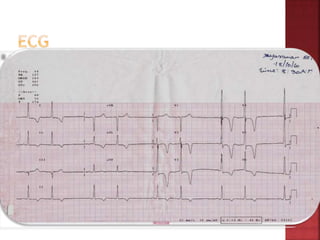
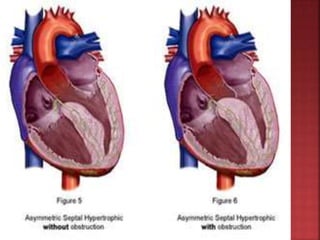
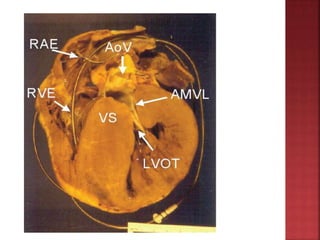
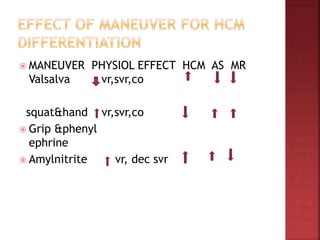
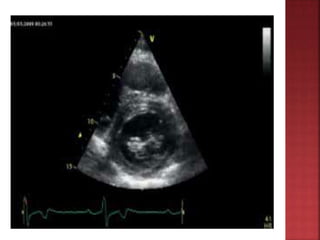
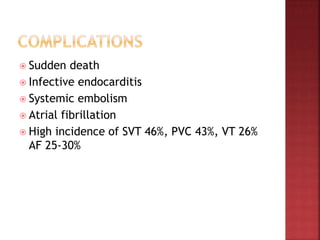
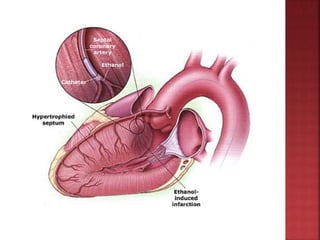
A 55-year-old male presented with shortness of breath for 7 days and chest pain for 6 days. Examination revealed a systolic murmur, cardiomegaly on chest x-ray, and ECG findings consistent with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. The patient was diagnosed with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, an inherited heart condition characterized by thickened heart muscle and small ventricle size. Risks include sudden cardiac death, heart failure, and embolic events. Treatment focuses on symptom management through medication and potentially surgery to reduce risks.