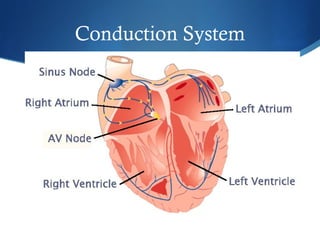
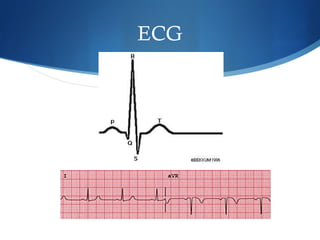
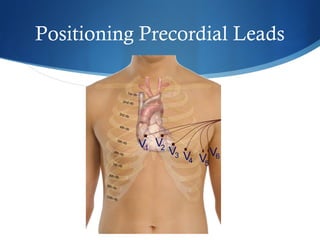
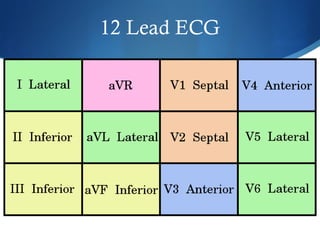
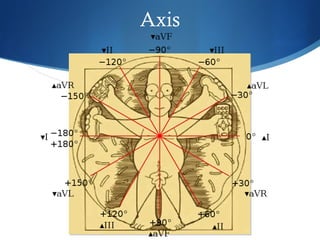
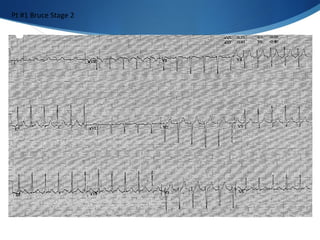
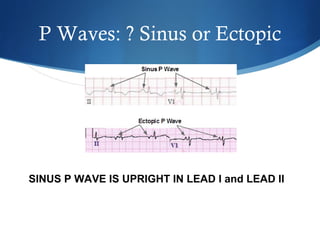
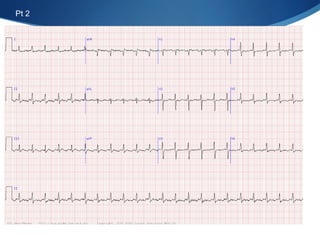
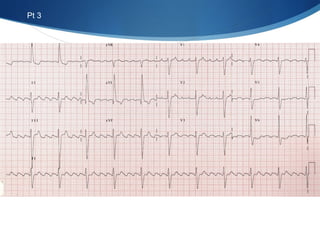
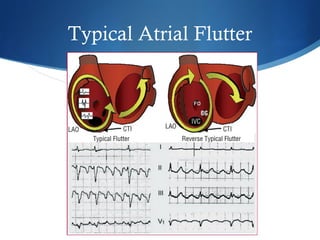
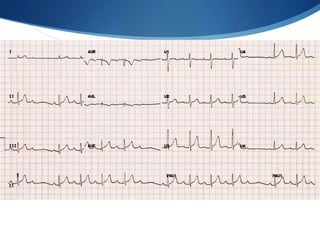
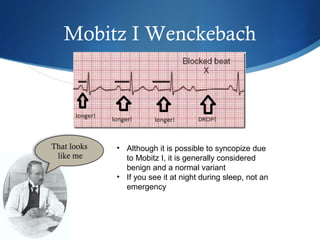
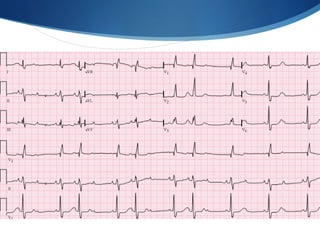
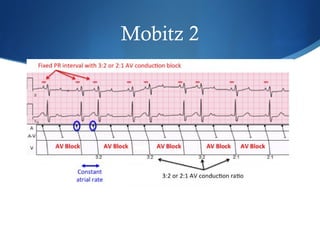
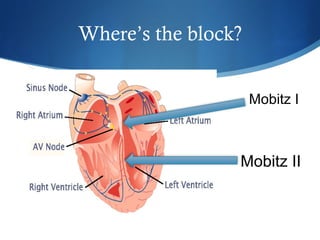
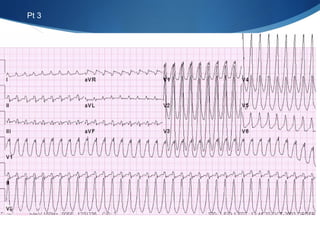
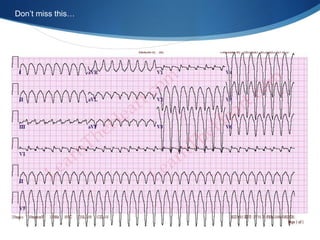
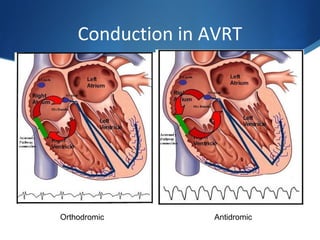
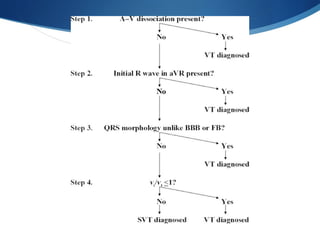
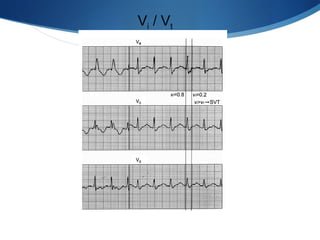
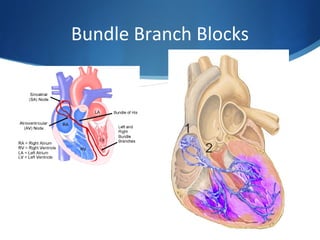
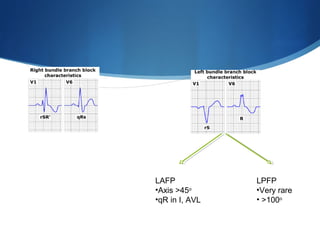
