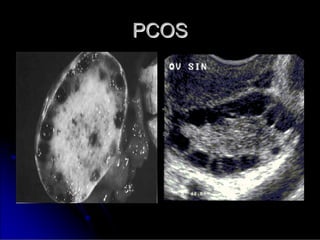
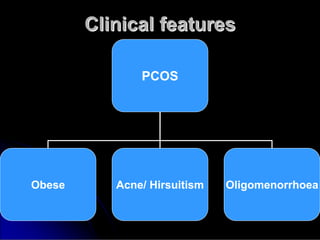
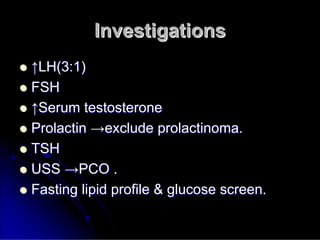
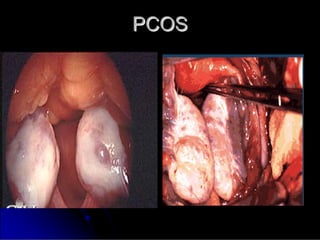
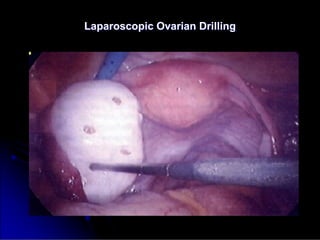
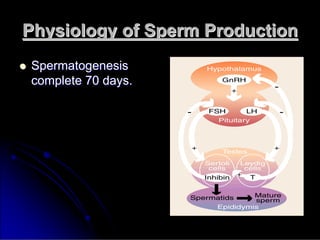
Subfertility, or difficulty conceiving, affects 15% of couples. It is defined as failure to conceive after one year of unprotected intercourse. There are several potential causes of subfertility, including problems with ovulation, sperm production/function, tubal damage, cervical factors, or sexual function. A thorough history, examination, and testing of both partners is needed to identify the underlying cause so appropriate treatment can be initiated.