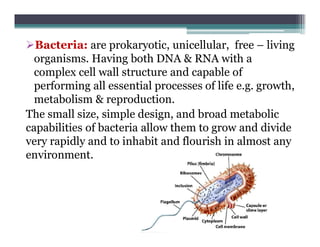
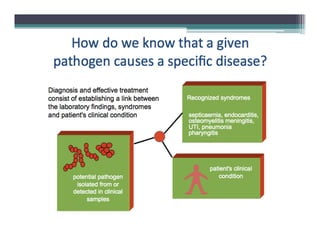
Clinical bacteriology involves the diagnosis and treatment of infectious diseases through microbiological techniques. It determines the causative agents of infections, and tests the effectiveness of antibiotics against isolated bacteria. Bacteria are unicellular prokaryotes that can rapidly grow and inhabit many environments. In clinical bacteriology, physicians want to know if a specimen contains pathogens, what type, and their antibiotic susceptibility. Appropriate specimens are collected and tested through staining, culturing, and antibiotic susceptibility testing to identify pathogens and determine the most effective treatments. The final report is used by physicians to interpret and treat patients.