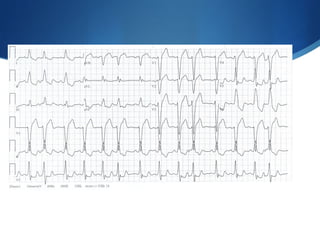
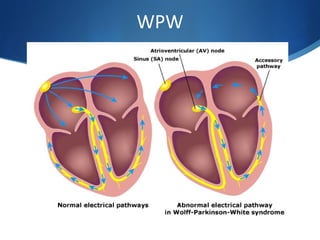
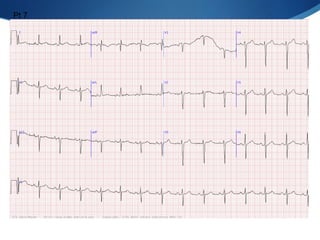
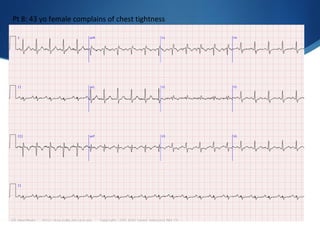
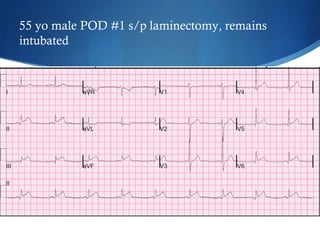
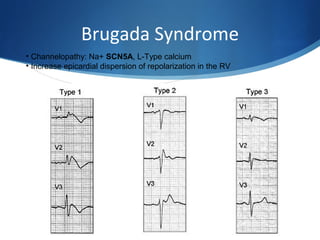
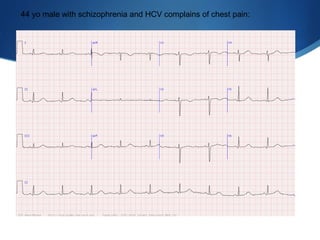
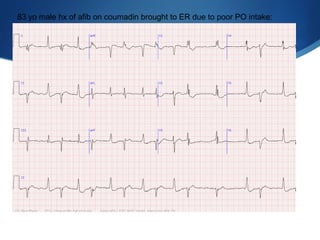
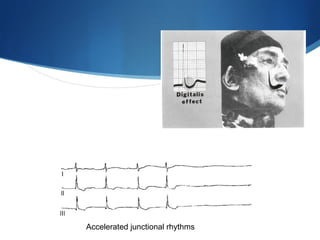
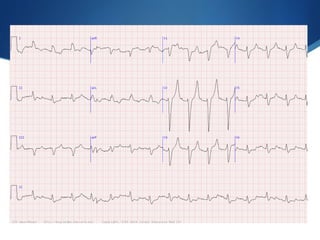
This document summarizes an ECG conference that reviewed basic ECG principles and interpretation methodology. It presented several patient cases to demonstrate sinus rhythm, atrial arrhythmias, STEMI patterns, ischemia, wide complex tachycardia, conduction blocks, axis deviations, AV nodal reentrant tachycardia, Brugada syndrome, digoxin toxicity, and more. The conference emphasized analyzing the ECG in terms of rhythm, axis, waveforms, and overall clinical picture.